Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Map Legends and Their Significance
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Map Legends and Their Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Map Legends and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Map Legends and Their Significance
Maps are powerful tools for navigating the physical and conceptual landscapes we inhabit. They condense vast amounts of information into a visual format, allowing us to understand spatial relationships, identify locations, and gain insights into the world around us. However, the true value of a map lies not just in its visual representation, but also in its ability to communicate effectively through the use of symbols and legends.
A map legend, also known as a map key, serves as a crucial bridge between the visual elements of a map and the information they represent. It acts as a glossary, translating the symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map into understandable language. Without a clear and comprehensive legend, a map can be confusing, misleading, and ultimately useless.
Exploring the Building Blocks of Map Legends:
Map legends typically consist of three key components:
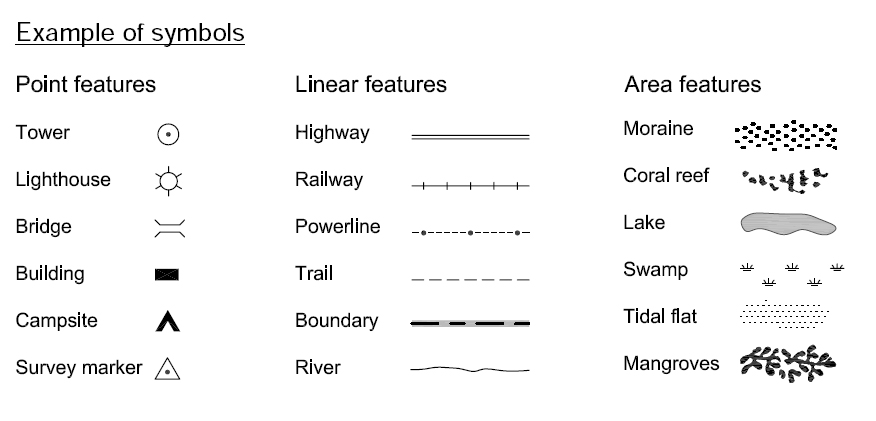
- Symbols: These are the visual elements used on the map to represent specific features, entities, or data points. Symbols can take various forms, including points, lines, areas, and icons.
- Labels: Each symbol is accompanied by a label that provides a textual description of what the symbol represents. Labels can be simple, such as "Roads" or "Rivers," or more specific, like "Interstate Highways" or "Major Rivers."
- Color and Pattern: Color and pattern are powerful tools for visually differentiating features on a map. They can be used to highlight specific areas, categorize data, or represent different types of information.
Illustrative Examples of Map Legends:
To illustrate the importance of map legends, let’s explore several examples:
1. Topographic Maps:
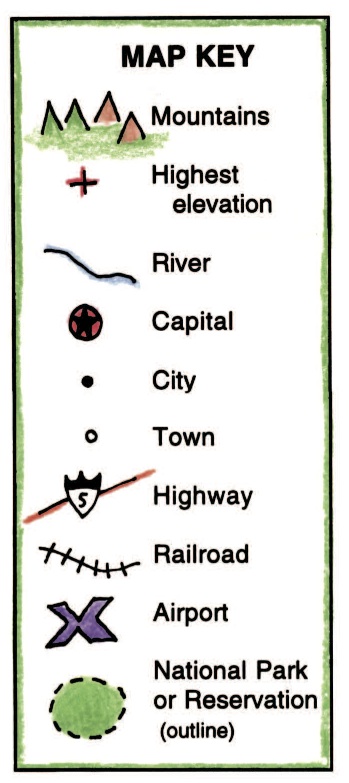
Topographic maps depict the physical features of a region, including elevation, terrain, and water bodies. They utilize contour lines to represent elevation changes, with thicker lines indicating steeper slopes. The legend might include a table showing the elevation corresponding to different contour intervals, along with symbols for features like rivers, lakes, forests, and buildings. This legend allows users to interpret the map’s visual representation and understand the physical characteristics of the depicted area.
2. Road Maps:
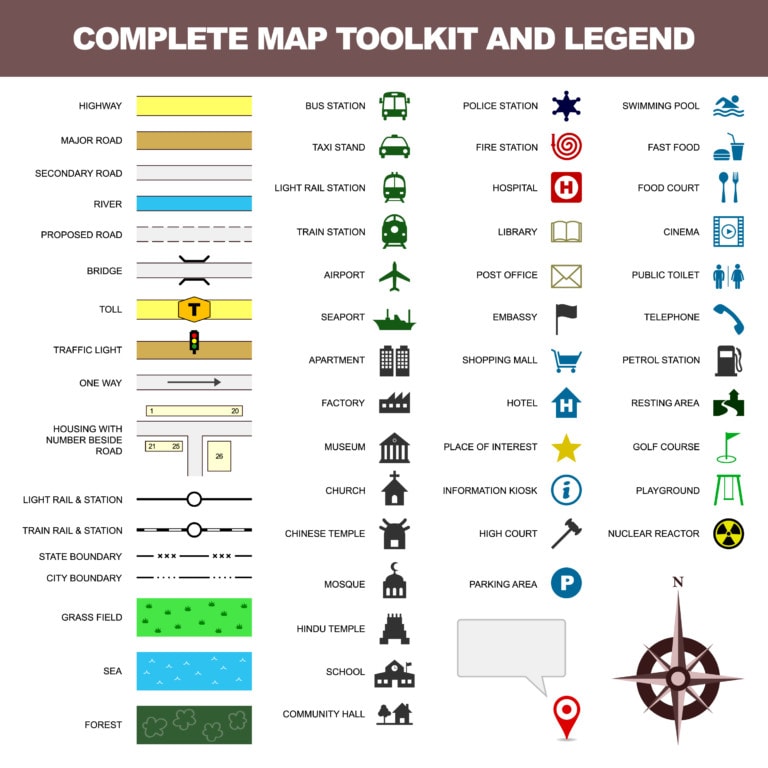
Road maps focus on transportation networks, displaying highways, roads, and other routes. The legend might include different line thicknesses or colors to distinguish between major highways, secondary roads, and local streets. Symbols for points of interest, such as gas stations, restaurants, and hotels, are also commonly included. This legend helps users navigate effectively, locate essential services, and plan their journeys.
3. Thematic Maps:
Thematic maps focus on specific themes, such as population density, rainfall distribution, or economic activity. These maps often use color gradients or patterns to represent data values. For example, a map showing population density might use darker shades of blue for areas with higher population concentrations. The legend would then provide a scale or key that translates the color gradient into numerical values, allowing users to understand the spatial distribution of the data.
4. Choropleth Maps:
Choropleth maps use different colors or patterns to represent data values across geographic areas, such as counties, states, or countries. The legend typically includes a color scale or pattern key that links the colors or patterns used on the map to specific data values. This allows users to compare data across different regions and identify areas with high or low values.
5. Cartograms:
Cartograms distort the shapes and sizes of geographic areas to emphasize specific data values. For example, a cartogram showing population distribution might enlarge areas with higher populations, making them appear larger than areas with lower populations. The legend would explain the distortion principle and provide a key that relates the size of each area to the data value it represents.
FAQs on Map Legends:
1. Why are map legends crucial?
Map legends are crucial for understanding the information presented on a map. They provide a key to decoding the symbols, colors, and patterns used to represent different features, data points, and themes. Without a legend, the map becomes an indecipherable visual puzzle.
2. What types of information are typically included in a map legend?
Map legends typically include information on symbols, colors, patterns, scales, north arrows, and data sources. The specific content varies depending on the map’s purpose and the type of information being presented.
3. How can I create an effective map legend?
An effective map legend should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. It should use consistent terminology, avoid technical jargon, and be visually appealing. The legend should be placed in a prominent location on the map and be easily accessible to users.
4. Are there any guidelines for designing map legends?
Yes, there are several guidelines for designing effective map legends. These include:
- Simplicity: Avoid overcrowding the legend with too much information.
- Clarity: Use clear and concise language, avoiding technical jargon.
- Consistency: Use consistent symbols, colors, and patterns throughout the legend and the map.
- Visual Appeal: Design the legend to be visually appealing and easy to navigate.
Tips for Interpreting Map Legends:
- Read the legend carefully: Pay attention to the symbols, colors, patterns, and labels used in the legend.
- Look for key information: Identify the key elements of the legend, such as the scale, north arrow, and data sources.
- Relate the legend to the map: Use the legend to interpret the symbols, colors, and patterns on the map.
- Ask questions if needed: If you are unsure about the meaning of any symbols or information in the legend, do not hesitate to seek clarification.
Conclusion:
Map legends are essential components of effective cartography, serving as the bridge between visual representation and meaningful interpretation. They provide a clear and concise explanation of the symbols, colors, and patterns used on a map, enabling users to understand the information presented and extract valuable insights. By understanding the purpose and structure of map legends, we can unlock the full potential of maps as powerful tools for navigating the world and exploring its complexities.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: A Guide to Map Legends and Their Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!