Maintaining the Foundation: A Deep Dive into Map Health Management
Related Articles: Maintaining the Foundation: A Deep Dive into Map Health Management
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Maintaining the Foundation: A Deep Dive into Map Health Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Maintaining the Foundation: A Deep Dive into Map Health Management
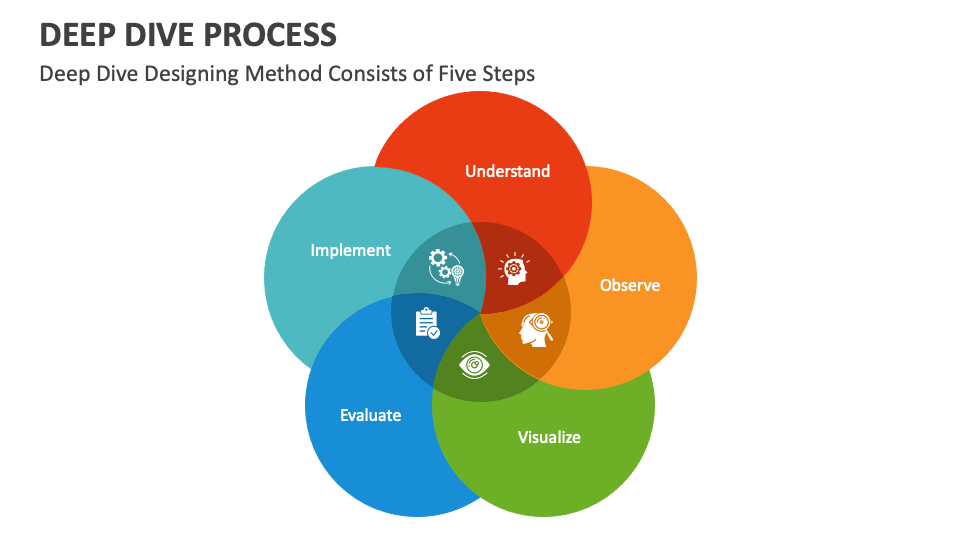
In an era defined by data-driven decision-making, maps have emerged as indispensable tools for navigating complex landscapes, both literal and figurative. From guiding travelers through unfamiliar terrain to visualizing intricate business processes, maps serve as powerful visual representations of information. However, the effectiveness of these maps hinges on their accuracy, consistency, and overall health. This is where the concept of map health management comes into play.
Understanding the Significance of Map Health
Map health management encompasses the systematic processes and practices aimed at ensuring the quality, reliability, and usability of maps over time. Just as a physical map requires regular maintenance to remain accurate and relevant, digital maps necessitate ongoing attention to preserve their integrity. Neglecting map health can lead to a cascade of negative consequences, including:
- Erroneous Decisions: Outdated or inaccurate maps can lead to misguided decisions, impacting everything from resource allocation to strategic planning.
- Missed Opportunities: Unreliable maps can hinder the identification of valuable insights and prevent businesses from capitalizing on potential opportunities.
- Loss of Trust and Credibility: Maps with inconsistencies or errors erode user confidence and undermine the credibility of the data they represent.
- Increased Costs: Addressing issues arising from poor map health can be costly, requiring time and resources to rectify inaccuracies and update information.
Key Elements of Map Health Management
Effective map health management involves a multifaceted approach that addresses various aspects of map quality:
1. Data Accuracy and Completeness:
- Data Validation and Verification: Implementing rigorous processes to ensure the accuracy and consistency of underlying data sources. This involves cross-checking information against reliable external sources and implementing data quality checks.
- Data Enrichment and Completeness: Continuously updating maps with new information, filling in gaps, and addressing missing data points. This can involve integrating data from diverse sources, including sensor networks, satellite imagery, and crowdsourced information.
- Data Governance: Establishing clear ownership and responsibility for data quality, defining data standards, and implementing data management policies.
2. Map Consistency and Standardization:
- Map Style and Symbolism: Maintaining consistent map styles, legends, and symbols across different maps to ensure user understanding and ease of interpretation.
- Coordinate Systems and Projections: Utilizing appropriate coordinate systems and projections to maintain spatial accuracy and ensure seamless integration with other geographic data.
- Metadata Management: Maintaining comprehensive metadata that describes the source, creation date, and other relevant information about the map, facilitating its understanding and use.
3. Map Maintenance and Updates:
- Regular Review and Updates: Implementing regular processes to review and update maps based on changes in the real world, such as infrastructure development, natural disasters, or demographic shifts.
- Version Control and Change Management: Tracking changes made to maps, maintaining historical versions, and documenting the rationale behind updates to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Automated Updates: Exploring the use of automated processes and tools to streamline map updates and ensure timely integration of new information.
4. User Experience and Accessibility:
- Map Usability and Navigation: Designing maps for intuitive user interaction, ensuring clear labels, legible text, and user-friendly navigation tools.
- Accessibility Considerations: Making maps accessible to users with disabilities by incorporating features like alternative text descriptions and keyboard navigation.
- Map Visualization and Communication: Utilizing effective visualization techniques to convey information clearly and effectively, employing appropriate colors, symbols, and data representations.
Benefits of Implementing Map Health Management
By prioritizing map health management, organizations can reap numerous benefits:
- Improved Decision-Making: Accurate and up-to-date maps provide a reliable foundation for informed decisions, leading to better resource allocation, strategic planning, and operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: User-friendly and reliable maps create a positive customer experience, fostering trust and satisfaction.
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency: Well-maintained maps streamline workflows, reduce errors, and improve overall productivity by providing clear and accurate spatial information.
- Reduced Costs: Addressing map health proactively can prevent costly errors and rework, ultimately saving time and resources in the long run.
- Enhanced Reputation and Credibility: Maps that are consistently accurate and reliable enhance an organization’s reputation and credibility, building trust among stakeholders.
FAQs on Map Health Management
1. What are the common indicators of poor map health?
Common indicators of poor map health include:
- Outdated information: Maps that do not reflect current conditions, leading to inaccuracies and misleading interpretations.
- Inconsistent data: Discrepancies in data sources, leading to conflicts and unreliable representations.
- Missing data: Incomplete information resulting in gaps and limitations in map analysis.
- Poor map design: Confusing or cluttered maps that hinder user understanding and navigation.
- Lack of metadata: Insufficient information about map creation, data sources, and updates, making it difficult to assess map reliability.
2. How can organizations ensure map health?
Organizations can ensure map health by implementing a comprehensive map health management program that includes:
- Establishing clear policies and procedures: Defining standards for data quality, map creation, and maintenance.
- Investing in data management tools: Utilizing software solutions for data validation, verification, and enrichment.
- Building a dedicated team: Assigning responsibility for map health management to a team of professionals with expertise in data management and cartography.
- Regularly monitoring and auditing maps: Implementing processes to identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
- Promoting a culture of data quality: Encouraging employees to prioritize data accuracy and report any inconsistencies or errors.
3. What are the best practices for map health management?
Best practices for map health management include:
- Utilizing reliable data sources: Sourcing data from reputable and trustworthy sources.
- Implementing data validation and verification procedures: Implementing rigorous checks to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Maintaining a consistent map style and symbolism: Ensuring maps are visually consistent and easy to understand.
- Regularly reviewing and updating maps: Implementing processes for ongoing maintenance and updates based on real-world changes.
- Documenting map updates and changes: Tracking changes to maps and documenting the rationale behind updates.
- Providing user feedback mechanisms: Gathering user feedback to identify areas for improvement and address usability issues.
Tips for Effective Map Health Management
- Prioritize data quality: Ensure that the foundation of your maps is built on accurate and reliable data.
- Embrace automation: Leverage tools and technologies to automate data updates and map maintenance processes.
- Foster collaboration: Encourage communication and collaboration between data managers, cartographers, and map users to ensure alignment on map health priorities.
- Invest in training and development: Equip your team with the skills and knowledge needed to effectively manage map health.
- Continuously improve: Regularly review and refine your map health management processes to ensure they are efficient and effective.
Conclusion
In a world increasingly reliant on data and visual representations, map health management is not a luxury but a necessity. By implementing robust strategies and fostering a culture of data quality, organizations can ensure that their maps remain accurate, reliable, and valuable tools for decision-making, innovation, and success. Investing in map health is an investment in the integrity and effectiveness of your data-driven endeavors, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a more informed future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Maintaining the Foundation: A Deep Dive into Map Health Management. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!