A Look at Maryland’s Congressional Map: Shaping Representation and Political Landscape
Related Articles: A Look at Maryland’s Congressional Map: Shaping Representation and Political Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Look at Maryland’s Congressional Map: Shaping Representation and Political Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Look at Maryland’s Congressional Map: Shaping Representation and Political Landscape
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Look at Maryland’s Congressional Map: Shaping Representation and Political Landscape
- 3.1 Historical Evolution: A Tale of Redistricting and Legal Battles
- 3.2 The Current Map: A Complex Web of Districts
- 3.3 The Importance of Maryland’s Congressional Map: Impact on Representation and Policy
- 3.4 FAQs on Maryland’s Congressional Map
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding Maryland’s Congressional Map
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Complex System with Far-Reaching Implications
- 4 Closure
A Look at Maryland’s Congressional Map: Shaping Representation and Political Landscape

Maryland’s congressional map, a complex tapestry of lines and districts, holds significant sway over the state’s political landscape. This map, a product of a meticulous process involving the state legislature and, in some instances, the courts, determines the boundaries of each congressional district, influencing the composition of the state’s delegation in the U.S. House of Representatives. Understanding the intricacies of Maryland’s congressional map provides crucial insight into the state’s political dynamics and the representation of its diverse population.
Historical Evolution: A Tale of Redistricting and Legal Battles
Maryland’s congressional map has undergone numerous transformations over the decades, reflecting shifts in population, political power, and legal challenges. The state’s initial congressional districts, established in the late 18th century, were based on a simple, county-centric approach. However, as the state’s population grew and its political landscape evolved, redistricting became necessary to ensure equitable representation.
The 20th century witnessed significant changes in Maryland’s congressional map. The rise of urban areas, particularly in Baltimore City, led to the creation of districts that concentrated urban populations. This process often involved gerrymandering, a practice that manipulates district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group.
The 1960s brought about a crucial shift in redistricting principles with the landmark Supreme Court case, Reynolds v. Sims. This case established the "one person, one vote" principle, requiring districts to be roughly equal in population. This principle significantly impacted Maryland’s congressional map, leading to the creation of more compact and geographically balanced districts.
The 1990s and 2000s saw continued legal challenges to Maryland’s congressional map, with concerns raised about racial gerrymandering and the dilution of minority voting power. These challenges, often brought before the courts, highlighted the complex interplay between redistricting, representation, and legal principles.
The Current Map: A Complex Web of Districts
Maryland’s current congressional map, adopted in 2011, features eight congressional districts. These districts vary significantly in size and shape, reflecting the state’s diverse geography and population distribution. The map’s most prominent feature is the concentration of Democratic-leaning districts in the Baltimore metropolitan area and the Washington, D.C., suburbs, while the state’s eastern and western regions tend to lean Republican.
The map’s design has sparked significant debate, with critics arguing that it unfairly favors Democrats and dilutes the voting power of Republicans. Proponents, however, maintain that the map is necessary to ensure fair representation for all Marylanders, particularly minority communities.
The Importance of Maryland’s Congressional Map: Impact on Representation and Policy
Maryland’s congressional map plays a pivotal role in shaping the state’s political landscape, influencing the composition of the state’s delegation in the U.S. House of Representatives. The map’s design directly affects the representation of different communities and political ideologies, influencing the outcome of elections and the direction of policy.
The map’s impact on representation is particularly significant for minority communities. The creation of districts with concentrated minority populations, often referred to as "majority-minority" districts, aims to ensure that these communities have a voice in Congress. However, these districts can also be subject to criticism, with some arguing that they create segregated communities and limit the political power of minority voters outside these districts.
The map’s influence on policy is equally significant. The composition of the state’s congressional delegation, determined by the map’s design, impacts the state’s ability to secure federal funding and influence national legislation. A delegation dominated by one party can have a significant impact on the passage of legislation that aligns with its political agenda.
FAQs on Maryland’s Congressional Map
1. Who is responsible for drawing Maryland’s congressional map?
Maryland’s congressional map is drawn by the state legislature. The process involves a complex interplay between legislative committees, political parties, and public input.
2. How often is Maryland’s congressional map redrawn?
Maryland’s congressional map is redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census. This process ensures that districts reflect changes in population distribution and maintain roughly equal population sizes.
3. What are the criteria used to draw Maryland’s congressional map?
The criteria used to draw Maryland’s congressional map include:
- Equal population: Districts must have roughly equal population sizes to comply with the "one person, one vote" principle.
- Contiguity: Districts must be geographically contiguous, meaning that all parts of the district are connected.
- Compactness: Districts should be as compact as possible, avoiding sprawling and irregularly shaped boundaries.
- Respect for communities of interest: Districts should respect existing communities and avoid splitting them across multiple districts.
4. What are the legal challenges associated with Maryland’s congressional map?
Maryland’s congressional map has faced numerous legal challenges over the years, primarily related to:
- Racial gerrymandering: Concerns about the manipulation of district boundaries to dilute the voting power of minority communities.
- Political gerrymandering: Concerns about the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular political party.
5. What are the potential consequences of gerrymandering in Maryland?
Gerrymandering can have significant consequences, including:
- Reduced voter choice: Gerrymandered districts can create safe seats for one party, reducing the number of competitive elections.
- Increased political polarization: Gerrymandering can contribute to a more polarized political landscape by creating districts that are overwhelmingly dominated by one party.
- Underrepresentation of minority communities: Gerrymandering can dilute the voting power of minority communities, making it more difficult for them to elect representatives who reflect their interests.
Tips for Understanding Maryland’s Congressional Map
1. Explore the map’s history: Understanding the historical context of Maryland’s congressional map provides valuable insights into the forces that have shaped its evolution.
2. Analyze district demographics: Examining the demographic characteristics of each district can reveal the map’s impact on representation and the needs of different communities.
3. Follow redistricting processes: Staying informed about the redistricting process, including public hearings and legal challenges, helps understand the dynamics of map creation.
4. Engage in political discourse: Participating in discussions and debates about Maryland’s congressional map allows for informed dialogue and critical analysis of its impact.
5. Seek out diverse perspectives: Reading articles and analyses from various sources provides a broader understanding of the map’s implications and the diverse opinions surrounding it.
Conclusion: A Complex System with Far-Reaching Implications
Maryland’s congressional map, a complex web of lines and districts, plays a critical role in shaping the state’s political landscape. Its design influences the representation of diverse communities, the outcome of elections, and the direction of policy. Understanding the map’s intricacies, its historical evolution, and the legal challenges it faces is crucial for engaging in informed political discourse and advocating for fair and equitable representation. As the state continues to evolve, so too will its congressional map, demanding ongoing scrutiny and analysis to ensure that it accurately reflects the needs and aspirations of all Marylanders.
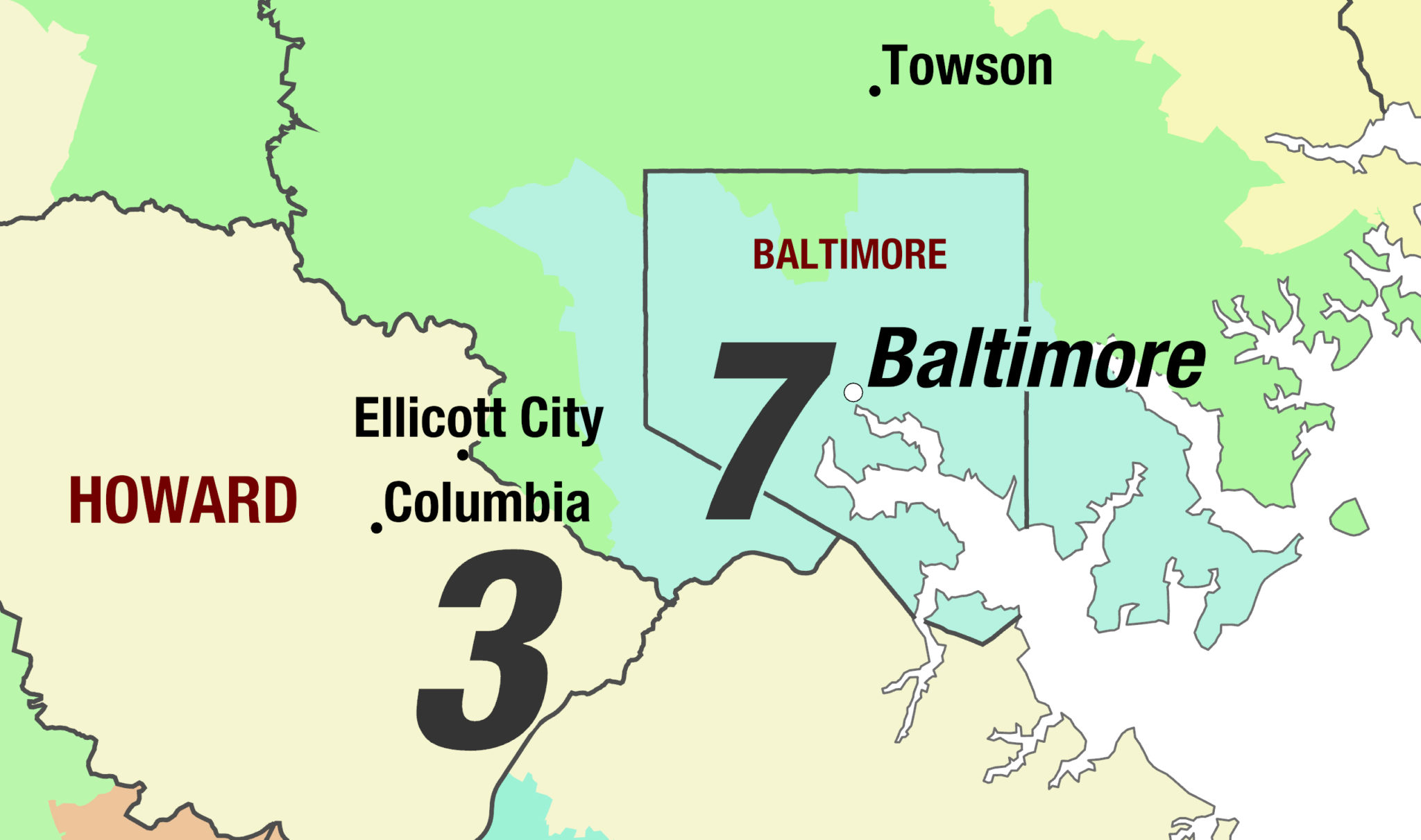
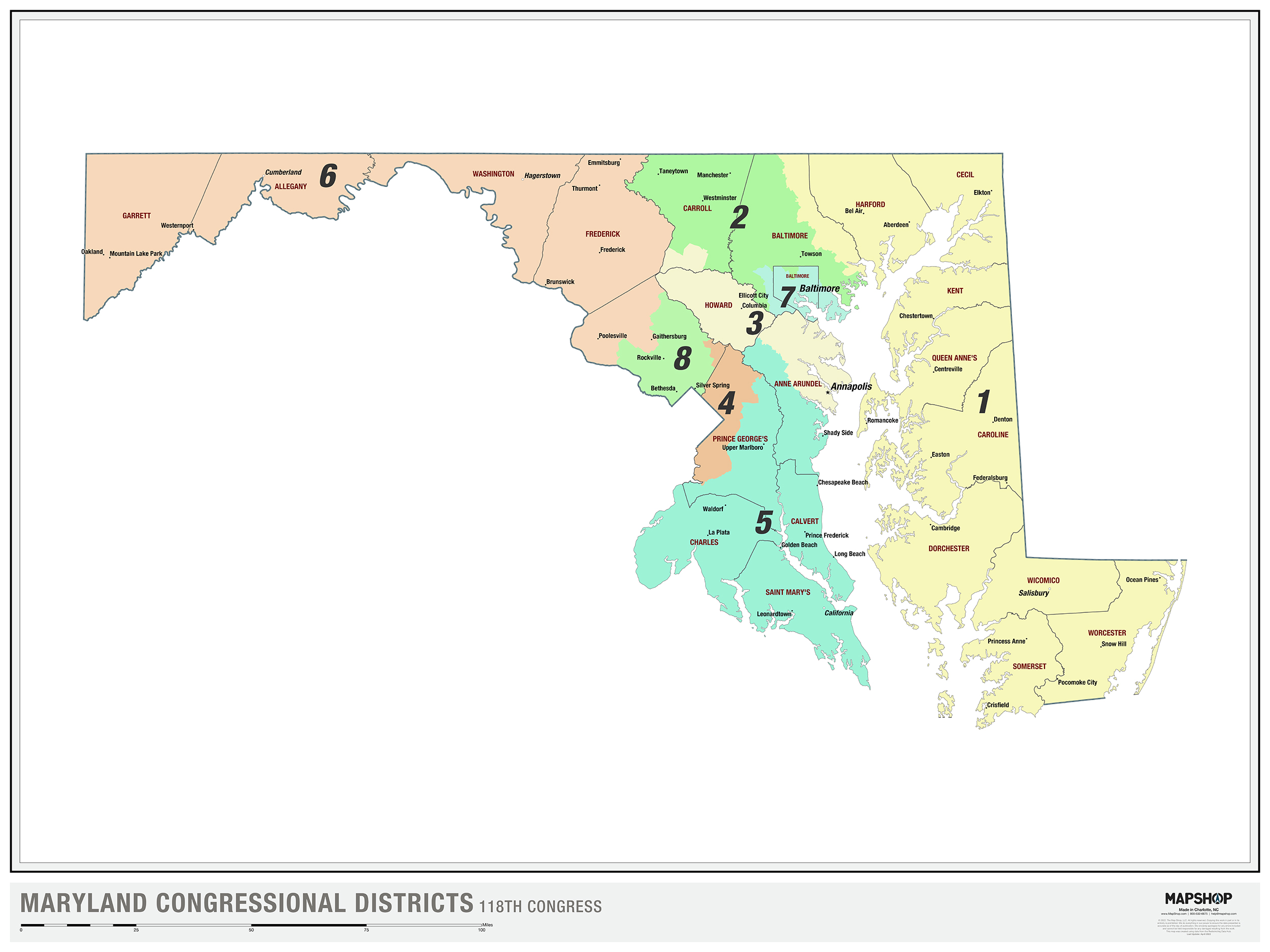





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Look at Maryland’s Congressional Map: Shaping Representation and Political Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
