Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Southwest Asia Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Southwest Asia Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Southwest Asia Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Southwest Asia Map
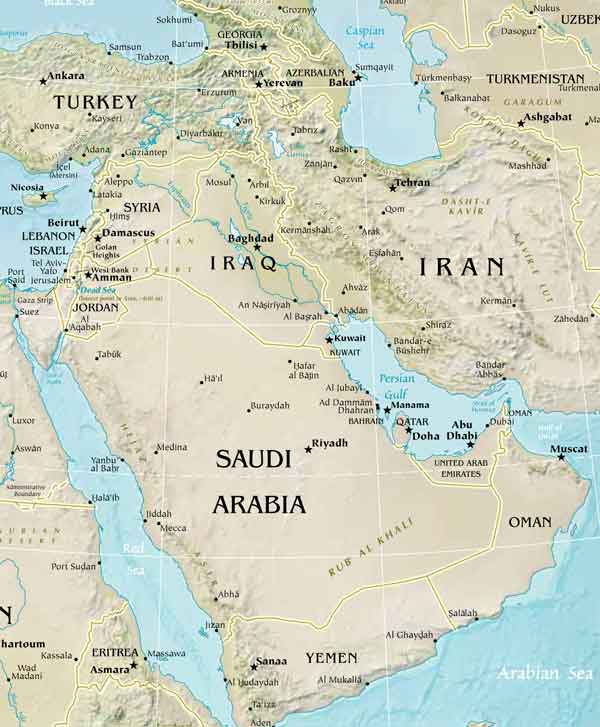
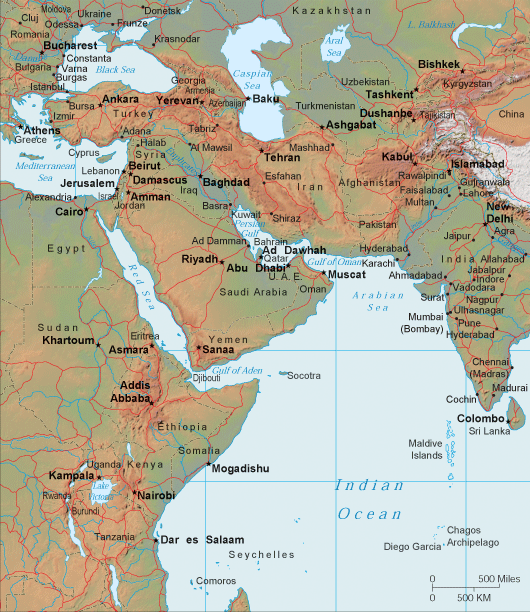
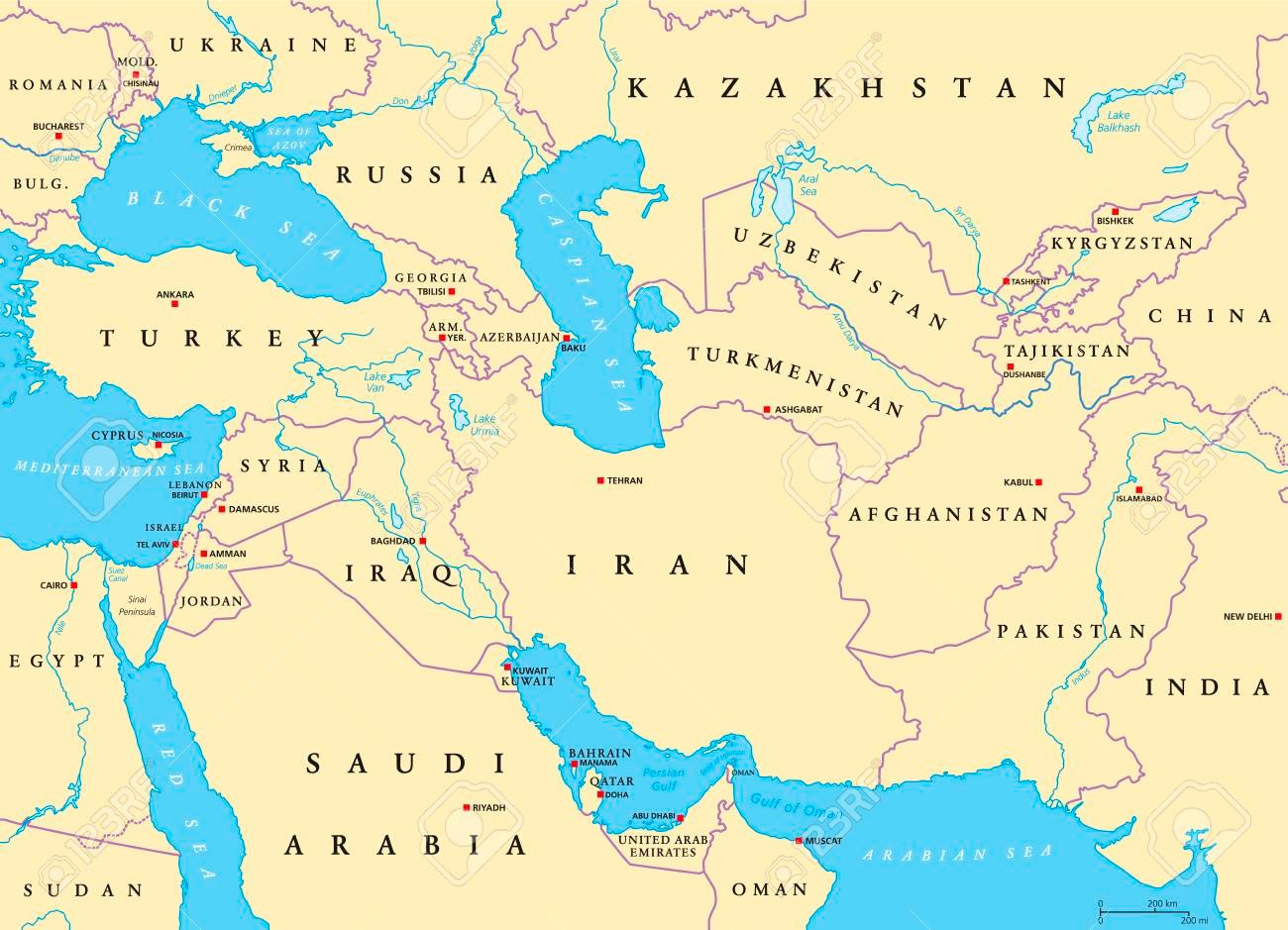
Southwest Asia, a region often referred to as the Middle East, is a dynamic and complex tapestry of cultures, languages, religions, and landscapes. Understanding this region requires a clear grasp of its geographical features, which are intricately intertwined with its history, politics, and social dynamics. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the Southwest Asia map, highlighting its key features and exploring its significance in shaping the region’s past, present, and future.
The Geographical Mosaic:
Southwest Asia is geographically diverse, ranging from the vast, arid plains of the Arabian Peninsula to the fertile valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The region is characterized by several defining geographical features:
- The Arabian Peninsula: The largest peninsula in the world, dominated by vast deserts and characterized by a harsh, arid climate. This region is home to significant oil reserves, playing a crucial role in global energy markets.
- The Levant: A fertile crescent bordering the Mediterranean Sea, comprising countries like Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Palestine. This region has historically been a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, with its rich agricultural lands supporting ancient civilizations.
- The Zagros Mountains: A mountain range stretching from Turkey to Iran, forming a natural barrier between the Iranian Plateau and the Mesopotamian Plain. These mountains hold significant cultural and historical value, with evidence of ancient settlements and archaeological sites.
- The Anatolian Plateau: A large plateau in Turkey, characterized by its high elevation and diverse landscapes, ranging from fertile plains to rugged mountains. This region holds historical significance as the birthplace of the Hittite Empire and is a vital hub for agriculture and industry.
- The Iranian Plateau: A vast, elevated plateau in Iran, known for its dry climate and rugged terrain. This region is home to ancient cities like Persepolis and is a significant center for culture, art, and history.
Beyond Physical Boundaries: The Significance of Southwest Asia
The Southwest Asia map is not merely a collection of geographical features; it is a canvas upon which history, culture, and politics have unfolded for millennia. The region’s unique geography has profoundly shaped its development:
- Cradle of Civilization: Southwest Asia is considered the cradle of civilization, with ancient Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Egypt witnessing the rise of some of the world’s first cities, empires, and civilizations. The region’s fertile lands, abundant water resources, and strategic location along major trade routes facilitated the development of complex societies and cultural innovations.
- Crossroads of Cultures: The region has been a meeting point for diverse cultures and religions, with the spread of Islam, Christianity, and Judaism leaving an indelible mark on the region’s cultural landscape. The interaction of these different faiths and traditions has led to a rich tapestry of beliefs, practices, and artistic expressions.
- Global Power Dynamics: Southwest Asia holds significant geopolitical importance, straddling crucial trade routes and possessing vast energy reserves. The region’s strategic location has made it a focal point for international diplomacy and conflict, with its political landscape often reflecting global power dynamics.
- Resource-Rich Region: The region possesses vast natural resources, including oil, natural gas, and minerals, making it a crucial player in the global economy. However, the uneven distribution of these resources and their exploitation have often fueled conflict and inequality within the region.
Navigating the Complexities: FAQs
1. Why is Southwest Asia often referred to as the Middle East?
The term "Middle East" is a Western-centric term that reflects the region’s geographical position between Europe and Asia. However, the term "Southwest Asia" is increasingly preferred as it avoids the potential for misinterpretations and emphasizes the region’s unique identity.
2. What are the major cultural and religious influences in Southwest Asia?
Southwest Asia is home to a diverse array of cultures and religions, with Islam, Christianity, and Judaism being the most prominent. The region’s cultural landscape is also influenced by ancient traditions, nomadic cultures, and the legacy of empires like the Ottoman and Persian empires.
3. What are the major challenges facing Southwest Asia today?
The region faces numerous challenges, including political instability, conflict, poverty, environmental degradation, and the impact of climate change. These challenges are often interconnected and require regional and international cooperation for effective solutions.
4. What is the role of Southwest Asia in the global economy?
Southwest Asia plays a crucial role in the global economy, particularly in the energy sector. The region’s vast oil and natural gas reserves make it a key supplier of these resources to the world. However, the region also faces economic challenges related to inequality, unemployment, and the need for diversification.
5. How can we better understand and engage with Southwest Asia?
Understanding Southwest Asia requires a nuanced approach that considers its complex history, cultural diversity, and geopolitical realities. Engagement with the region should be based on respect, dialogue, and a commitment to understanding and addressing the challenges it faces.
Tips for Understanding the Southwest Asia Map:
- Go beyond the map: Engage with the region’s history, culture, and literature to gain a deeper understanding of its complexities.
- Embrace diversity: Recognize the region’s cultural and religious diversity and appreciate the richness it brings.
- Challenge stereotypes: Be critical of generalizations and stereotypes about the region and its people.
- Engage in dialogue: Seek out opportunities to engage with individuals and communities from Southwest Asia to foster understanding and build bridges.
Conclusion:
The Southwest Asia map is more than a geographical representation; it is a window into a region rich in history, culture, and human experience. By understanding the region’s unique geography, its historical significance, and the challenges it faces, we can better navigate the complexities of this crucial part of the world and contribute to a more peaceful and prosperous future for all.
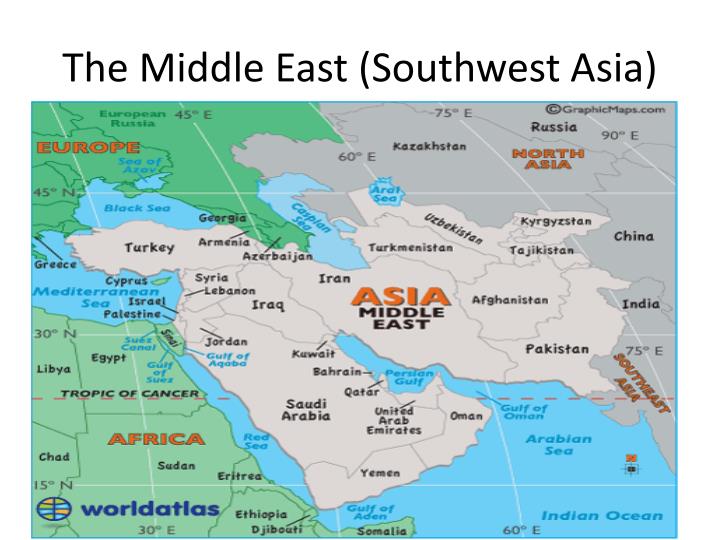
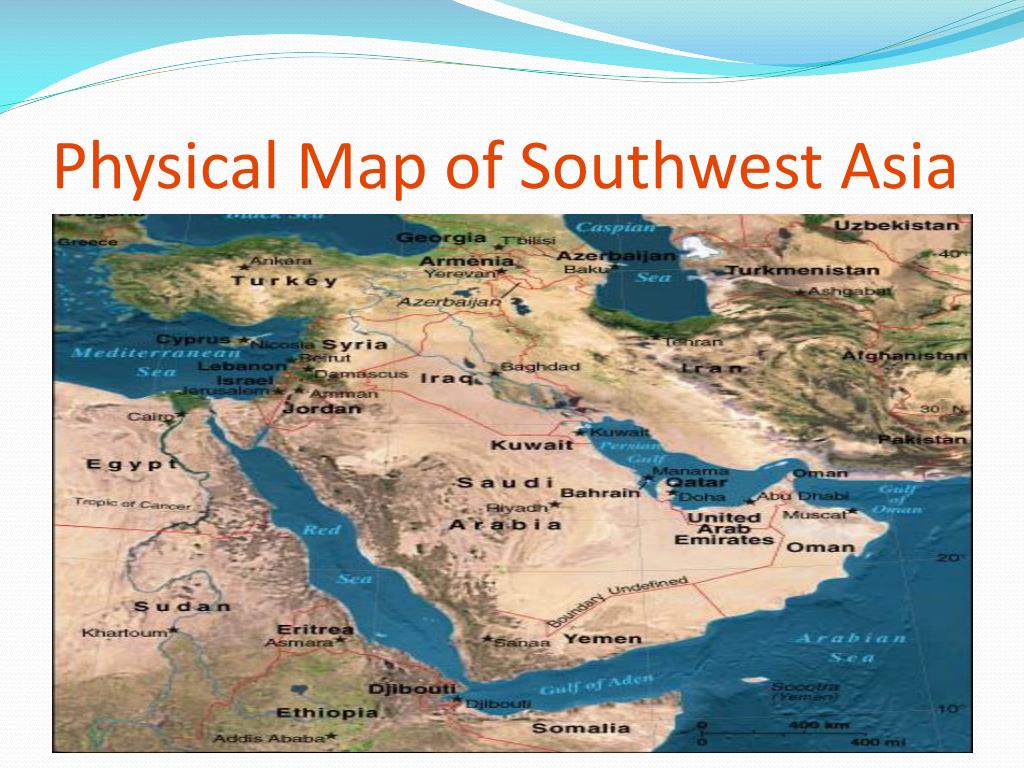



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Southwest Asia Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!