Mapping Ancient Canaan: A Journey Through Time and History
Related Articles: Mapping Ancient Canaan: A Journey Through Time and History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Ancient Canaan: A Journey Through Time and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Ancient Canaan: A Journey Through Time and History
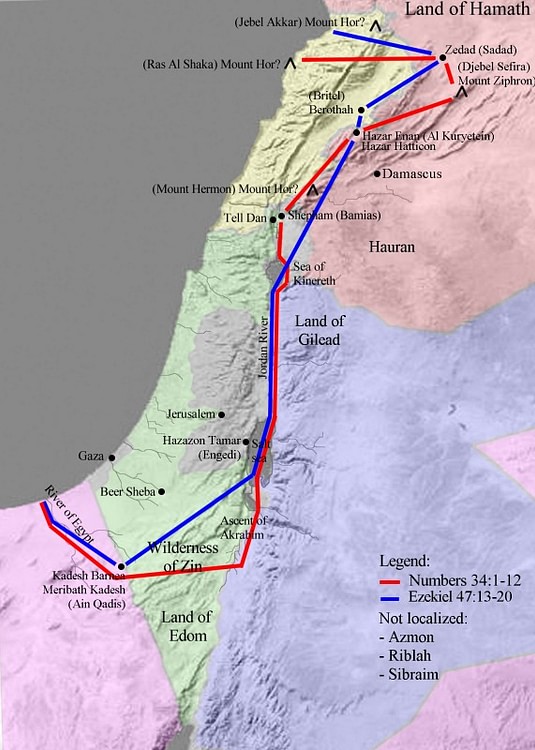
The land of Canaan, a region steeped in history and religious significance, holds a prominent place in the narrative of the ancient world. Its geographical location, nestled between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, has played a crucial role in shaping the cultural and political landscape of the Near East for millennia. Understanding the geography of ancient Canaan is essential for comprehending the complexities of its history, the rise and fall of civilizations, and the enduring legacy of its people.
A Mosaic of Landscapes:
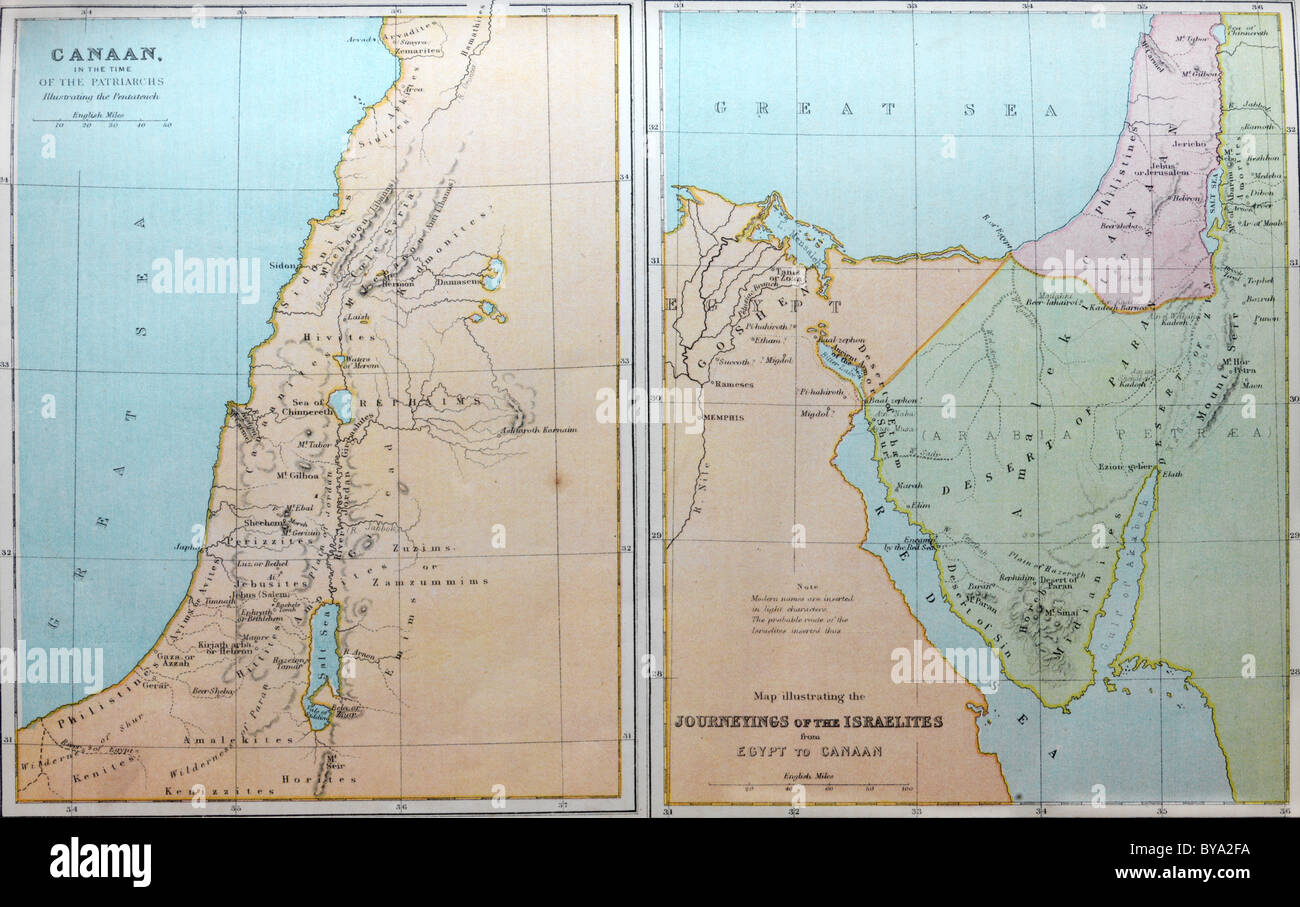
The map of ancient Canaan reveals a diverse landscape, encompassing coastal plains, rolling hills, fertile valleys, and rugged mountains. The Mediterranean Sea, a vital trade route, provided access to the wider world, while the Jordan River, a life-giving artery, nourished the land and fostered human settlements.
-
The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea was a hub of trade and commerce, attracting both indigenous and foreign populations. Cities like Tyre, Sidon, and Ashdod flourished as centers of maritime activity, their influence extending across the region.
-
The Central Highlands: This mountainous region, encompassing the Judean Hills and the Samaritan Mountains, was a haven for independent tribes and kingdoms. The rugged terrain provided natural defenses, allowing for the development of distinct cultures and political entities. Jerusalem, strategically located in the Judean Hills, became a focal point of religious and political power.
-
The Jordan Valley: This fertile rift valley, bisected by the Jordan River, provided rich agricultural land and served as a conduit for communication and trade. Cities like Jericho, one of the oldest known cities in the world, emerged along its banks, benefiting from its strategic location.
-
The Transjordan: This region east of the Jordan River was a land of diverse landscapes, from the fertile plains of Gilead to the arid steppes of Moab. It hosted nomadic tribes and independent kingdoms, playing a crucial role in the regional power dynamics.
A Crossroads of Cultures:
The map of ancient Canaan also reflects the confluence of diverse cultures and civilizations. The region witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the interaction of different ethnic groups, and the dissemination of cultural ideas.
-
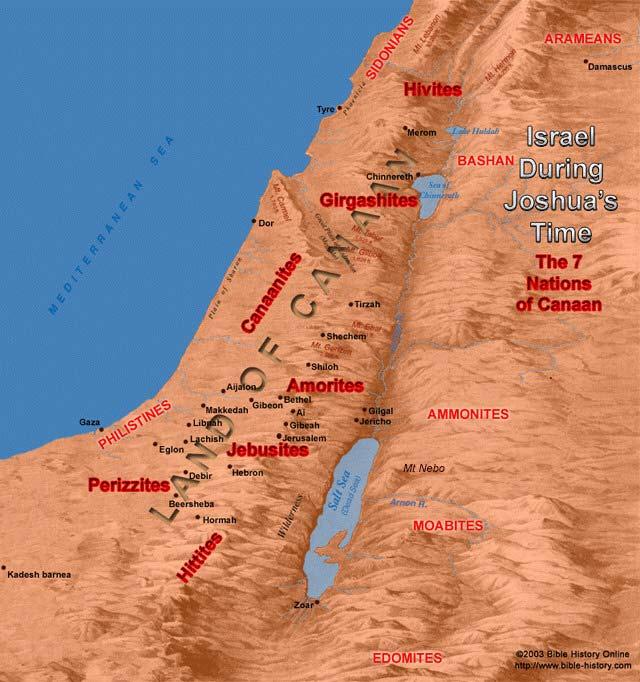
The Canaanites: The indigenous inhabitants of the land, known as the Canaanites, developed a sophisticated urban civilization, characterized by their advanced agriculture, trade networks, and religious practices. Their influence spread throughout the region, leaving a lasting imprint on the cultural landscape.
-
The Egyptians: Egypt, a powerful neighbor to the south, exerted significant influence on Canaan, particularly during the New Kingdom period. Egyptian pharaohs controlled parts of Canaan, leaving behind their architectural and artistic legacy.
-
The Amorites: This Semitic group migrated into Canaan from the north, establishing powerful kingdoms in the central highlands. Their influence is evident in the development of city-states like Jerusalem and Hebron.
-
The Philistines: Originating from the Aegean Sea, the Philistines settled along the southern coast of Canaan, establishing a distinct culture and challenging the dominance of the Canaanite city-states. Their influence is evident in the development of ironworking and the introduction of new military technologies.
A Tapestry of Religions:
The map of ancient Canaan also reveals the diversity of religious practices that flourished in the region. From the polytheistic Canaanite pantheon to the emerging monotheistic beliefs of the Israelites, the land witnessed a dynamic interplay of religious ideas.
-
Canaanite Religion: The Canaanites worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses, each representing different aspects of nature and human life. Their religious practices included rituals, sacrifices, and temple worship.
-
Israelite Religion: The Israelites, who emerged from within the Canaanite population, developed a unique monotheistic religion centered on the worship of Yahweh. Their religious beliefs and practices, enshrined in the Hebrew Bible, had a profound impact on the development of Judaism and Christianity.
The Importance of Mapping Ancient Canaan:
The map of ancient Canaan serves as a vital tool for understanding the complexities of the region’s history, culture, and religion. It provides a visual framework for tracing the movements of peoples, the rise and fall of civilizations, and the development of religious ideas. By illuminating the geographical context, the map helps us to appreciate the dynamic interactions between human societies and the natural environment.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the geographical extent of ancient Canaan?
- The geographical extent of ancient Canaan varied over time, but it generally encompassed the region between the Mediterranean Sea to the west, the Jordan River to the east, the Lebanon Mountains to the north, and the Sinai Peninsula to the south.
-
What are the major cities of ancient Canaan?
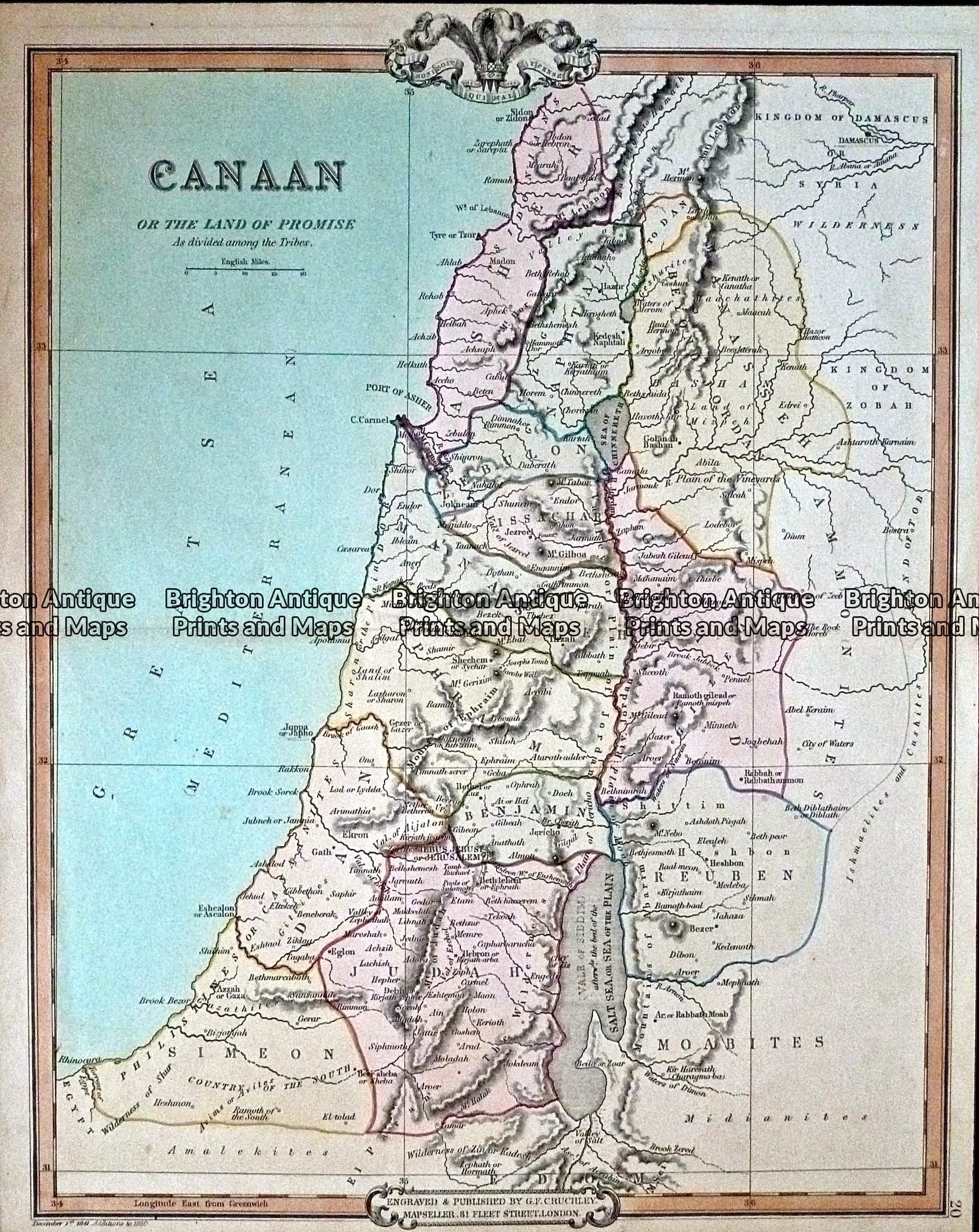
- Some of the major cities of ancient Canaan include Jerusalem, Jericho, Tyre, Sidon, Ashdod, Gaza, Hebron, and Megiddo.
-
What are the main cultural influences on ancient Canaan?
- Ancient Canaan was influenced by a variety of cultures, including the Egyptians, the Amorites, the Philistines, and the Hittites.
-
What are the main religious practices in ancient Canaan?
- Ancient Canaan was home to a variety of religious practices, including the polytheistic worship of the Canaanite pantheon, the emerging monotheistic beliefs of the Israelites, and the religious practices of other groups, such as the Egyptians and the Amorites.
Tips for Studying the Map of Ancient Canaan:
- Use a reliable map: Consult reputable historical atlases or online resources to ensure the accuracy of the map.
- Identify key geographical features: Pay attention to the major rivers, mountains, and coastal areas, as they played a crucial role in shaping the region’s history.
- Trace the movements of peoples: Follow the routes of migration and conquest to understand the dynamics of population movements.
- Examine the location of cities: Note the strategic locations of major cities and their role in trade, politics, and religion.
- Explore the cultural and religious influences: Identify the different cultures and religions that shaped the region’s history and traditions.
Conclusion:
The map of ancient Canaan provides a window into a rich and complex world, revealing the intricate interplay of geography, history, culture, and religion. It allows us to trace the footsteps of ancient civilizations, understand the forces that shaped their destinies, and appreciate the enduring legacy of their contributions to human history. By exploring the map, we gain a deeper understanding of the ancient world and its enduring influence on our own time.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Ancient Canaan: A Journey Through Time and History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!