A World of Fire: Exploring the Global Distribution of Active Volcanoes
Related Articles: A World of Fire: Exploring the Global Distribution of Active Volcanoes
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A World of Fire: Exploring the Global Distribution of Active Volcanoes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A World of Fire: Exploring the Global Distribution of Active Volcanoes
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A World of Fire: Exploring the Global Distribution of Active Volcanoes
- 3.1 Mapping the Earth’s Fiery Heart: Understanding the Distribution of Active Volcanoes
- 3.2 The Importance of Understanding Active Volcanoes
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions About Active Volcanoes
- 3.4 Tips for Understanding and Using Maps of Active Volcanoes
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
A World of Fire: Exploring the Global Distribution of Active Volcanoes

The Earth’s surface is a dynamic and ever-changing landscape, sculpted by the forces of plate tectonics. One of the most dramatic and awe-inspiring manifestations of these forces is volcanic activity. Volcanoes, with their fiery eruptions and imposing silhouettes, serve as potent reminders of the planet’s inner dynamism. A map of active volcanoes offers a unique window into this subterranean world, revealing the distribution and intensity of volcanic activity across the globe.
Mapping the Earth’s Fiery Heart: Understanding the Distribution of Active Volcanoes
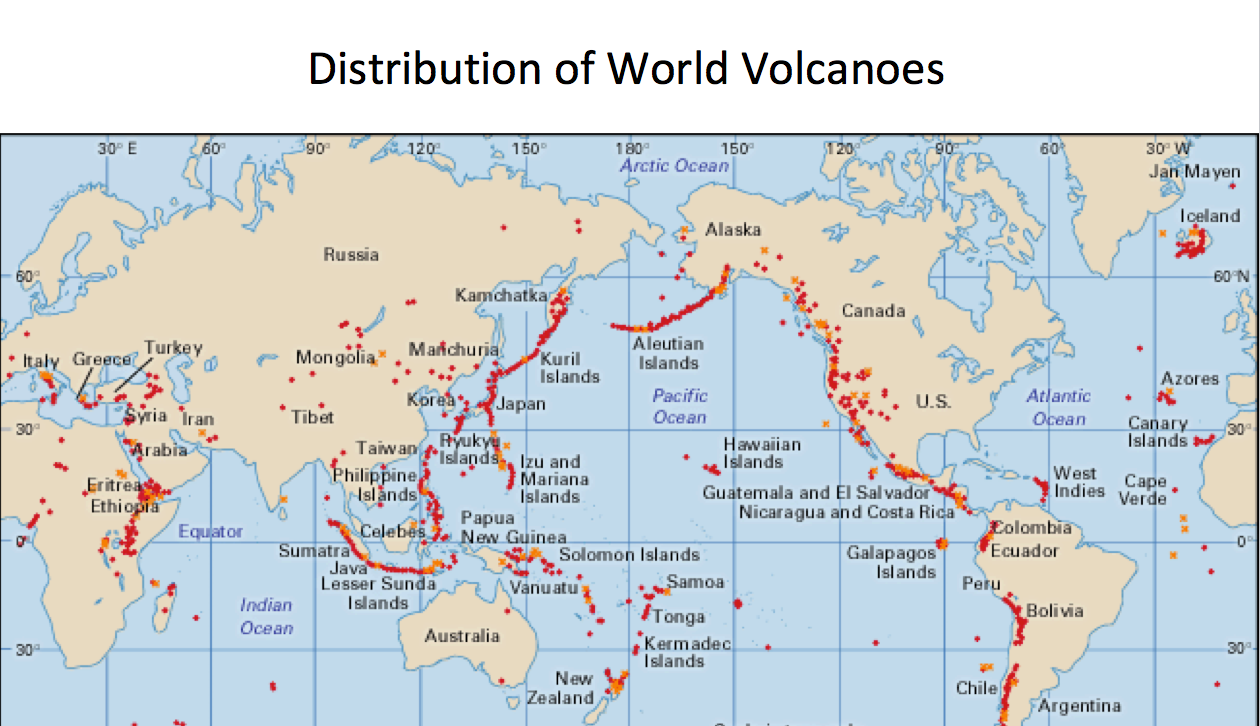
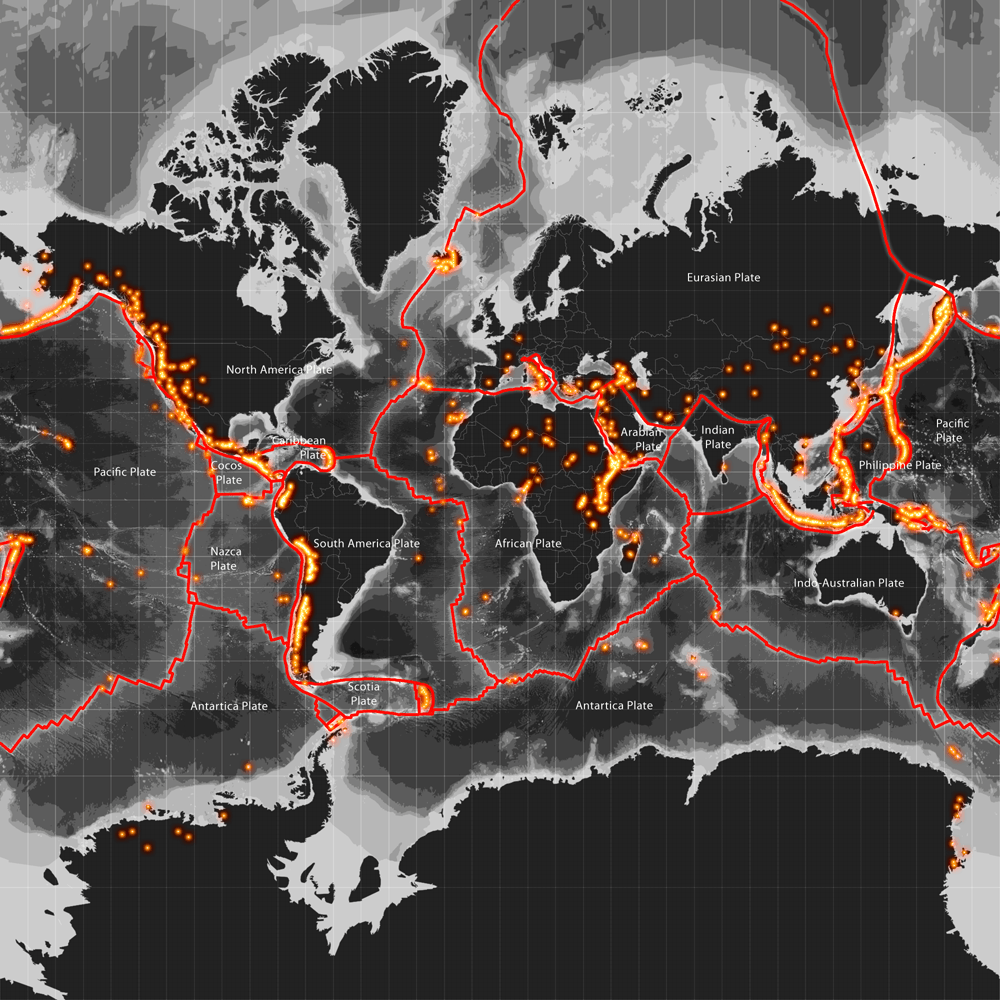
Volcanoes are not randomly scattered across the planet. Their distribution is closely tied to the movement of tectonic plates, the giant slabs of rock that make up the Earth’s crust. These plates are constantly in motion, interacting with each other in a complex dance of collision, separation, and sliding.
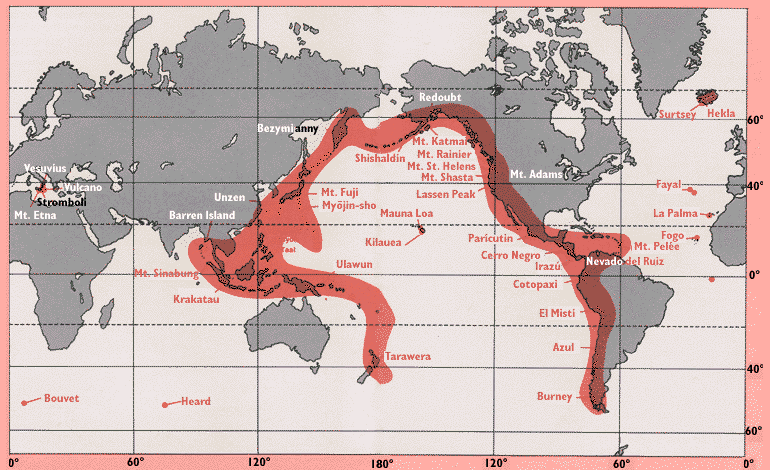
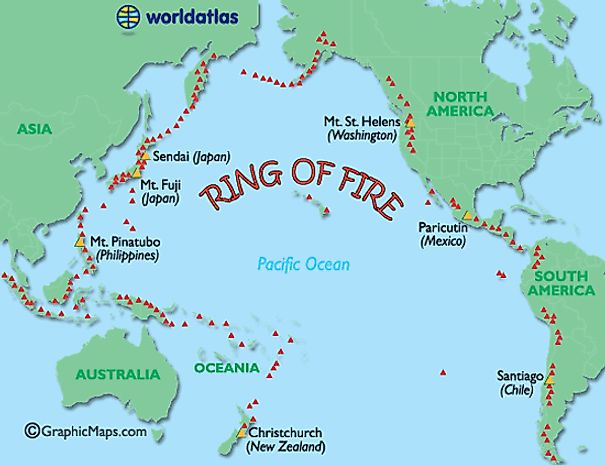
1. Convergent Plate Boundaries: Where tectonic plates collide, one plate often subducts (slides) beneath the other. As the descending plate melts, the molten rock rises to the surface, creating volcanoes. The Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped zone encircling the Pacific Ocean, is a prime example of this phenomenon. It is home to a vast majority of the world’s active volcanoes, including iconic peaks like Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Vesuvius in Italy, and Mount St. Helens in the United States.
2. Divergent Plate Boundaries: Where plates pull apart, magma rises from the mantle, forming new crust and creating volcanoes. This process is most evident at mid-ocean ridges, underwater mountain ranges that span the globe. While these underwater volcanoes are often hidden from view, they are responsible for the continuous formation of new oceanic crust.
3. Hotspots: These areas of volcanic activity are not directly associated with plate boundaries. They are thought to be caused by plumes of hot mantle material rising to the surface. Hawaii, with its chain of volcanic islands, is a classic example of a hotspot.
The Importance of Understanding Active Volcanoes
Mapping active volcanoes is not just an academic exercise. It serves a crucial role in safeguarding human lives and property:
1. Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions: By monitoring active volcanoes, scientists can identify precursors to eruptions, such as increased seismic activity, ground deformation, and gas emissions. This information allows authorities to issue timely warnings, enabling communities to evacuate and take necessary precautions.
2. Assessing Volcanic Hazards: Maps of active volcanoes help identify areas at risk from volcanic hazards like lava flows, ashfall, and pyroclastic flows. This information informs land-use planning, infrastructure development, and emergency response strategies.
3. Understanding Earth’s Dynamics: Studying volcanic activity provides valuable insights into the Earth’s internal processes. Volcanoes offer a window into the composition and dynamics of the mantle, helping scientists understand the forces that shape our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions About Active Volcanoes
1. What is the difference between active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes?
- Active volcanoes: Volcanoes that have erupted in the past 10,000 years or are currently erupting.
- Dormant volcanoes: Volcanoes that have not erupted in the past 10,000 years but have the potential to erupt again.
- Extinct volcanoes: Volcanoes that are unlikely to erupt again.
2. How can I find a map of active volcanoes?
Several websites and organizations provide maps of active volcanoes, including:
- The Global Volcanism Program (GVP): https://volcano.si.edu/
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS): https://www.usgs.gov/
- The Smithsonian Institution: https://www.si.edu/
3. What are some of the most famous active volcanoes in the world?
- Mount Vesuvius (Italy): Famous for its eruption in 79 AD that buried the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum.
- Mount Etna (Italy): Europe’s largest and most active volcano.
- Mount Fuji (Japan): A sacred mountain and a symbol of Japan.
- Mount Kilimanjaro (Tanzania): Africa’s highest mountain, with three volcanic cones.
- Mount St. Helens (United States): Known for its devastating eruption in 1980.
Tips for Understanding and Using Maps of Active Volcanoes
- Pay attention to the scale: Maps can be at different scales, so be sure to understand the area covered by the map.
- Look for key information: Maps often include information on the location of volcanoes, their eruption history, and potential hazards.
- Use multiple sources: Compare information from different sources to get a comprehensive understanding of volcanic activity.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on volcanic activity by following news reports and official websites.
Conclusion
A map of active volcanoes is a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s dynamic nature. It highlights the interconnectedness of geological processes and provides valuable information for hazard mitigation, land-use planning, and scientific research. By studying and monitoring these fiery giants, we can better understand our planet and prepare for the challenges they present.

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World of Fire: Exploring the Global Distribution of Active Volcanoes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!