China’s Position on the World Map: A Global Powerhouse
Related Articles: China’s Position on the World Map: A Global Powerhouse
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to China’s Position on the World Map: A Global Powerhouse. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
China’s Position on the World Map: A Global Powerhouse
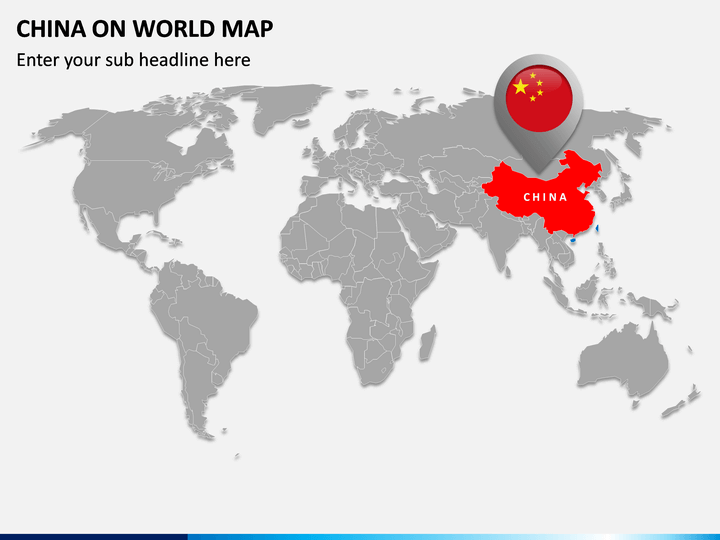
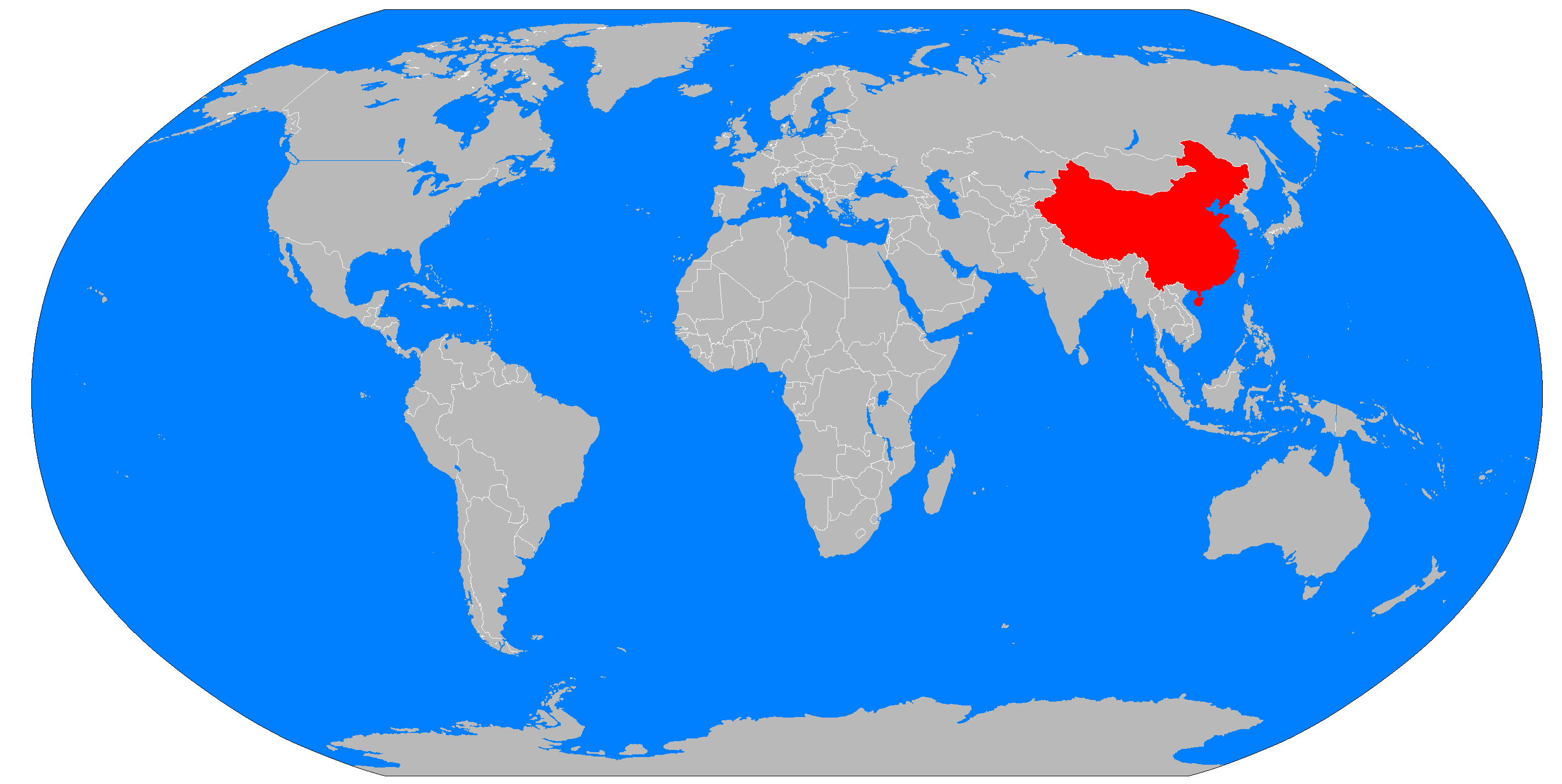
China, the world’s most populous nation, is situated in East Asia. Its vast territory spans a significant portion of the Eurasian continent, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes, from towering mountains to fertile plains and sprawling deserts. Understanding China’s geographical location is crucial for appreciating its historical development, its influence on global affairs, and its role in the modern world.
The East Asian Giant:
China’s position on the world map is defined by its location in East Asia, specifically on the eastern edge of the Eurasian continent. This strategically important location has shaped China’s history and its interactions with other nations. Its proximity to major trading routes, including the Silk Road, has facilitated cultural exchange and economic development for centuries.
A Vast and Diverse Landscape:
China’s geographical expanse is immense, covering over 9.6 million square kilometers, making it the world’s fourth-largest country by land area. This vast territory encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, including:
- The Himalayas: The world’s highest mountain range, with Mount Everest, the highest peak, forming a natural border between China and Nepal.
- The Tibetan Plateau: A high-altitude plateau known for its unique ecosystem and cultural significance.
- The North China Plain: A fertile plain that has been the cradle of Chinese civilization for millennia.
- The Gobi Desert: A vast desert region in northern China, known for its harsh conditions and unique biodiversity.
- The Yangtze River: The longest river in Asia, flowing through central China and supporting a significant population.
- The Yellow River: The second-longest river in China, known for its yellow sediment and historical significance.
A Nation of Diverse Cultures and Ethnicities:
China’s vast and diverse landscape has nurtured a rich tapestry of cultures and ethnicities. The Han Chinese constitute the majority population, but the country is also home to 55 officially recognized ethnic minority groups, each with its unique traditions, languages, and customs. This cultural diversity adds to China’s richness and complexity.
Strategic Importance and Global Influence:
China’s geographical location and its burgeoning economy have made it a global power with significant influence. Its proximity to key maritime trade routes in the Pacific Ocean and its growing military capabilities have positioned it as a major player in regional and global affairs.
The Importance of Understanding China’s Geography:
Understanding China’s geographical position is crucial for several reasons:
- Economic Growth and Development: China’s vast natural resources, including fertile land, abundant water resources, and mineral deposits, have fueled its economic growth. Its strategic location has also facilitated trade and investment, making it a global economic powerhouse.
- Political and Diplomatic Relations: China’s geographical location has influenced its political and diplomatic relations with neighboring countries. Its complex relationship with Taiwan, its territorial disputes with neighboring countries, and its growing influence in the South China Sea are all shaped by its strategic position.
- Cultural Exchange and Diversity: China’s location has facilitated cultural exchange and interaction with other nations throughout history. Its rich cultural heritage, encompassing ancient traditions, art forms, and philosophies, has had a profound impact on the world.
- Environmental Challenges and Sustainability: China faces significant environmental challenges, including air pollution, water scarcity, and deforestation, which are exacerbated by its rapid economic growth and population density. Understanding the geographical factors contributing to these challenges is crucial for finding sustainable solutions.
FAQs about China’s Geography:
Q: What are the major cities in China?
A: China has several major cities, including Beijing (the capital), Shanghai (the largest city by population), Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Chongqing.
Q: What are the main geographical features of China?
A: China’s major geographical features include the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, the North China Plain, the Gobi Desert, the Yangtze River, and the Yellow River.
Q: What are the climate zones in China?
A: China experiences a wide range of climates, from humid subtropical in the south to arid and semi-arid in the north and west.
Q: What are the major natural resources in China?
A: China is rich in natural resources, including coal, iron ore, oil, natural gas, and hydropower.
Q: What are the major ethnic groups in China?
A: The Han Chinese constitute the majority population, but China is also home to 55 officially recognized ethnic minority groups, including the Zhuang, Hui, Manchu, Uygur, and Tibetan.
Tips for Understanding China’s Geography:
- Use a map: A physical map of China can help you visualize its geographical features and understand its location in relation to other countries.
- Read about China’s history: China’s history is closely intertwined with its geography. Understanding its historical development can shed light on its current situation.
- Travel to China: Visiting China firsthand allows you to experience its diverse landscapes, cultures, and people, providing a deeper understanding of its geography.
- Follow news and current events: Staying informed about China’s current events and political developments can help you understand the impact of its geography on its global role.
Conclusion:
China’s geographical position on the world map is a testament to its historical development, its cultural diversity, and its growing influence on global affairs. From its vast and diverse landscape to its strategic location in East Asia, China’s geography has played a defining role in shaping its history, its economy, and its future. Understanding China’s geographical context is crucial for appreciating its role in the modern world and for navigating the complex challenges and opportunities it presents.
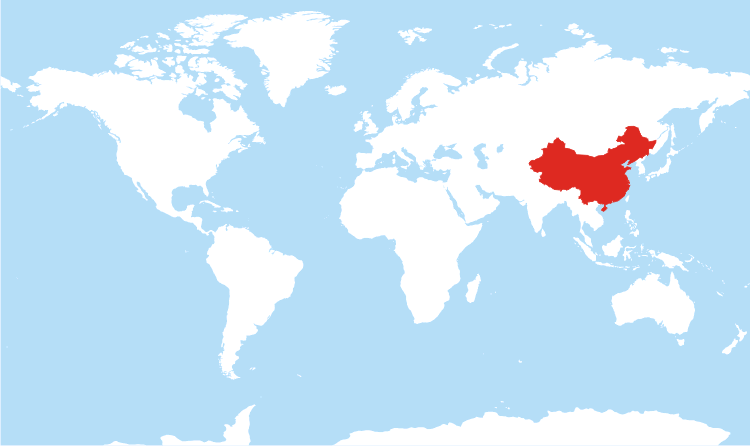
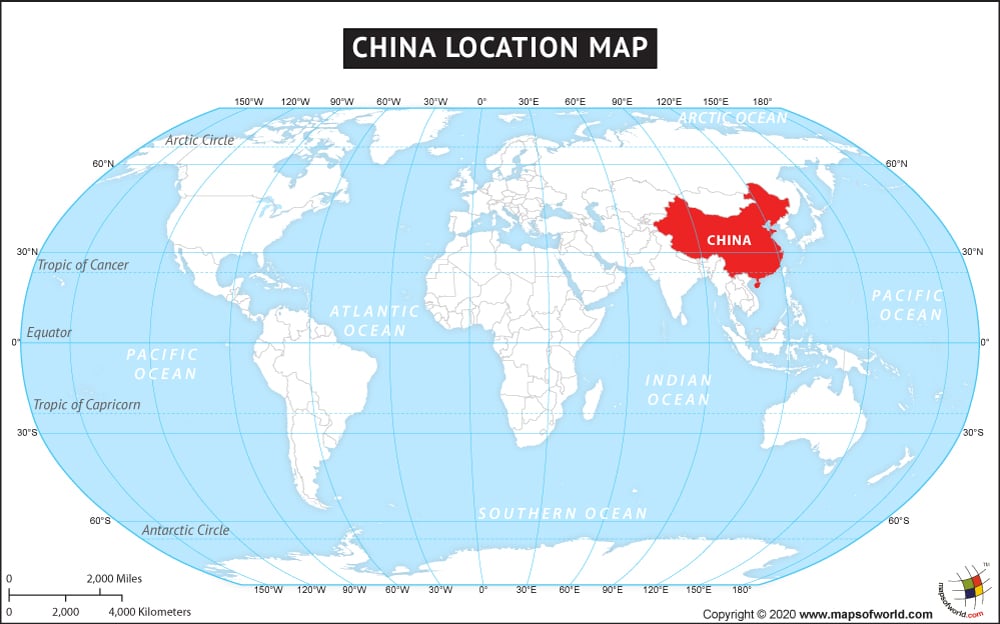



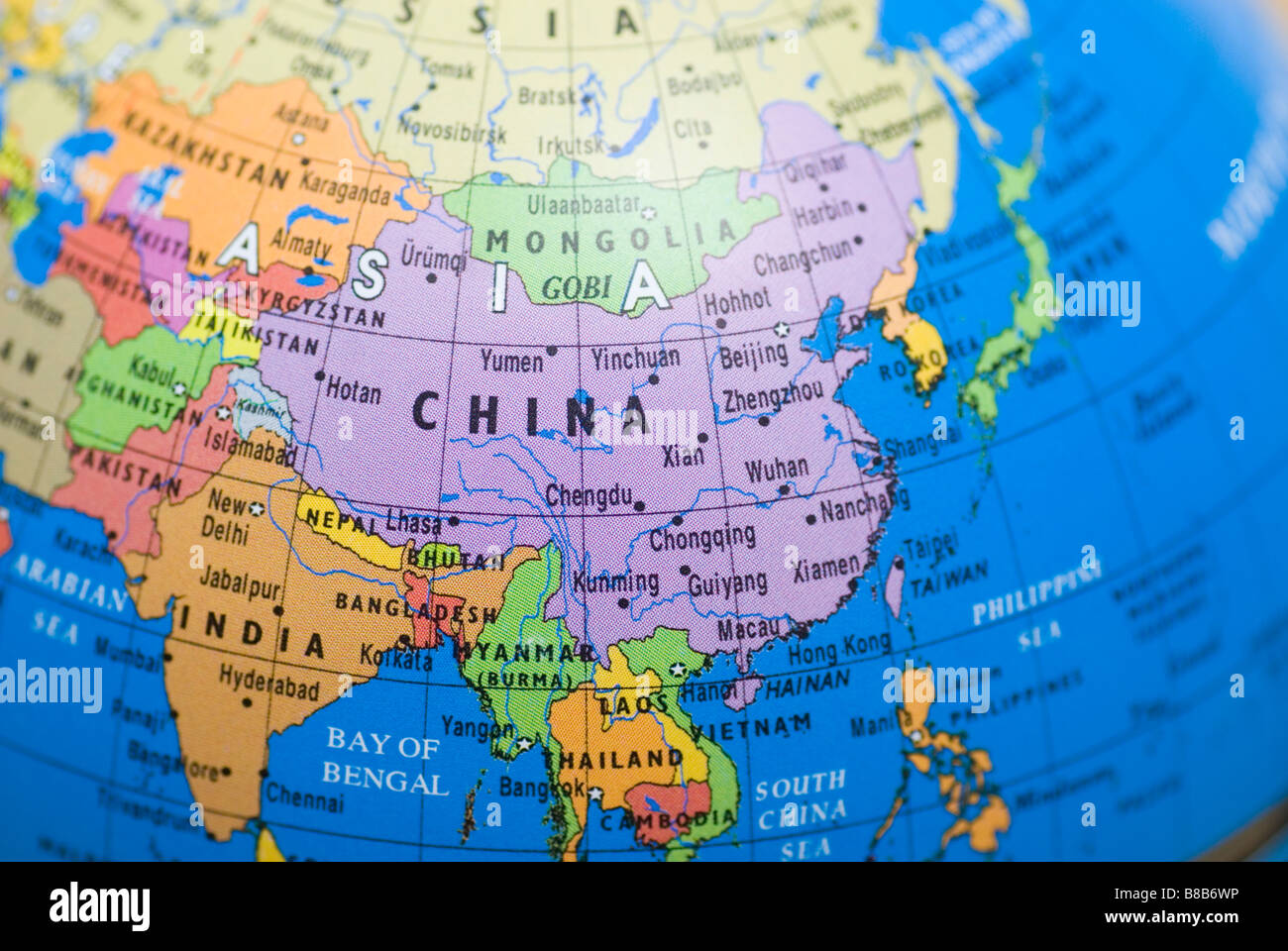
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into China’s Position on the World Map: A Global Powerhouse. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!