A Journey Through California’s Diverse Wine Regions: Exploring the American Viticultural Areas (AVAs)
Related Articles: A Journey Through California’s Diverse Wine Regions: Exploring the American Viticultural Areas (AVAs)
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through California’s Diverse Wine Regions: Exploring the American Viticultural Areas (AVAs). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through California’s Diverse Wine Regions: Exploring the American Viticultural Areas (AVAs)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/alexander-valley-autumn-1061574216-690f4bcc6f8542e2a05996654a1ce6bd.jpg)
California, renowned for its sun-drenched vineyards and award-winning wines, boasts a complex tapestry of viticultural regions, each with its own unique character and terroir. The American Viticultural Areas (AVAs) system, established by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB), provides a framework for understanding these distinct regions and their contribution to the state’s diverse wine landscape.
Defining California’s Wine Landscape: The AVA System
The AVA system is a hierarchical classification system, dividing the United States into geographically defined regions that share common viticultural characteristics. These characteristics include climate, soil type, elevation, and grape varietal suitability, all factors that influence the final expression of the wine.
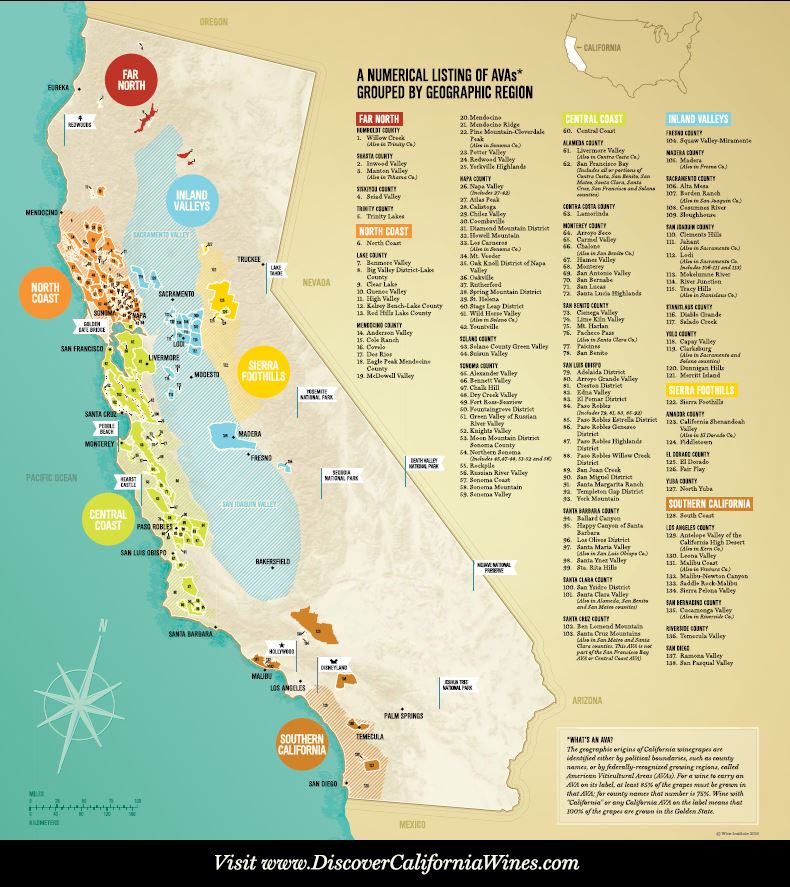
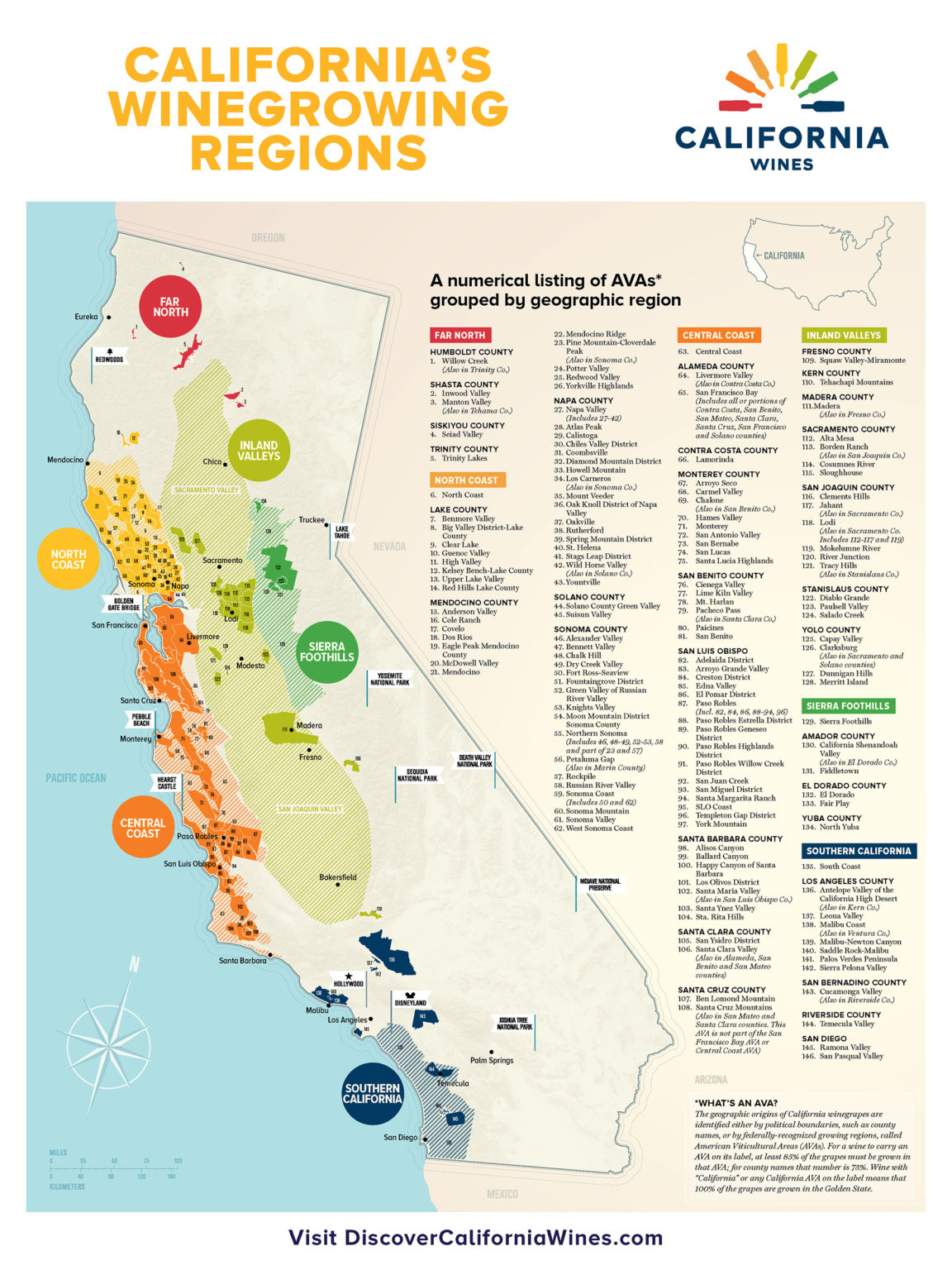
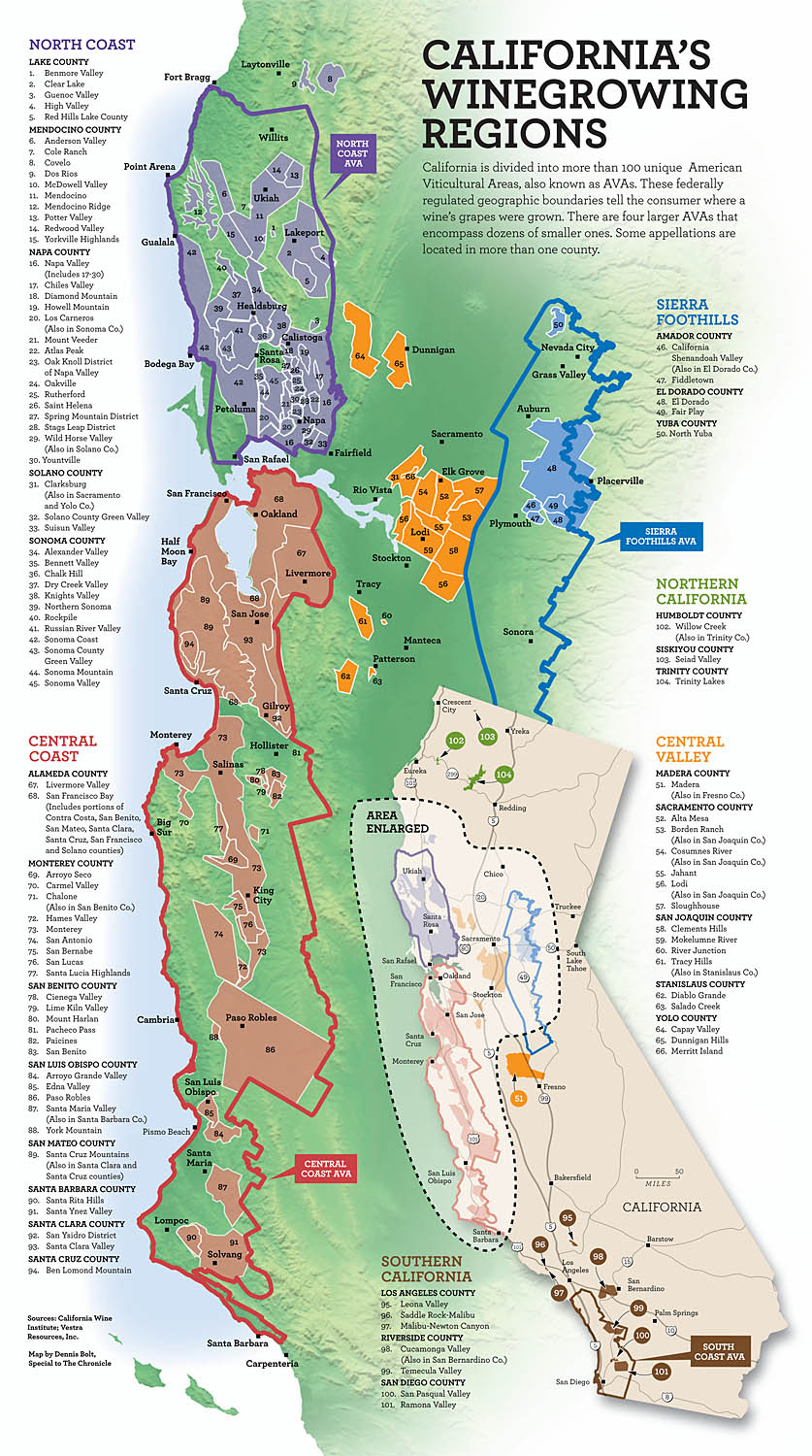
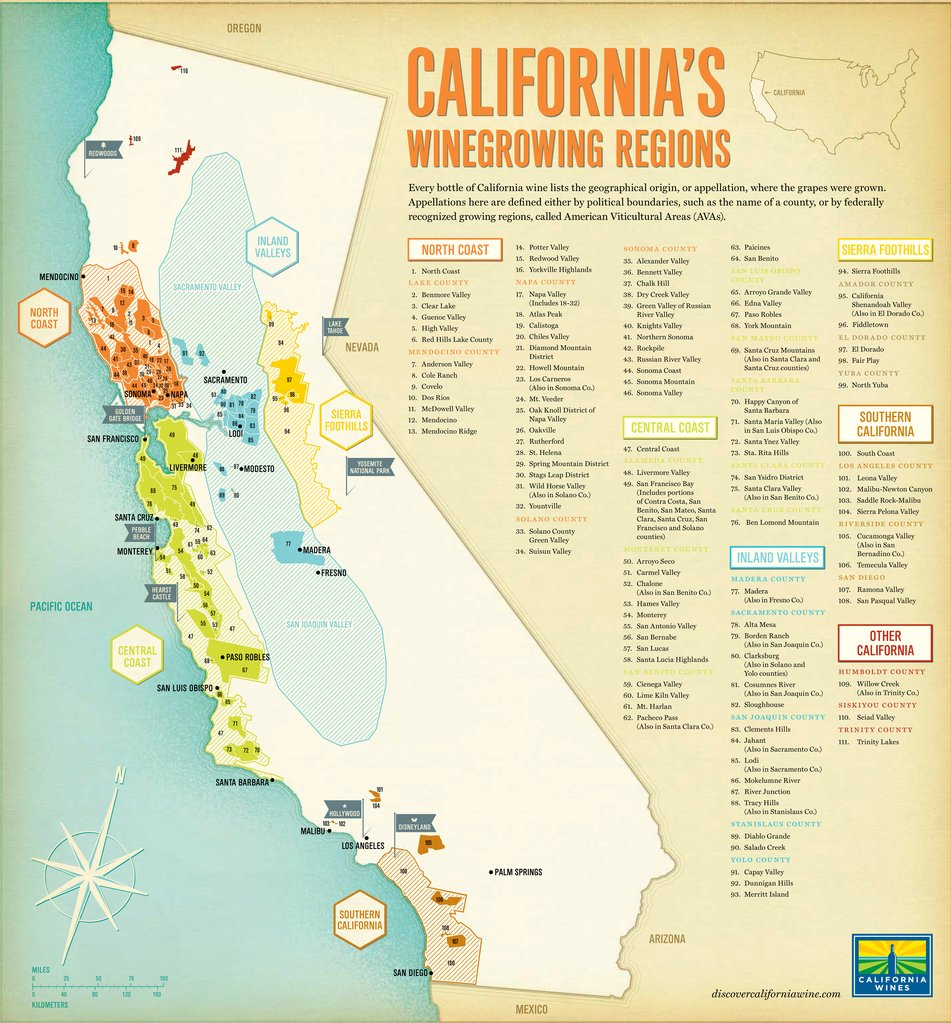
California, with its vast geographic diversity, has a particularly intricate AVA system, encompassing 147 distinct regions. These AVAs range from the cool coastal areas of the Pacific Ocean to the scorching desert valleys of the interior, showcasing a remarkable spectrum of microclimates and soil types.
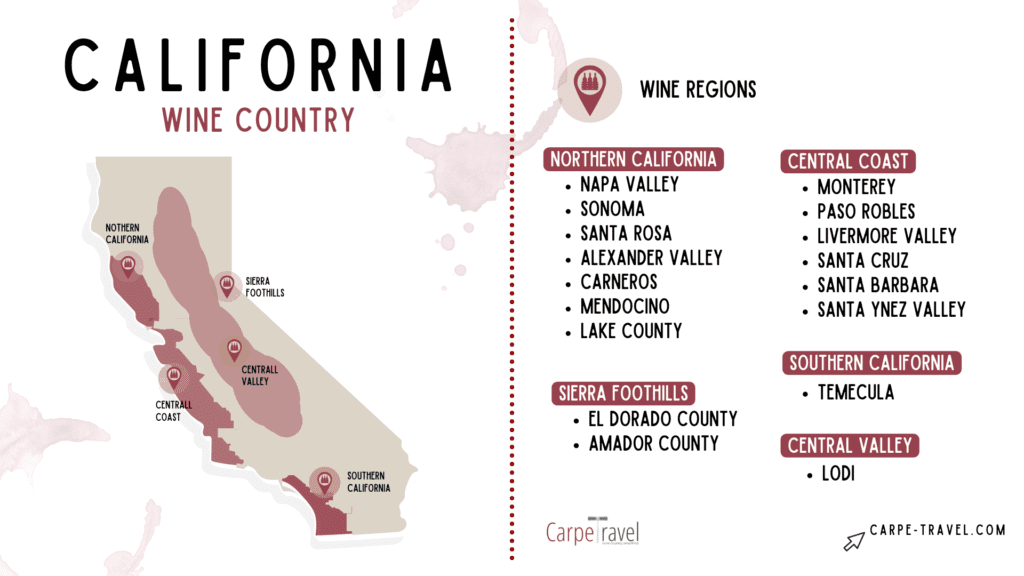
Navigating California’s Wine Map
To understand California’s wine map, it’s helpful to consider its primary geographic divisions:
- Coastal Regions: These areas, characterized by cool, fog-laden summers and moderate temperatures, are ideal for producing crisp, refreshing wines. They include the Sonoma Coast, Santa Cruz Mountains, Paso Robles, and Santa Barbara County, among others.
- Interior Valleys: These regions, located inland, experience hotter summers and cooler winters, creating a unique terroir for producing bold, full-bodied wines. Notable interior valleys include Napa Valley, Lodi, San Joaquin Valley, and Central Coast.
- Mountain Regions: California’s mountainous areas, with their varying elevations and unique microclimates, offer a diverse range of growing conditions. These regions, such as the Sierra Foothills, Mendocino, and Lake County, are known for their distinctive wines with complex flavor profiles.
A Glimpse into the Diversity of California’s AVAs
Let’s delve into a few specific examples to illustrate the unique characteristics of California’s AVAs:
- Napa Valley: This iconic region, synonymous with Cabernet Sauvignon, enjoys warm days and cool nights, fostering ripe fruit development. Its volcanic soils contribute to the wines’ rich structure and long aging potential.
- Sonoma Coast: The cool, foggy climate of the Sonoma Coast lends itself to producing elegant, balanced Pinot Noir and Chardonnay. The region’s diverse soils, ranging from sandy loam to clay, contribute to the wines’ complexity and minerality.
- Paso Robles: This Central Coast AVA, known for its Mediterranean climate and diverse soils, offers a wide range of grape varietals, including Zinfandel, Cabernet Sauvignon, and Syrah. The region’s warm days and cool nights create wines with bold fruit flavors and concentrated tannins.
- Santa Barbara County: This diverse AVA, with its coastal influence and inland valleys, produces a variety of wines, including Sauvignon Blanc, Pinot Noir, and Rhône varietals. The region’s unique microclimates and soil types contribute to the wines’ distinct character and complexity.
The Importance of AVAs in Winemaking and Consumer Understanding
The AVA system serves several key purposes:
- Geographic Identity: AVAs provide a framework for identifying and understanding the unique characteristics of different wine regions. This allows consumers to make informed choices based on their preferences for specific styles and flavors.
- Quality Control: The AVA system encourages winemakers to focus on producing wines that reflect the unique terroir of their designated region. This promotes quality and consistency within each AVA.
- Marketing and Branding: AVAs serve as valuable marketing tools, allowing consumers to readily identify wines from specific regions and understand their distinct characteristics.
- Research and Development: The AVA system provides a valuable framework for researchers and winemakers to study the impact of different geographic factors on wine quality and style.
FAQs about California’s AVAs
Q: How many AVAs are there in California?
A: As of 2023, California has 147 designated AVAs.
Q: What is the smallest AVA in California?
A: The smallest AVA in California is the Los Alamos AVA, located in Santa Barbara County.
Q: What is the largest AVA in California?
A: The largest AVA in California is the Central Coast AVA, encompassing a vast region from the Santa Barbara County to Monterey County.
Q: Can an AVA be located within another AVA?
A: Yes, AVAs can be nested within other AVAs. For example, the Stags Leap District AVA is located within the Napa Valley AVA.
Q: What are the benefits of understanding California’s AVAs?
A: Understanding California’s AVAs allows consumers to make informed wine selections, appreciate the diversity of the state’s wine landscape, and explore the unique characteristics of different regions.
Tips for Exploring California’s Wine Regions
- Start with a Map: A map of California’s AVAs can be a helpful tool for planning your wine exploration.
- Research the Regions: Take time to learn about the specific characteristics of each AVA, including climate, soil type, and dominant grape varietals.
- Visit Wineries: Plan visits to wineries within your chosen AVAs to experience the wines firsthand and learn about the winemaking process.
- Attend Wine Tastings: Participate in wine tastings to explore a variety of wines from different AVAs and discover new favorites.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask winemakers and tasting room staff about the wines and the region’s unique terroir.
Conclusion
California’s American Viticultural Areas (AVAs) represent a fascinating tapestry of viticultural regions, each with its own unique character and terroir. Understanding the AVA system provides valuable insights into the diversity of California’s wine landscape, allowing consumers to make informed choices and appreciate the artistry of winemaking in this iconic state. By exploring California’s AVAs, wine enthusiasts can embark on a journey of discovery, appreciating the nuances of terroir and the remarkable diversity of California’s wine regions.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through California’s Diverse Wine Regions: Exploring the American Viticultural Areas (AVAs). We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!