A Comprehensive Look at the Regions of North America
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at the Regions of North America
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at the Regions of North America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at the Regions of North America
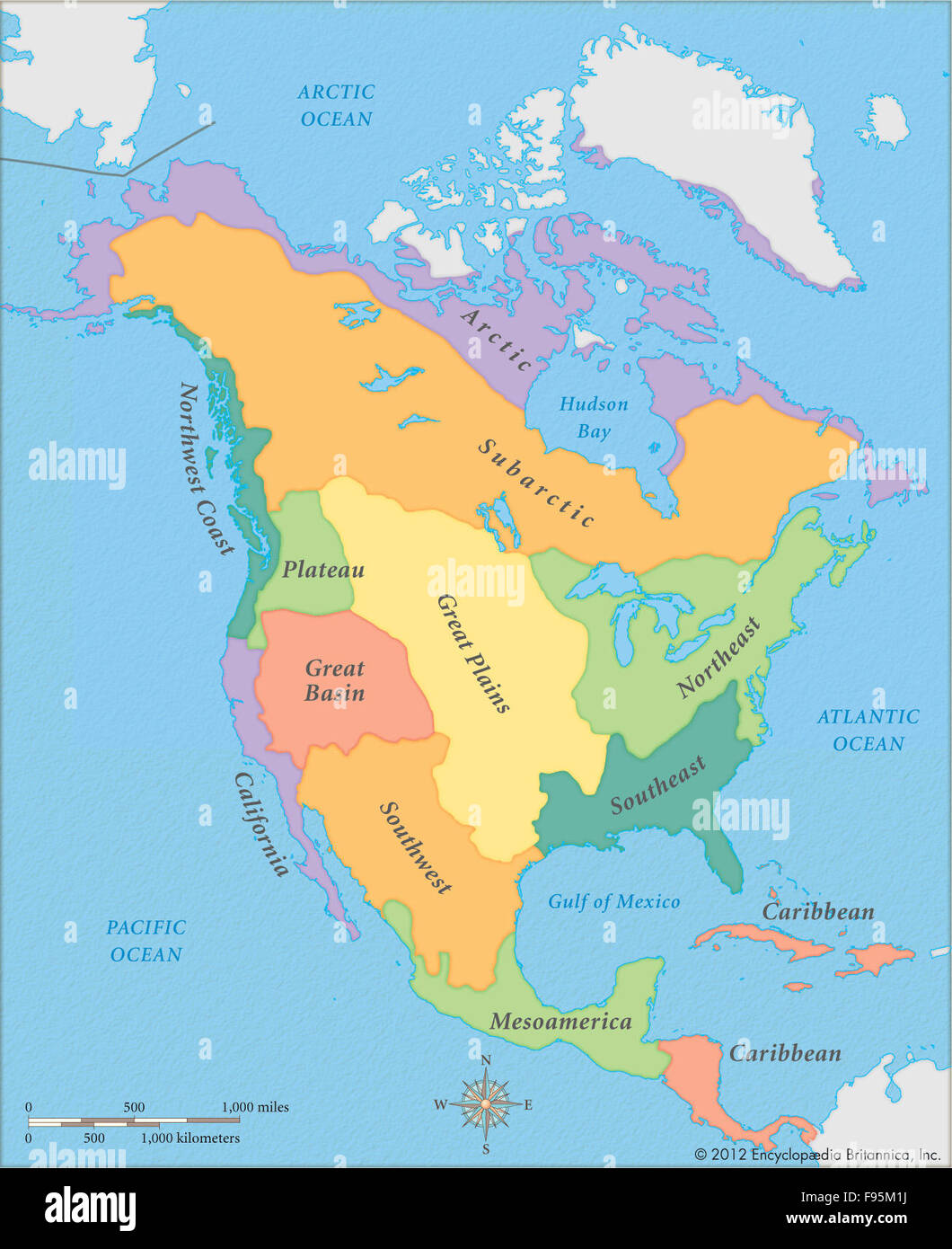
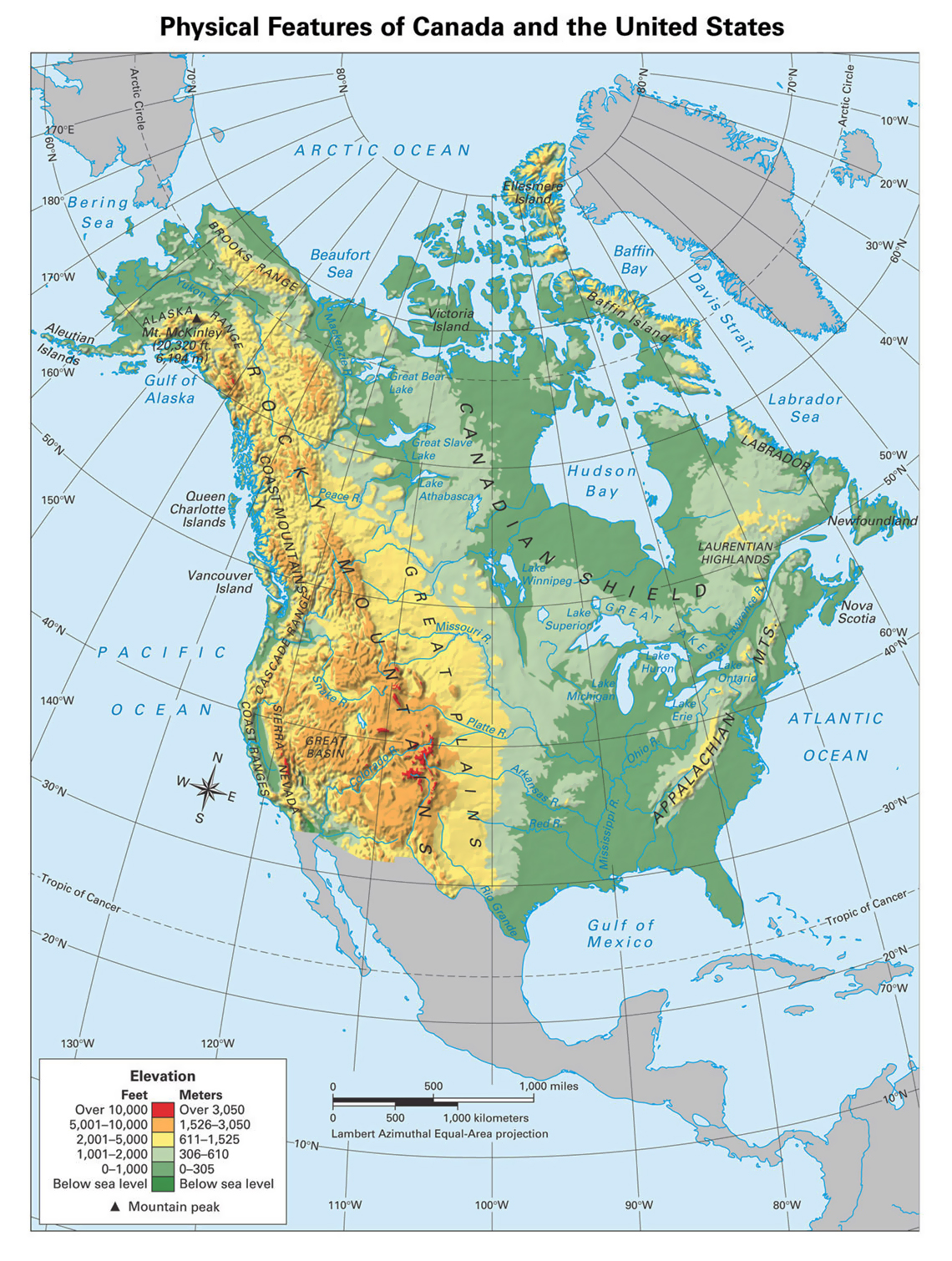
North America, the third largest continent, encompasses a vast expanse of diverse landscapes, cultures, and economies. Understanding the geographical divisions of this continent is crucial for comprehending its history, current affairs, and future prospects. This article delves into the various regional maps of North America, exploring their significance and providing a comprehensive overview of the continent’s distinct characteristics.
Regional Maps: A Framework for Understanding
Regional maps of North America serve as valuable tools for organizing and interpreting the continent’s complex tapestry. They provide a structured framework for analyzing its diverse geographical features, cultural nuances, and economic activities. These maps typically categorize North America into distinct regions, each possessing unique characteristics that set it apart from the others.
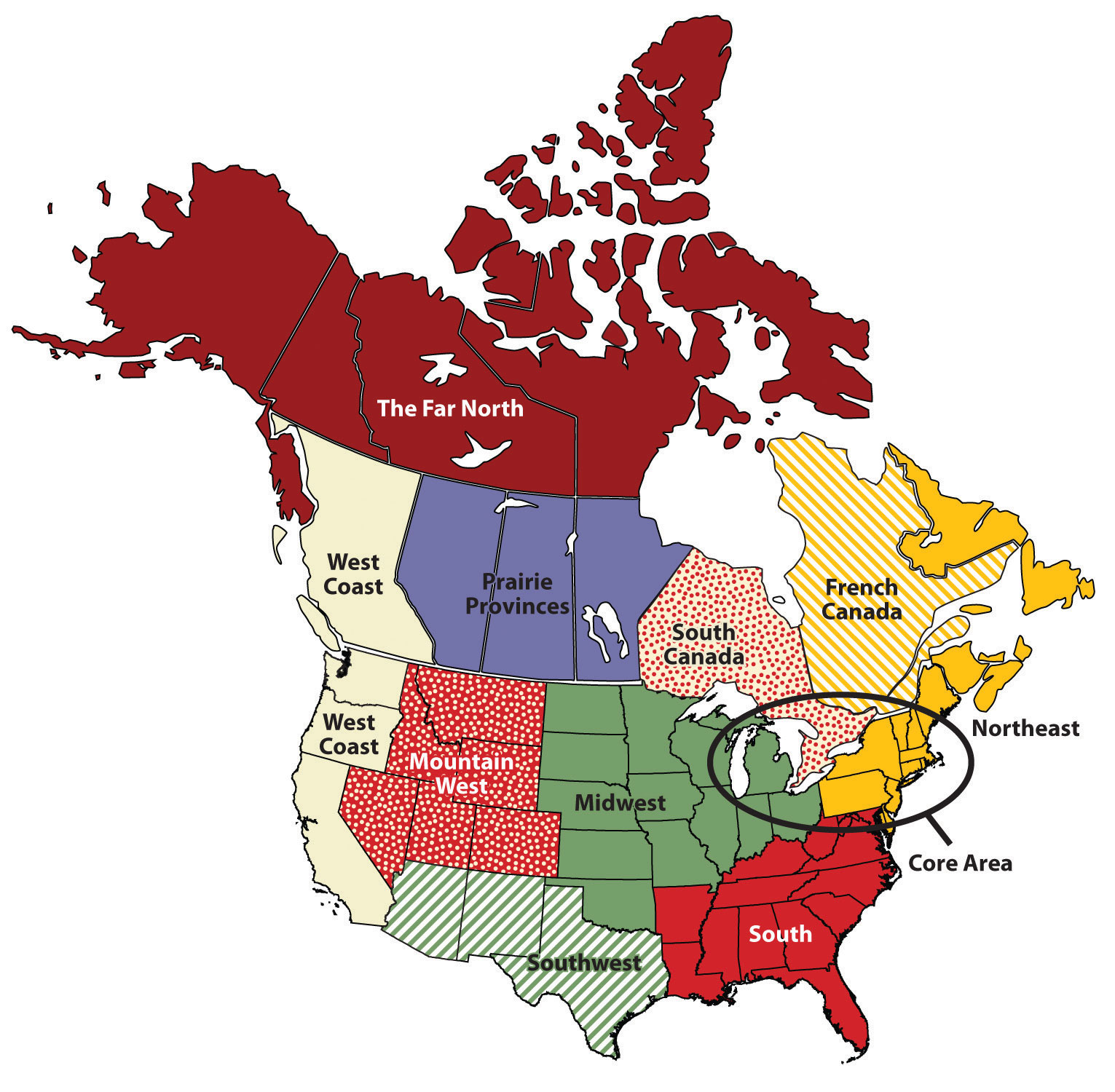
Common Regional Divisions of North America
While different sources may employ varying classifications, the following regional divisions are widely recognized:
1. Eastern North America: This region encompasses the eastern portion of the continent, stretching from the Atlantic coast westward to the Great Plains. It includes the following subregions:
- Northeast: This subregion comprises the states of Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. It is known for its dense population, historic cities, and a strong industrial base.
- Mid-Atlantic: This subregion includes the states of Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and North Carolina. It is characterized by a diverse economy, a rich history, and a blend of urban and rural areas.
- Southeast: This subregion includes the states of South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Tennessee, Kentucky, and Arkansas. It is known for its warm climate, agricultural production, and a growing tourism industry.
- Great Lakes Region: This subregion includes the states of Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. It is characterized by its vast freshwater lakes, industrial legacy, and a strong agricultural sector.
2. Central North America: This region encompasses the central portion of the continent, stretching from the Great Plains eastward to the Rocky Mountains. It includes the following subregions:
- Great Plains: This subregion includes the states of Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. It is known for its vast prairies, agricultural production, and oil and gas reserves.
- Midwest: This subregion includes the states of Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, and Ohio. It is known for its agricultural dominance, manufacturing industry, and a strong middle class.
3. Western North America: This region encompasses the western portion of the continent, stretching from the Rocky Mountains westward to the Pacific Ocean. It includes the following subregions:
- Rocky Mountains: This subregion includes the states of Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, Idaho, and Nevada. It is known for its towering mountains, abundant natural resources, and a growing tourism industry.
- Southwest: This subregion includes the states of Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, and California. It is characterized by its arid climate, diverse landscapes, and a booming technology sector.
- Pacific Northwest: This subregion includes the states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is known for its lush forests, rugged coastline, and a strong timber industry.
- California: This state, often considered a region in itself, is known for its diverse economy, vibrant culture, and a strong technology and entertainment industry.
4. Arctic North America: This region encompasses the northernmost portion of the continent, including parts of Canada, Alaska, and Greenland. It is characterized by its harsh climate, frozen landscapes, and a unique indigenous culture.
Understanding the Importance of Regional Maps
Regional maps of North America play a crucial role in various fields, including:
- Geography and Geology: They provide a visual representation of the continent’s diverse landscapes, geological formations, and natural resources.
- History and Culture: They help understand the historical development of different regions, their unique cultural identities, and the interactions between them.
- Economics and Trade: They shed light on the distribution of economic activities, trade patterns, and regional disparities in development.
- Politics and Governance: They provide a framework for understanding the political landscape, regional alliances, and the distribution of power.
- Environmental Studies: They facilitate the analysis of environmental issues, climate change impacts, and conservation efforts.
Benefits of Using Regional Maps
Using regional maps offers several benefits:
- Improved Understanding: They provide a clear and concise way to visualize the continent’s geographical and cultural diversity.
- Enhanced Analysis: They enable a deeper analysis of regional trends, patterns, and relationships.
- Better Planning and Decision-Making: They aid in strategic planning, resource allocation, and policy formulation.
- Facilitation of Collaboration: They foster communication and collaboration between different regions.
- Increased Awareness and Appreciation: They promote a greater understanding and appreciation for the continent’s rich heritage and diverse landscapes.
FAQs by Regions Map of North America
Q1: What are the major geographical features of each region in North America?
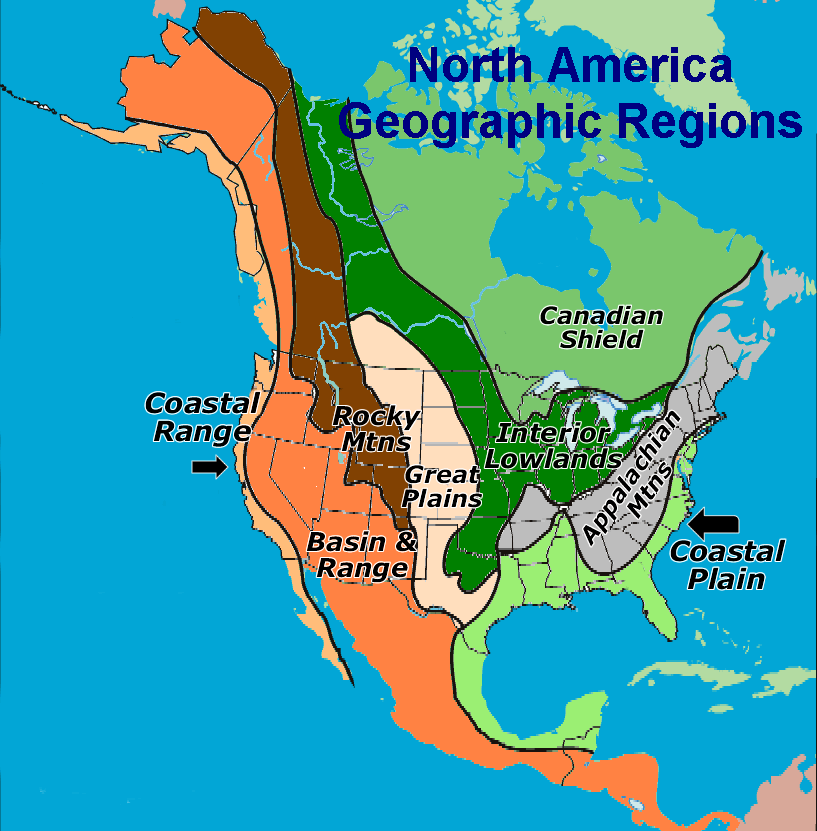
A1: Eastern North America is characterized by its Appalachian Mountains, vast coastal plains, and numerous rivers. Central North America is dominated by the Great Plains, the Mississippi River, and the Rocky Mountains. Western North America is known for its Pacific Coast, the Sierra Nevada Mountains, and the vast deserts. Arctic North America is characterized by its vast tundra, permafrost, and ice sheets.
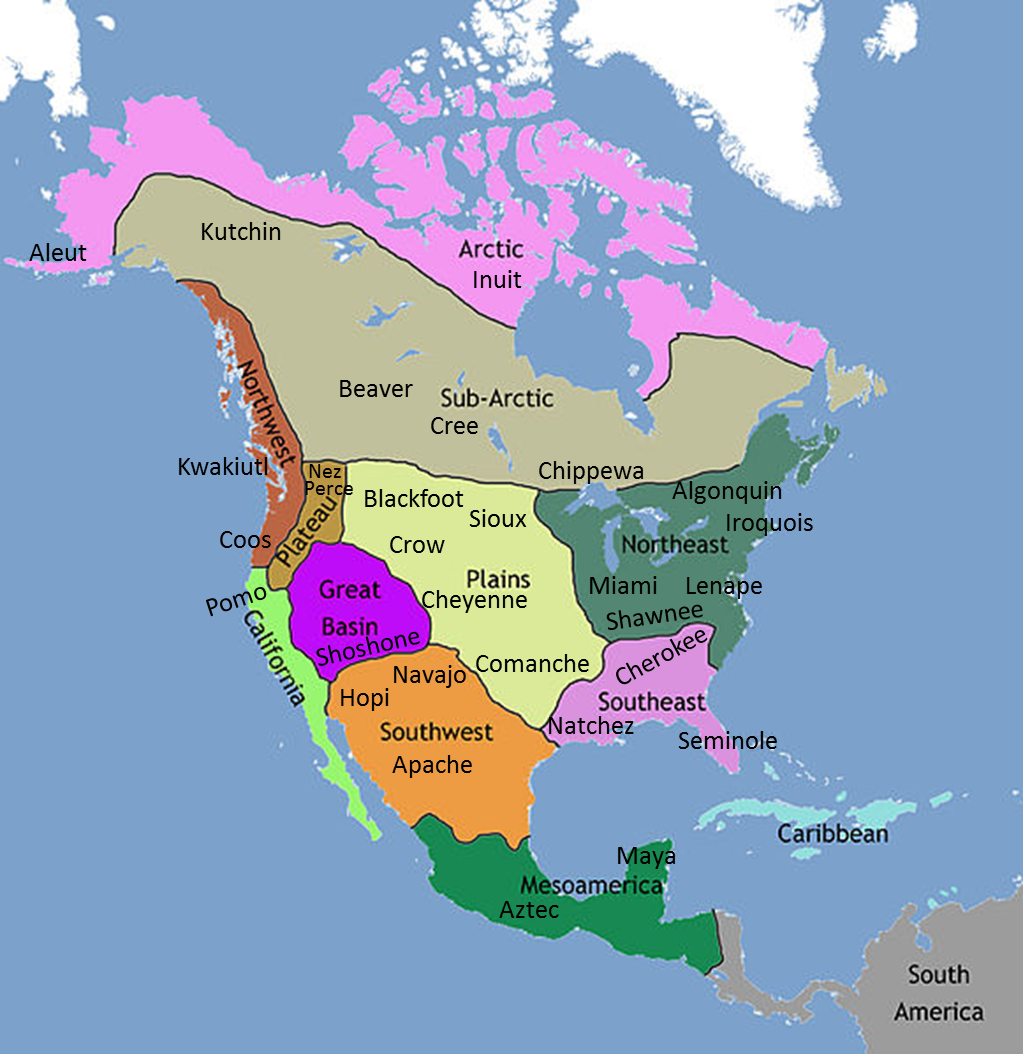
Q2: What are the dominant cultural influences in each region of North America?
A2: Eastern North America is influenced by European colonial history, African American culture, and Native American traditions. Central North America is shaped by a mix of European and Native American influences, with strong agricultural and industrial traditions. Western North America is characterized by a blend of Native American, Hispanic, and Asian influences, reflecting its diverse history and immigration patterns. Arctic North America is dominated by indigenous cultures, with a strong emphasis on survival and adaptation to harsh environments.
Q3: What are the major economic activities in each region of North America?
A3: Eastern North America is home to a diverse economy, with strong manufacturing, finance, and tourism sectors. Central North America is dominated by agriculture, manufacturing, and energy production. Western North America is characterized by a growing technology sector, tourism, and natural resource extraction. Arctic North America’s economy is largely based on resource extraction, tourism, and subsistence activities.
Q4: What are the major environmental challenges facing each region of North America?
A4: Eastern North America faces challenges related to air and water pollution, deforestation, and coastal erosion. Central North America grapples with issues related to agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, and climate change. Western North America faces challenges related to water scarcity, wildfires, and habitat loss. Arctic North America is particularly vulnerable to climate change, with rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and permafrost thawing posing significant threats.
Tips by Regions Map of North America
- Use a variety of maps: Explore different regional maps to gain a comprehensive understanding of North America’s diverse regions.
- Compare and contrast: Analyze the similarities and differences between different regions to gain insights into their unique characteristics.
- Consider historical context: Understand how historical events and processes have shaped the current regional divisions and characteristics.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from various sources, including academic research, cultural narratives, and community perspectives.
- Apply a critical lens: Analyze the biases and limitations of regional maps to gain a more nuanced understanding of the continent’s complexities.
Conclusion by Regions Map of North America
Regional maps of North America offer a valuable framework for understanding the continent’s diverse landscapes, cultures, economies, and challenges. By analyzing these maps and their underlying data, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of different regions, their unique contributions to the continent’s history and development, and the challenges they face in the present and future. Through a comprehensive understanding of regional divisions, we can foster greater collaboration, address shared challenges, and celebrate the rich tapestry of North America’s diverse heritage.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at the Regions of North America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!