Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Geographical Exploration of Egypt and Its Neighbors
Related Articles: Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Geographical Exploration of Egypt and Its Neighbors
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Geographical Exploration of Egypt and Its Neighbors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Geographical Exploration of Egypt and Its Neighbors

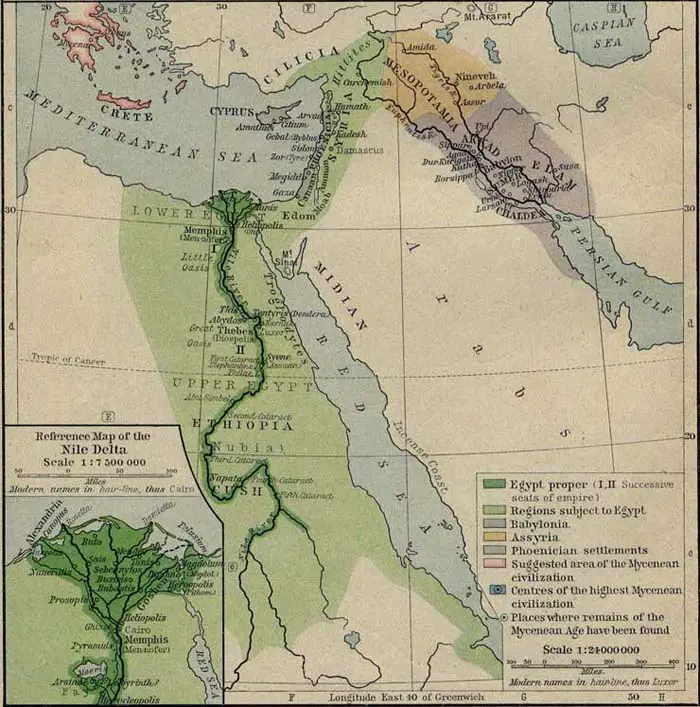
The map of Egypt and its surrounding countries reveals a tapestry of diverse landscapes, ancient civilizations, and dynamic cultural exchanges. This region, situated at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and Europe, has played a pivotal role in shaping the course of human history and continues to be a vital hub for trade, culture, and geopolitical influence.
A Land of Contrasts: Egypt’s Unique Geography
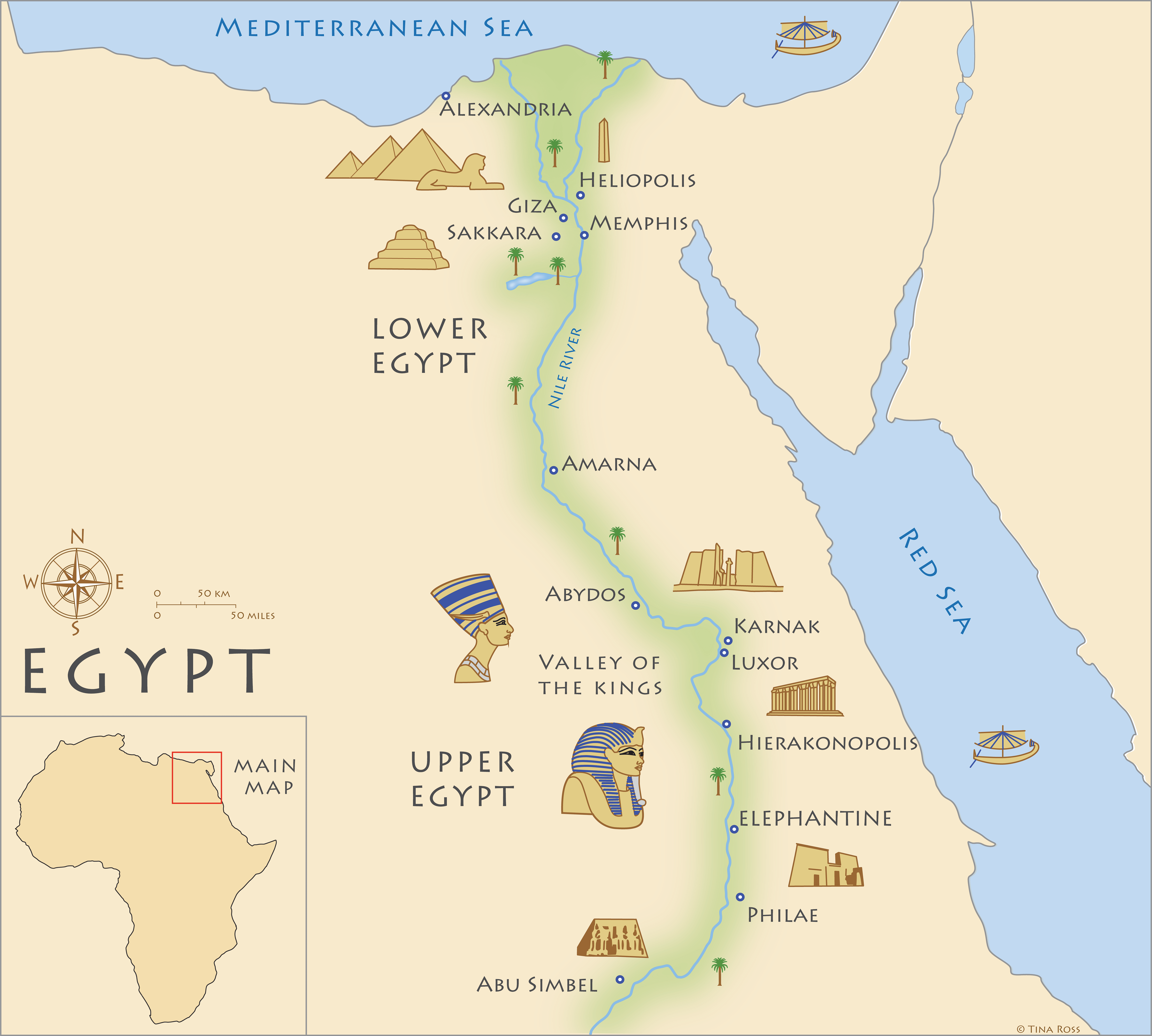
Egypt, the gift of the Nile, is a land of dramatic contrasts. The majority of its population resides within the narrow fertile strip along the Nile River, a lifeline that cuts through the vast, arid expanse of the Sahara Desert. This unique geography has shaped Egypt’s history, culture, and economy. The Nile, a source of life and sustenance, has enabled the development of ancient civilizations, while the desert has served as a natural barrier, influencing the country’s political and social dynamics.
Egypt’s Neighbors: A Diverse Tapestry of Cultures
Surrounding Egypt is a diverse collection of nations, each with its own unique history, culture, and landscape. To the north, the Mediterranean Sea connects Egypt to Europe, while the Red Sea to the east provides access to Asia and the Indian Ocean.
The North African Landscape:
- Libya: Sharing a long border with Egypt, Libya is characterized by its vast desert landscapes, rich oil reserves, and a complex history.
- Sudan: Egypt’s southern neighbor, Sudan, is a land of diverse landscapes, from the Nile Valley to the vast savannas and the Nubian Desert. It holds significant cultural and historical ties with Egypt, including the ancient Nubian civilization.
- Algeria: Across the western border, Algeria boasts a diverse landscape, including the Sahara Desert, the Atlas Mountains, and the Mediterranean coastline.
The Middle Eastern Connections:
- Israel: To the northeast, Israel is a nation with a complex history and a diverse population. The shared border has been a source of tension and conflict, but also a focal point for cooperation in various areas.
- Palestine: The Palestinian territories, located on the eastern Mediterranean coast, have a long history intertwined with Egypt and Israel. The region remains a subject of ongoing conflict and international scrutiny.
- Jordan: To the east, Jordan shares a border with both Israel and Palestine. Its landscape is characterized by the Jordan River, the Dead Sea, and the vast Wadi Rum desert.
The Red Sea Region:
- Saudi Arabia: Across the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia is a vast kingdom, home to the birthplace of Islam and vast oil reserves. Its close proximity to Egypt and its shared history with the region make it a significant geopolitical player.
- Yemen: The southern neighbor of Saudi Arabia, Yemen is a country grappling with conflict and economic challenges. Its strategic location on the Red Sea and its historical connections to Egypt have made it a focal point of regional politics.
Understanding the Importance of the Region
The map of Egypt and its surrounding countries highlights the interconnectedness of this region. Its strategic location at the crossroads of continents has made it a vital hub for trade, cultural exchange, and political influence throughout history.
- Trade Routes: The region has served as a vital corridor for trade routes connecting Africa, Asia, and Europe for millennia. The Nile River and the Red Sea have played a crucial role in facilitating trade, transporting goods, and fostering economic development.
- Cultural Exchange: The proximity of diverse cultures and civilizations has led to a vibrant exchange of ideas, beliefs, and practices. From the ancient Egyptian civilization to the vibrant cultures of the Middle East and North Africa, the region has witnessed a rich tapestry of cultural influences.
- Geopolitical Significance: The strategic location of Egypt and its surrounding countries has made it a focal point of geopolitical competition and conflict. The region is home to major oil reserves, strategic waterways, and a complex mix of political ideologies, making it a crucial area for global influence.
FAQs
1. What are the major geographical features of Egypt and its surrounding countries?
The region is characterized by a diverse range of geographical features, including vast deserts, fertile river valleys, mountain ranges, and coastlines. The Nile River is a defining feature of Egypt, while the Sahara Desert dominates the landscapes of Libya, Algeria, and Sudan. The Red Sea and the Mediterranean Sea are crucial waterways for trade and transportation, while the Jordan River and the Dead Sea are significant features of the Middle East.
2. What are the main cultural and historical connections between Egypt and its neighbors?
The region has a rich history of cultural exchange and shared heritage. Ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, Nubians, and Israelites have left lasting legacies in the region. The spread of Islam has also significantly shaped the cultural landscape of the region, with shared traditions and practices found in Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and other countries.
3. What are the major political and economic challenges facing the region?
The region faces a complex array of political and economic challenges, including conflict, instability, poverty, and resource scarcity. Ongoing conflicts in Israel-Palestine, Yemen, and other areas pose significant threats to regional stability. Economic disparities, dependence on oil resources, and challenges related to water scarcity are also significant issues.
4. What are the prospects for future cooperation and development in the region?
Despite the challenges, there is potential for future cooperation and development in the region. Collaborative efforts to address shared issues like water scarcity, economic development, and security threats could foster regional stability and prosperity. Initiatives promoting cultural exchange, trade, and infrastructure development could also contribute to a more integrated and prosperous region.
Tips for Studying the Region
- Engage with maps: Utilize maps to visualize the geographical relationships between countries, identify key geographical features, and understand the region’s strategic importance.
- Explore historical resources: Delve into the rich history of the region, studying the rise and fall of ancient civilizations, the impact of major empires, and the evolution of cultural and religious traditions.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about current events in the region, paying attention to political developments, economic trends, and social issues.
- Learn about different cultures: Immerse yourself in the diverse cultures of the region, exploring their traditions, languages, arts, and ways of life.
Conclusion
The map of Egypt and its surrounding countries reveals a complex and dynamic region with a rich history, diverse cultures, and significant geopolitical importance. Understanding the geography, history, and cultural connections of this region is crucial for appreciating its role in shaping the world and its future prospects. By engaging with its complexities and fostering understanding and cooperation, we can contribute to a more stable, prosperous, and peaceful future for this vital region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Crossroads of History: A Geographical Exploration of Egypt and Its Neighbors. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!