A Geographical Overview of Israel and Lebanon: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Related Articles: A Geographical Overview of Israel and Lebanon: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Overview of Israel and Lebanon: A Complex and Contested Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Overview of Israel and Lebanon: A Complex and Contested Landscape

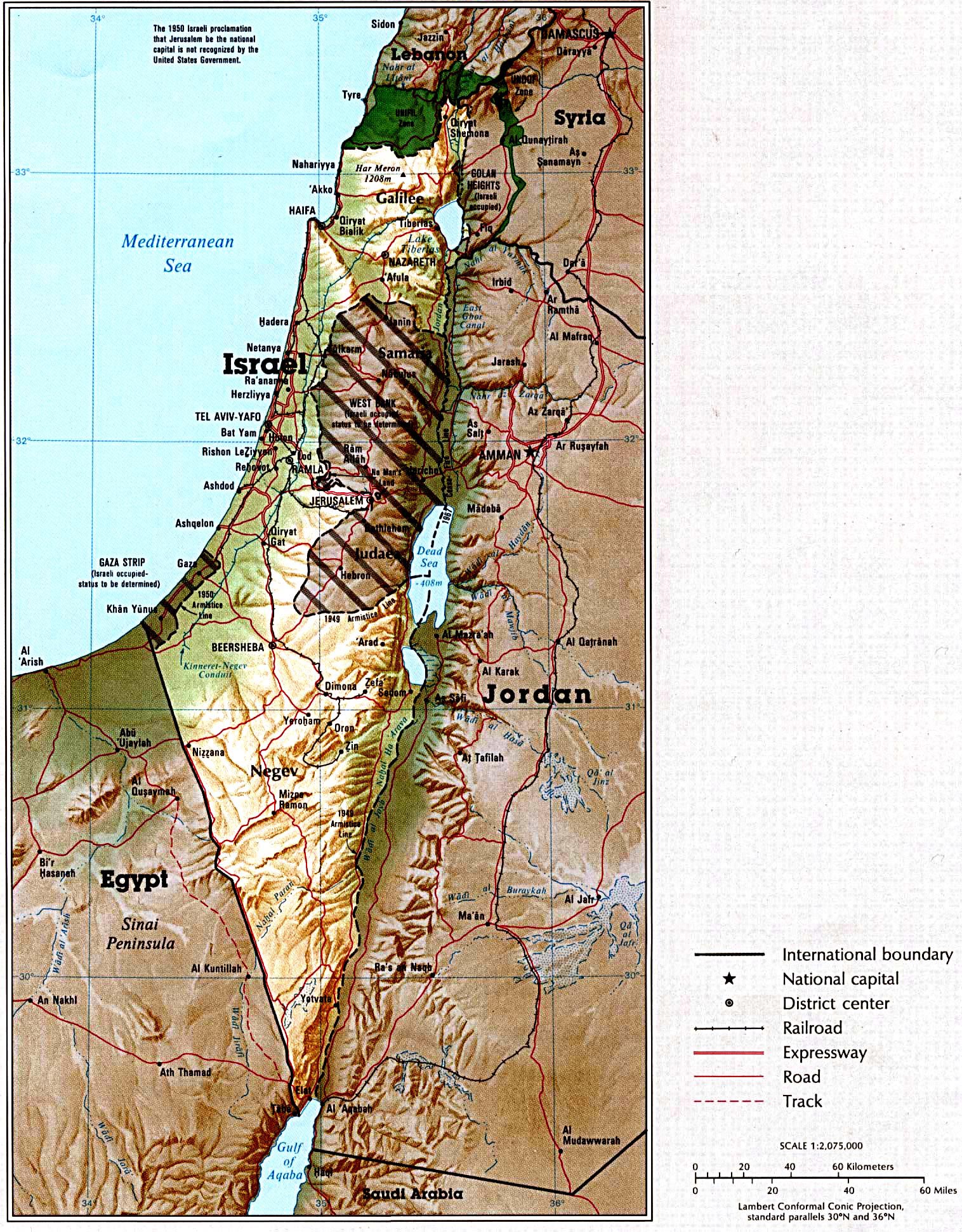
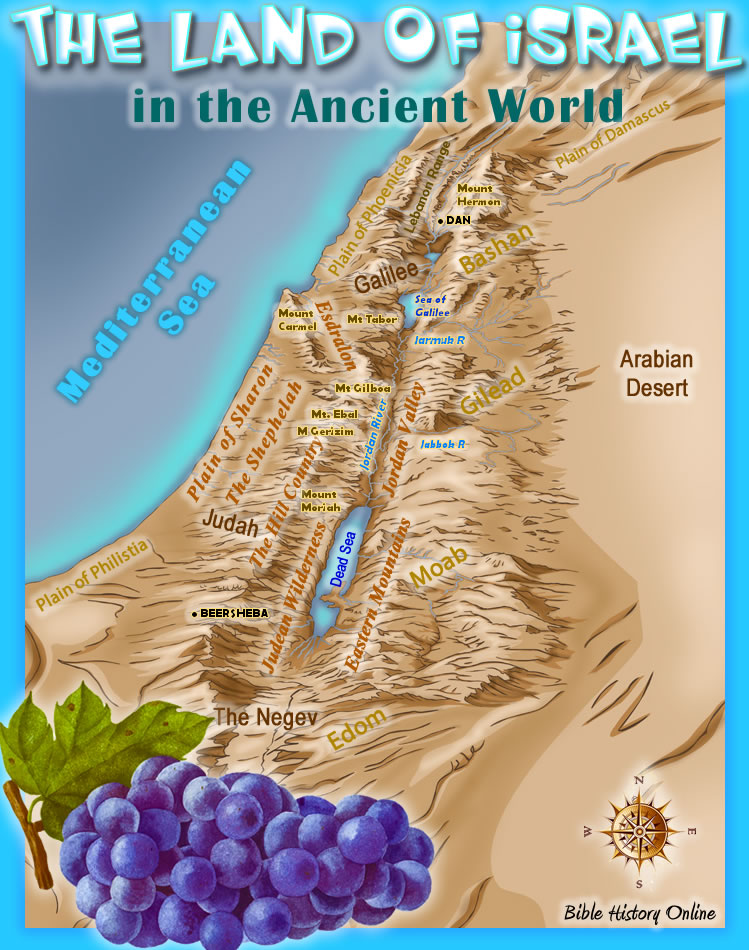
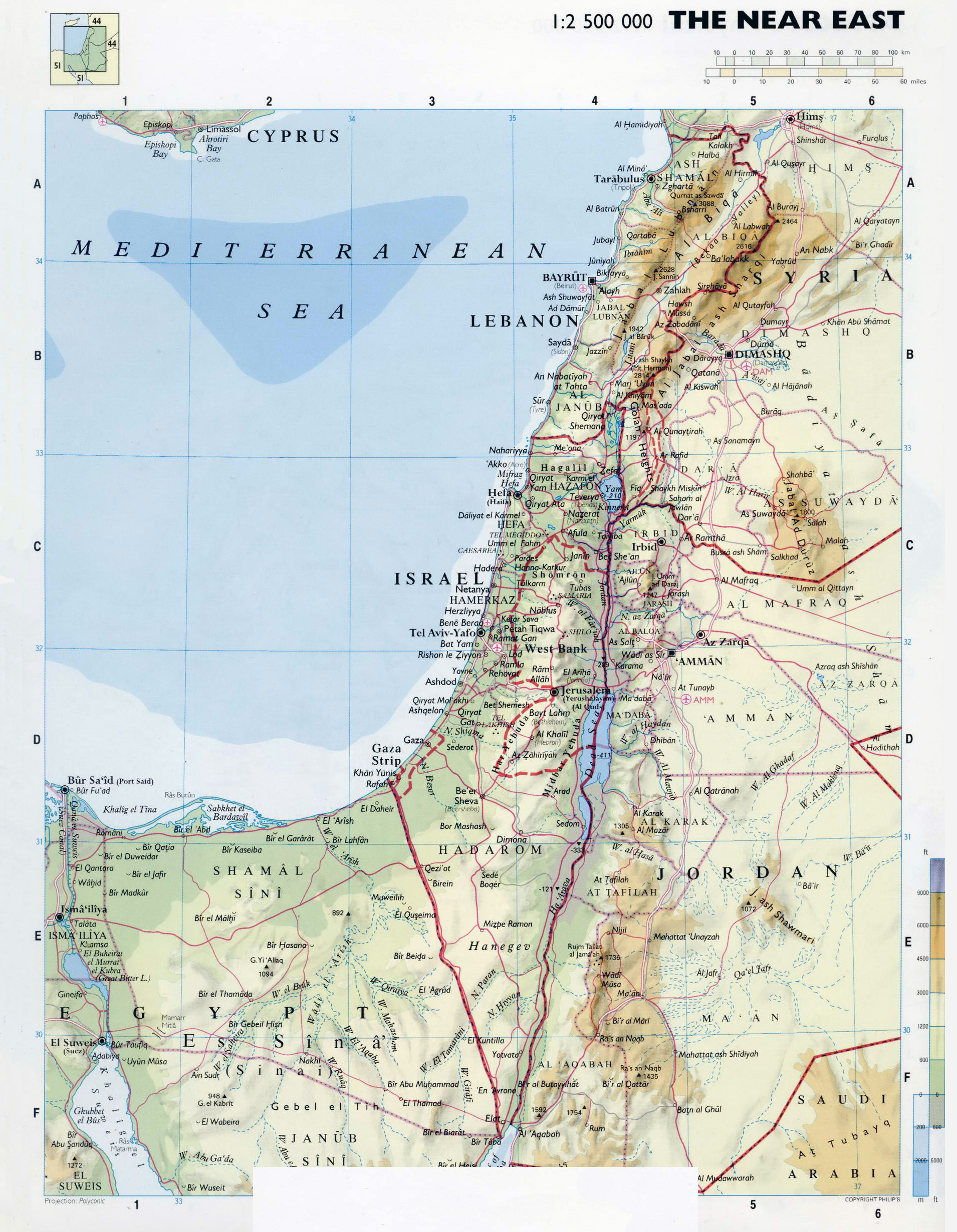
The intricate tapestry of the Middle East is woven with threads of history, religion, and politics, and nowhere is this more evident than in the geographically intertwined nations of Israel and Lebanon. Examining the map of these two countries reveals a landscape rich in both natural beauty and historical significance, but also marked by complex geopolitical dynamics. Understanding the geographic features and their historical context is crucial for appreciating the ongoing challenges and potential for cooperation in this region.
The Geography of Israel:
Israel, located on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea, is a relatively small country with a diverse landscape. Its territory encompasses a narrow coastal plain, the rolling hills of the Galilee and Samaria, the arid Negev Desert, and the Jordan Rift Valley, which forms a natural border with Jordan. The country’s geographical features have played a significant role in its history, shaping its agricultural practices, infrastructure development, and military strategy.
- The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip of land along the Mediterranean coast is home to major cities like Tel Aviv and Haifa. It is a vital economic hub for Israel, supporting agriculture, industry, and tourism.
- The Galilee and Samaria: These hilly regions in northern Israel are known for their agricultural potential and are home to a diverse population, including Jewish and Arab communities.
- The Negev Desert: Covering over 60% of Israel’s landmass, the Negev Desert is characterized by its arid climate and sparse population. However, it holds significant mineral resources and is undergoing development initiatives for agriculture and energy production.
- The Jordan Rift Valley: This deep geological depression, running through the eastern part of Israel, is home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and is a site of significant historical and religious importance.
The Geography of Lebanon:
Lebanon, nestled on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea, is a country of diverse landscapes, ranging from the high peaks of the Lebanon Mountain Range to the fertile Beqaa Valley. The country shares borders with Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Lebanon’s geography has contributed to its rich cultural heritage and unique agricultural practices.
- The Lebanon Mountain Range: This majestic mountain range, running parallel to the Mediterranean coast, is a defining feature of Lebanon’s landscape. It is home to cedar forests, alpine meadows, and numerous historical sites, including the ancient city of Baalbek.
- The Beqaa Valley: Located between the Lebanon Mountain Range and the Anti-Lebanon Range, the Beqaa Valley is a fertile plain known for its agriculture, particularly its production of fruits, vegetables, and wine.
- The Coastal Plain: Lebanon’s coastal plain is a narrow strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea, characterized by its sandy beaches and urban centers like Beirut, the country’s capital.
The Shared Geography and Its Significance:
The geographical proximity of Israel and Lebanon, coupled with their shared history and cultural heritage, has created a complex and often tense relationship. The two countries have been embroiled in conflict for decades, fueled by territorial disputes, political differences, and religious tensions. However, the shared geography also presents opportunities for cooperation, particularly in areas like water management, environmental protection, and economic development.
- The Litani River: This river, originating in the Lebanon Mountain Range, flows through Lebanon and forms part of the border with Israel. Its water resources have been a source of contention between the two countries, but also present potential for shared management.
- The Golan Heights: This strategically important plateau, overlooking the Galilee region of Israel, was captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War. Its status remains a source of ongoing conflict, with Syria claiming it as its own.
- The Mediterranean Sea: The shared coastline provides opportunities for economic cooperation, particularly in the areas of fishing, tourism, and energy exploration.
Understanding the Map:
The map of Israel and Lebanon reveals the complex interplay of geographical features, historical events, and political realities. It highlights the challenges of coexistence in a region marked by conflict and the potential for cooperation based on shared interests.
FAQs about the Map of Israel and Lebanon:
Q: What is the significance of the border between Israel and Lebanon?
A: The border between Israel and Lebanon has been a source of conflict for decades, with numerous armed clashes and incursions occurring throughout the years. The border remains a sensitive issue, with ongoing disputes over territory, security, and the presence of Hezbollah, a Lebanese Shia militia.
Q: What are the main geographical features that influence the relationship between Israel and Lebanon?
A: The Litani River, the Golan Heights, and the Mediterranean Sea are key geographical features that have shaped the relationship between Israel and Lebanon. The Litani River’s water resources have been a point of contention, while the Golan Heights remains a disputed territory. The Mediterranean Sea offers potential for cooperation but also presents challenges related to maritime boundaries and security.
Q: How does the geography of Israel and Lebanon impact their respective economies?
A: The geography of Israel and Lebanon plays a significant role in their economies. Israel’s coastal plain supports agriculture, industry, and tourism, while its Negev Desert holds mineral resources. Lebanon’s fertile Beqaa Valley is a major agricultural hub, and its coastal plain supports tourism and urban development. However, both countries face challenges related to limited natural resources, water scarcity, and the impact of climate change.
Tips for Using the Map of Israel and Lebanon:
- Study the geographical features: Familiarize yourself with the major mountains, rivers, and valleys, as these features have played a crucial role in the history and development of both countries.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the key historical events that have shaped the current situation, including wars, treaties, and political negotiations.
- Analyze the political landscape: Examine the political systems, major political parties, and influential figures in both countries to understand their respective perspectives and priorities.
- Explore the cultural and religious diversity: Recognize the diverse cultural and religious communities that coexist in Israel and Lebanon, and their impact on the social and political dynamics of both countries.
Conclusion:
The map of Israel and Lebanon offers a visual representation of a complex and contested landscape. It reveals the geographical features, historical events, and political realities that have shaped the relationship between these two countries. Understanding this map is crucial for appreciating the ongoing challenges and potential for cooperation in this region. As the Middle East continues to evolve, the map of Israel and Lebanon will remain a vital tool for navigating the complexities of this dynamic and often turbulent region.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Overview of Israel and Lebanon: A Complex and Contested Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!