A Geographic Portrait of the Middle East: Unveiling a Region of Diversity and Significance
Related Articles: A Geographic Portrait of the Middle East: Unveiling a Region of Diversity and Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Portrait of the Middle East: Unveiling a Region of Diversity and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Portrait of the Middle East: Unveiling a Region of Diversity and Significance
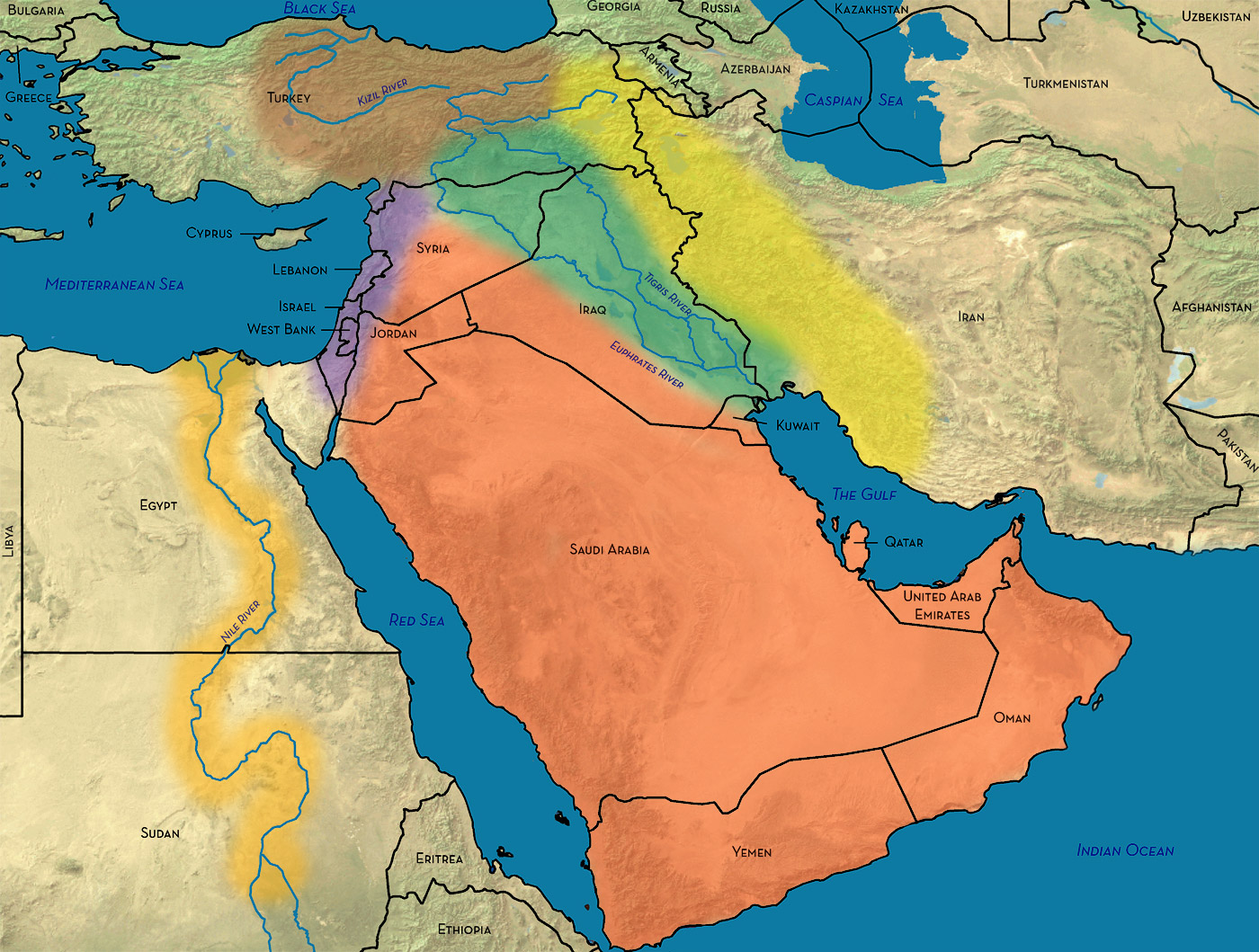
The Middle East, a region often characterized by its geopolitical complexities, possesses a captivating geographical tapestry that profoundly influences its history, culture, and present-day challenges. Understanding the Middle East’s geography is crucial for comprehending its intricate dynamics and appreciating the unique qualities that define it. This article delves into the diverse landscapes, climatic patterns, and resource endowments that shape the region, highlighting its importance in the global context.
A Land of Contrasts: Diverse Landscapes
The Middle East is a mosaic of contrasting landscapes, encompassing vast deserts, fertile plains, towering mountains, and vibrant coastlines.
-
Deserts: The most prominent feature of the Middle East is its vast expanse of deserts. The Arabian Desert, the largest in the world, dominates the Arabian Peninsula, while the Sahara Desert extends into parts of North Africa. These deserts are characterized by aridity, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation.
-
Fertile Plains: Despite the prevalence of deserts, the Middle East harbors pockets of fertile land, primarily along river valleys and coastal plains. The Nile River Valley in Egypt, the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in Mesopotamia, and the coastal plains of the Levant are renowned for their agricultural productivity.
-
Mountains: Mountain ranges traverse the Middle East, forming natural barriers and influencing regional climate patterns. The Zagros Mountains in Iran, the Taurus Mountains in Turkey, and the Atlas Mountains in North Africa are prominent examples. These mountain ranges are often rich in mineral resources and provide essential water sources.
-
Coastlines: The Middle East boasts extensive coastlines along the Red Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, the Persian Gulf, and the Arabian Sea. These coastlines have played a vital role in trade and cultural exchange throughout history, connecting the region to other parts of the world.
Climate and Resources: A Vital Interplay
The Middle East’s climate is predominantly arid, with hot summers and mild winters. However, significant variations exist within the region, influenced by factors such as latitude, altitude, and proximity to water bodies.
-
Aridity: The vast majority of the Middle East experiences an arid climate, characterized by low rainfall and high evaporation rates. This aridity has shaped the region’s vegetation, wildlife, and human settlement patterns.
-
Variations: While aridity is dominant, the Middle East exhibits significant climatic variations. Coastal regions experience milder temperatures and higher humidity, while mountainous areas receive greater rainfall and support diverse ecosystems.
-
Water Resources: The scarcity of water is a defining characteristic of the Middle East. The region relies heavily on rivers, groundwater, and rainfall for its water needs. However, water resources are unevenly distributed, leading to competition and conflict over access to this essential resource.
-
Energy Resources: The Middle East is home to vast reserves of oil and natural gas, making it a major global energy supplier. These energy resources have significantly impacted the region’s economy and geopolitical standing.
A Region of Interconnectedness: The Importance of Geography
The Middle East’s diverse geography has profound implications for its history, culture, and present-day challenges.
-
Trade Routes: The strategic location of the Middle East at the crossroads of continents has made it a hub for trade routes since ancient times. The Silk Road, a historic trade route connecting the East and West, traversed the region, facilitating cultural exchange and economic prosperity.
-
Cultural Exchange: The Middle East’s diverse landscapes and historical connections have fostered a rich tapestry of cultures. The region has been home to numerous civilizations, each contributing to the development of art, literature, science, and philosophy.
-
Geopolitical Dynamics: The Middle East’s geography has shaped its geopolitical dynamics. The region’s strategic location, coupled with its abundant energy resources, has made it a focal point of global power struggles.
-
Environmental Challenges: The Middle East faces significant environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and climate change. These challenges pose a threat to the region’s ecosystems, food security, and human well-being.
Navigating the Future: Understanding the Middle East’s Geography
Understanding the Middle East’s geography is crucial for navigating its complex challenges and fostering a more peaceful and prosperous future. By appreciating the region’s unique characteristics and the interconnectedness of its landscapes, resources, and cultures, we can better understand the forces that shape its destiny.
FAQs about Middle East Geography:
1. What is the largest desert in the Middle East?
The largest desert in the Middle East is the Arabian Desert, which covers most of the Arabian Peninsula.
2. What are the major rivers in the Middle East?
The major rivers in the Middle East include the Nile River, the Tigris River, and the Euphrates River.
3. What are the major mountain ranges in the Middle East?
The major mountain ranges in the Middle East include the Zagros Mountains, the Taurus Mountains, and the Atlas Mountains.
4. What are the major energy resources in the Middle East?
The Middle East is rich in oil and natural gas reserves, making it a major global energy supplier.
5. What are the major environmental challenges facing the Middle East?
The Middle East faces significant environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and climate change.
Tips for Understanding Middle East Geography:
- Utilize maps and atlases: Studying maps and atlases is essential for gaining a visual understanding of the Middle East’s geography.
- Read books and articles: Explore books and articles that delve into the region’s history, culture, and geography.
- Watch documentaries: Documentaries can provide a visual and engaging perspective on the Middle East’s diverse landscapes and challenges.
- Engage in discussions: Participate in discussions and forums that focus on the Middle East’s geography and its implications.
Conclusion:
The Middle East’s geography is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, climatic patterns, and resource endowments that have profoundly shaped its history, culture, and present-day challenges. Understanding this geographic context is vital for appreciating the region’s unique qualities and navigating its complex dynamics. By fostering a deeper understanding of the Middle East’s geography, we can contribute to a more peaceful, prosperous, and sustainable future for this vital region.
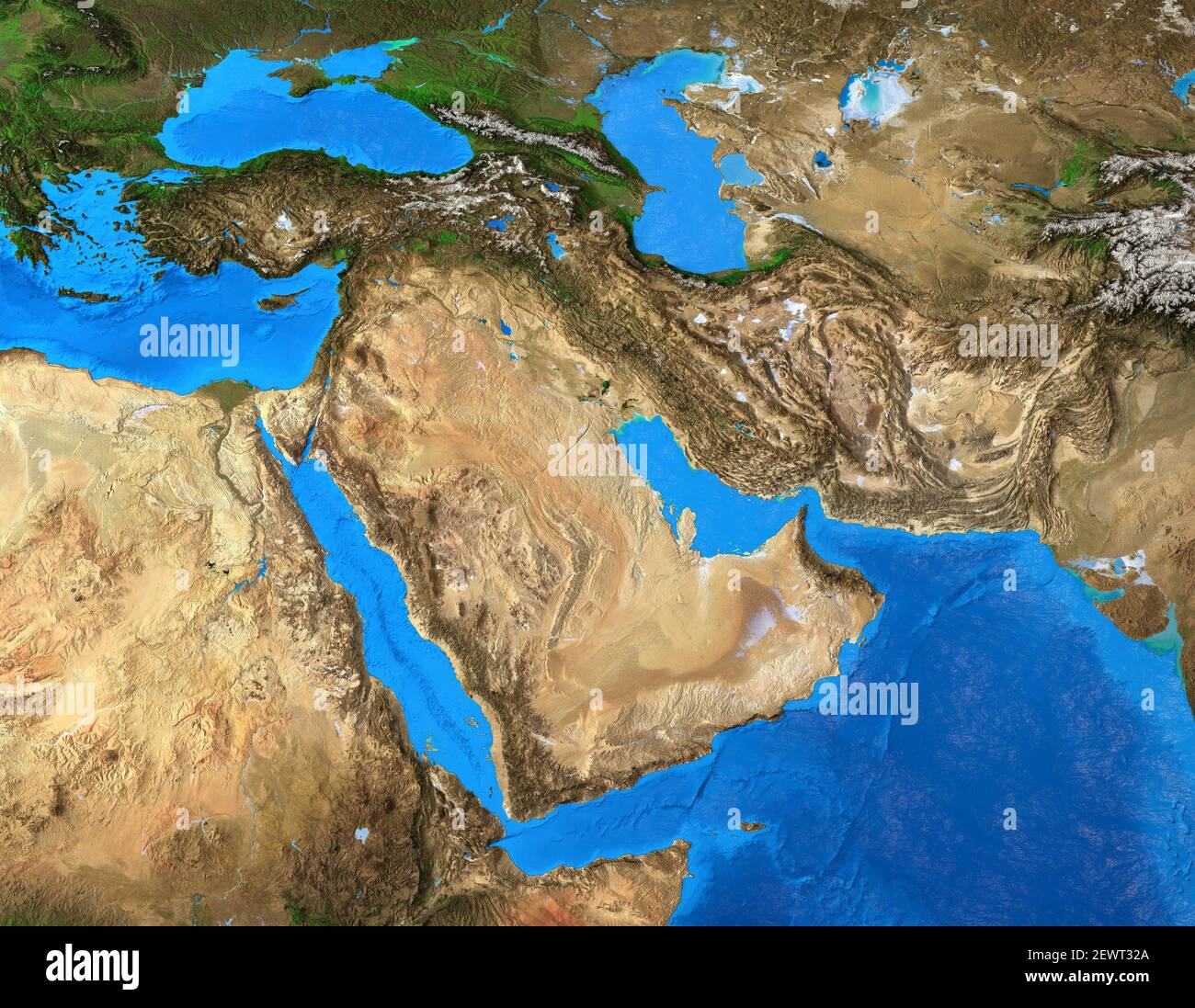





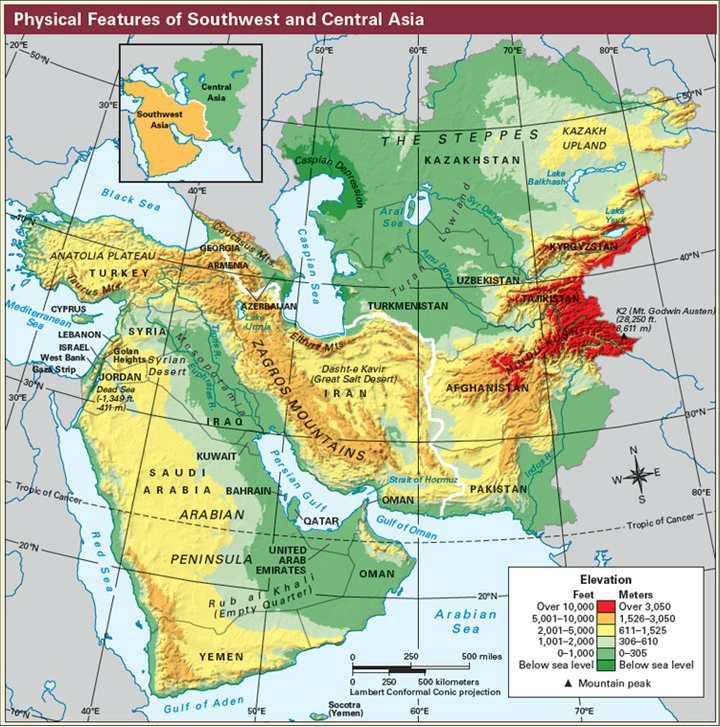
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Portrait of the Middle East: Unveiling a Region of Diversity and Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
