Navigating the Complexities: A Geographical Exploration of the Middle East and Europe
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities: A Geographical Exploration of the Middle East and Europe
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities: A Geographical Exploration of the Middle East and Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities: A Geographical Exploration of the Middle East and Europe
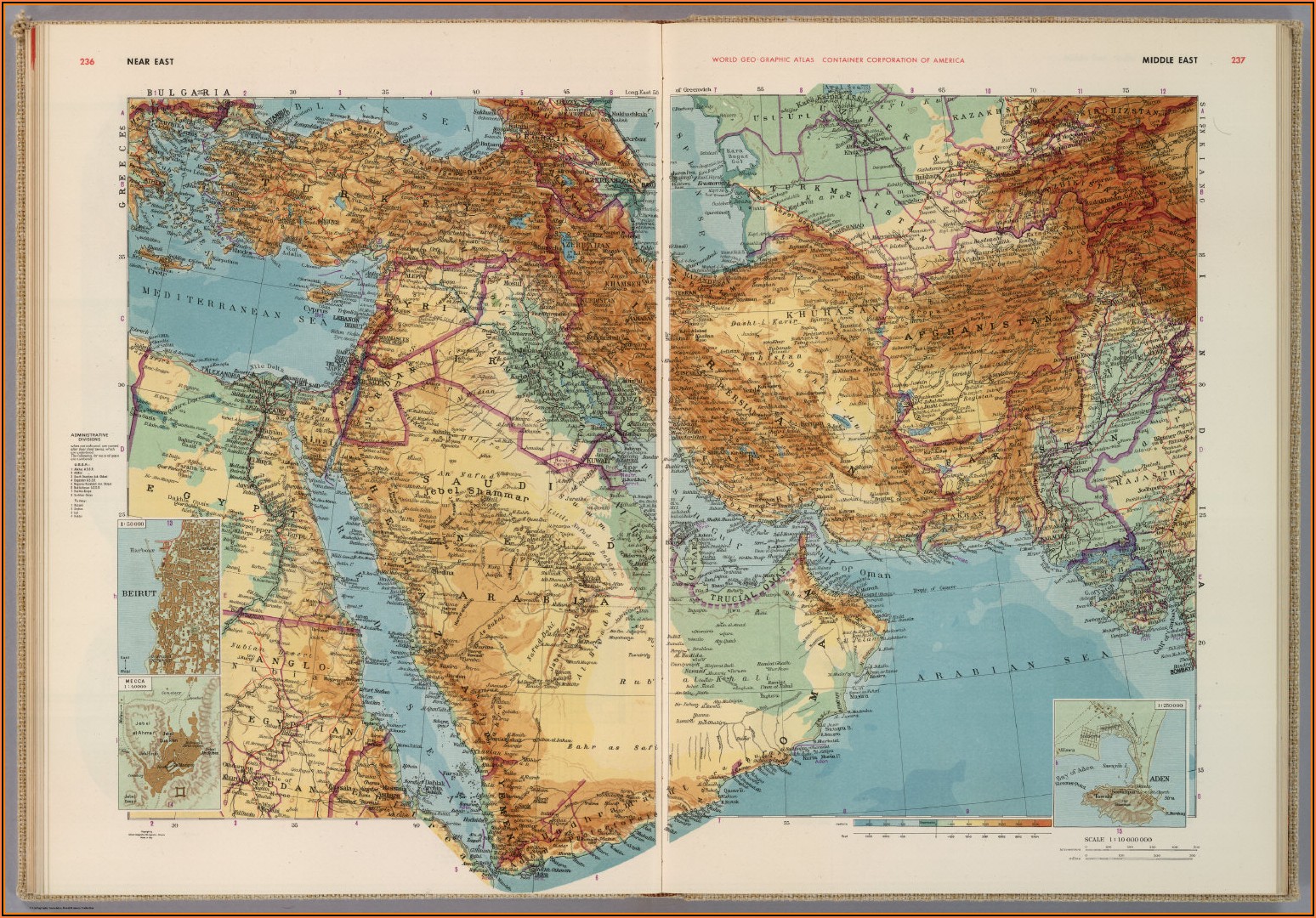
The terms "Middle East" and "Europe" often evoke distinct mental images, geographically separated by the vast expanse of the Mediterranean Sea. While this perception holds true in a general sense, the reality is far more nuanced. The regions of the Middle East and Europe are interconnected in ways that extend beyond geographical proximity, encompassing shared histories, cultural influences, and contemporary challenges. Understanding these intricate connections requires a deeper exploration of the geographical landscape, examining the specific areas that blur the lines between these seemingly distinct regions.
Defining the Middle East and Europe: A Geographical Overview
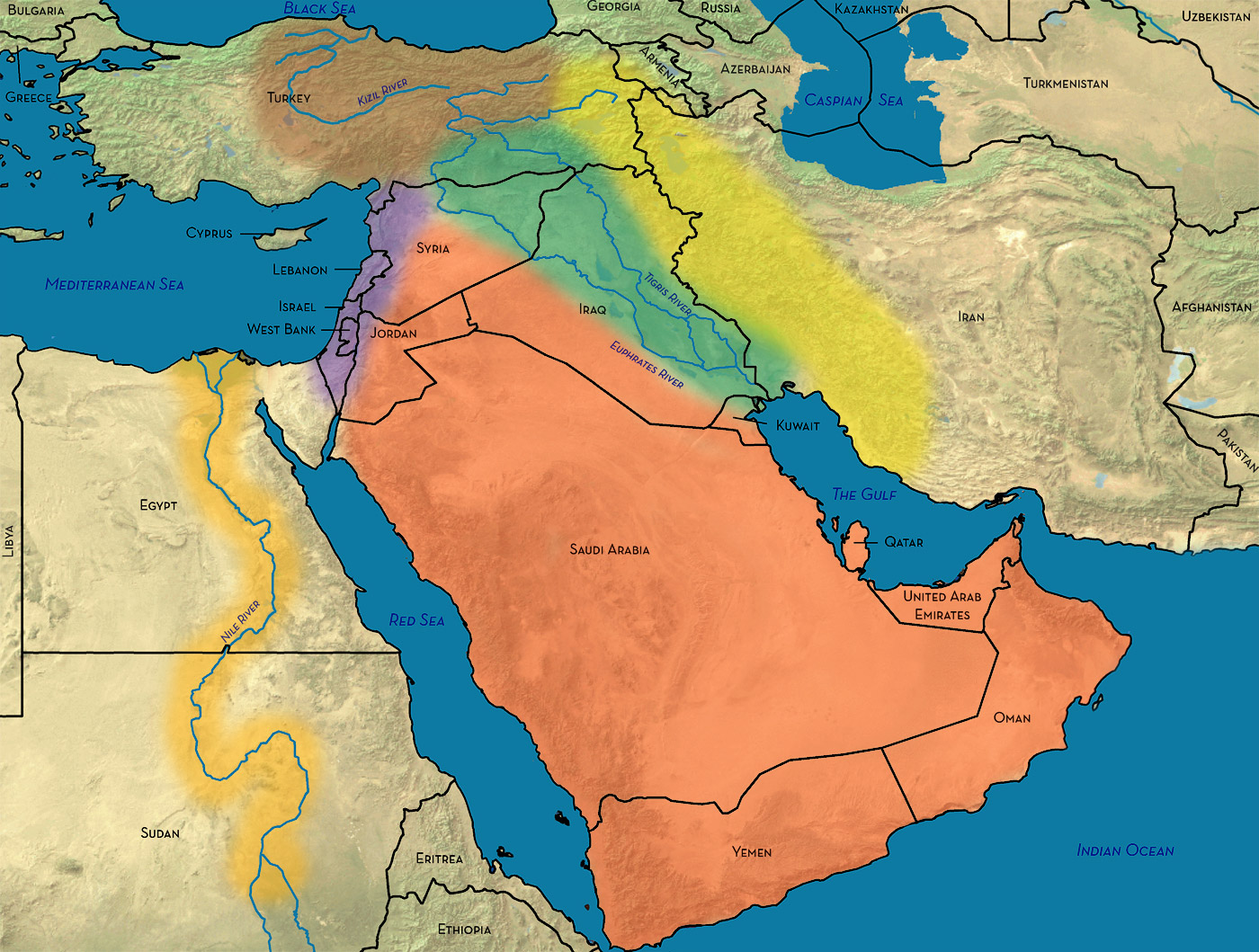
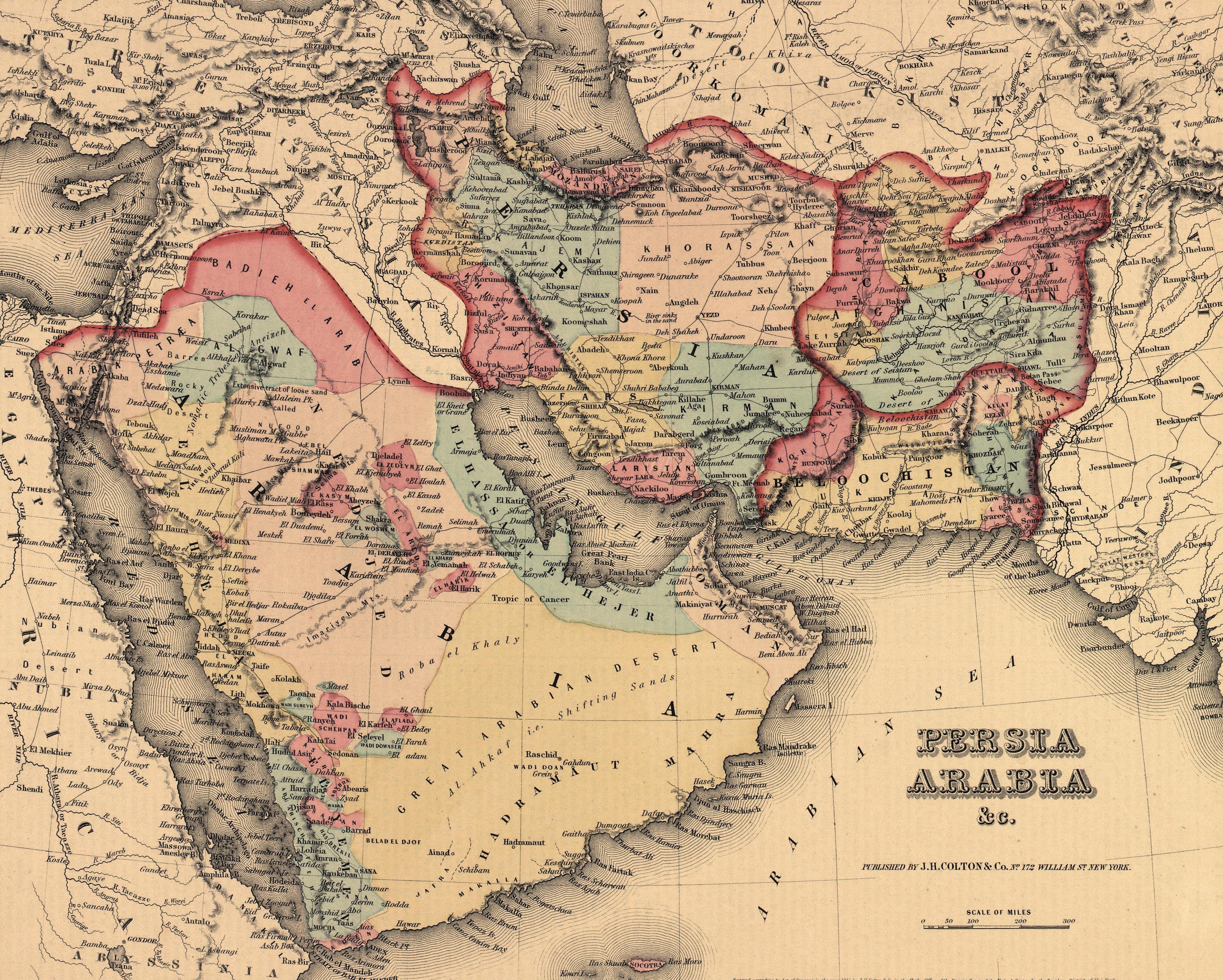
The "Middle East" is a geographically diverse region encompassing a vast swathe of land stretching from the eastern Mediterranean coast to the Arabian Peninsula. It encompasses countries like Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates. This region is characterized by its arid landscapes, diverse cultures, and rich historical heritage.
Europe, on the other hand, is a continent encompassing a diverse array of countries and cultures, stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Ural Mountains. It includes countries like France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom, Russia, Poland, Ukraine, and many others. Europe is known for its diverse landscapes, ranging from snow-capped mountains to rolling hills and fertile plains.
Bridging the Gap: The Mediterranean Sea and its Significance
The Mediterranean Sea serves as a crucial geographical nexus, connecting the Middle East and Europe. This vast body of water has historically facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and migration, creating a complex tapestry of interconnected histories. The Mediterranean basin encompasses countries from both the Middle East and Europe, including countries like Turkey, Greece, Cyprus, Italy, and Spain.
Beyond the Sea: Areas of Interconnection
While the Mediterranean Sea serves as a primary point of connection, the Middle East and Europe are intertwined in other ways:
- The Caucasus Region: This mountainous region located between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea encompasses countries like Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia. While geographically situated in the Middle East, the Caucasus region shares cultural and historical ties with both Europe and Asia.
- The Balkan Peninsula: Located in southeastern Europe, the Balkan Peninsula includes countries like Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, and Turkey. This region exhibits a complex mix of European and Middle Eastern influences, reflecting its historical role as a crossroads between the two continents.
- The Eastern Mediterranean: This region encompasses countries like Cyprus, Israel, Lebanon, Syria, and Turkey, showcasing a blend of cultural and historical influences from both the Middle East and Europe.
The Importance of Understanding the Interconnectedness
Understanding the intricate connections between the Middle East and Europe is crucial for several reasons:
- Historical Perspective: Recognizing the shared history and cultural exchange between the two regions provides a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics that have shaped their societies and relationships.
- Political and Economic Ties: The Middle East and Europe are inextricably linked through political and economic ties. This interconnectedness influences international relations, trade, and security issues.
- Cultural Exchange: The regions have historically been hubs of cultural exchange, influencing each other’s art, literature, music, and cuisine. Understanding these exchanges provides a richer appreciation of the diverse cultural tapestry of both regions.
- Contemporary Challenges: The interconnectedness of the Middle East and Europe presents both opportunities and challenges. Shared concerns like climate change, migration, and security threats require collaborative efforts to address effectively.
FAQs
1. What are the key geographical features that connect the Middle East and Europe?
The Mediterranean Sea, the Caucasus region, the Balkan Peninsula, and the Eastern Mediterranean are key geographical features that connect the Middle East and Europe.
2. How has the Mediterranean Sea influenced the relationship between the Middle East and Europe?
The Mediterranean Sea has historically served as a crucial conduit for trade, cultural exchange, and migration, fostering interconnectedness between the Middle East and Europe.
3. What are some examples of cultural exchange between the Middle East and Europe?
Examples include the spread of Arabic language and culture in parts of Europe, the influence of Byzantine art and architecture in the Middle East, and the exchange of culinary traditions.
4. What are some contemporary challenges that require collaboration between the Middle East and Europe?
Contemporary challenges include climate change, migration, security threats, and economic disparities.
5. How can understanding the interconnectedness of the Middle East and Europe be beneficial?
Understanding the interconnectedness fosters a deeper appreciation of the complex historical, cultural, and political relationships between the regions, promoting collaboration and cooperation in addressing shared challenges.
Tips
- Utilize maps and geographical resources: Studying maps and geographical resources provides a visual understanding of the regions and their interconnectedness.
- Explore historical texts and documents: Examining historical texts and documents reveals the complex interplay between the Middle East and Europe throughout history.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seeking out perspectives from scholars and individuals from both the Middle East and Europe provides a richer understanding of the complex dynamics at play.
- Follow current events: Staying informed about current events in both regions helps understand the ongoing challenges and opportunities for collaboration.
Conclusion
The Middle East and Europe are not geographically isolated entities but rather interconnected regions with shared histories, cultural influences, and contemporary challenges. Recognizing and understanding this interconnectedness is crucial for navigating the complex geopolitical landscape of the 21st century. By fostering dialogue, collaboration, and mutual understanding, we can build a more peaceful and prosperous future for all.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities: A Geographical Exploration of the Middle East and Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!