Navigating the Landscape of Ancient Greek Civilization: A Map-Based Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Ancient Greek Civilization: A Map-Based Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Ancient Greek Civilization: A Map-Based Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Ancient Greek Civilization: A Map-Based Exploration

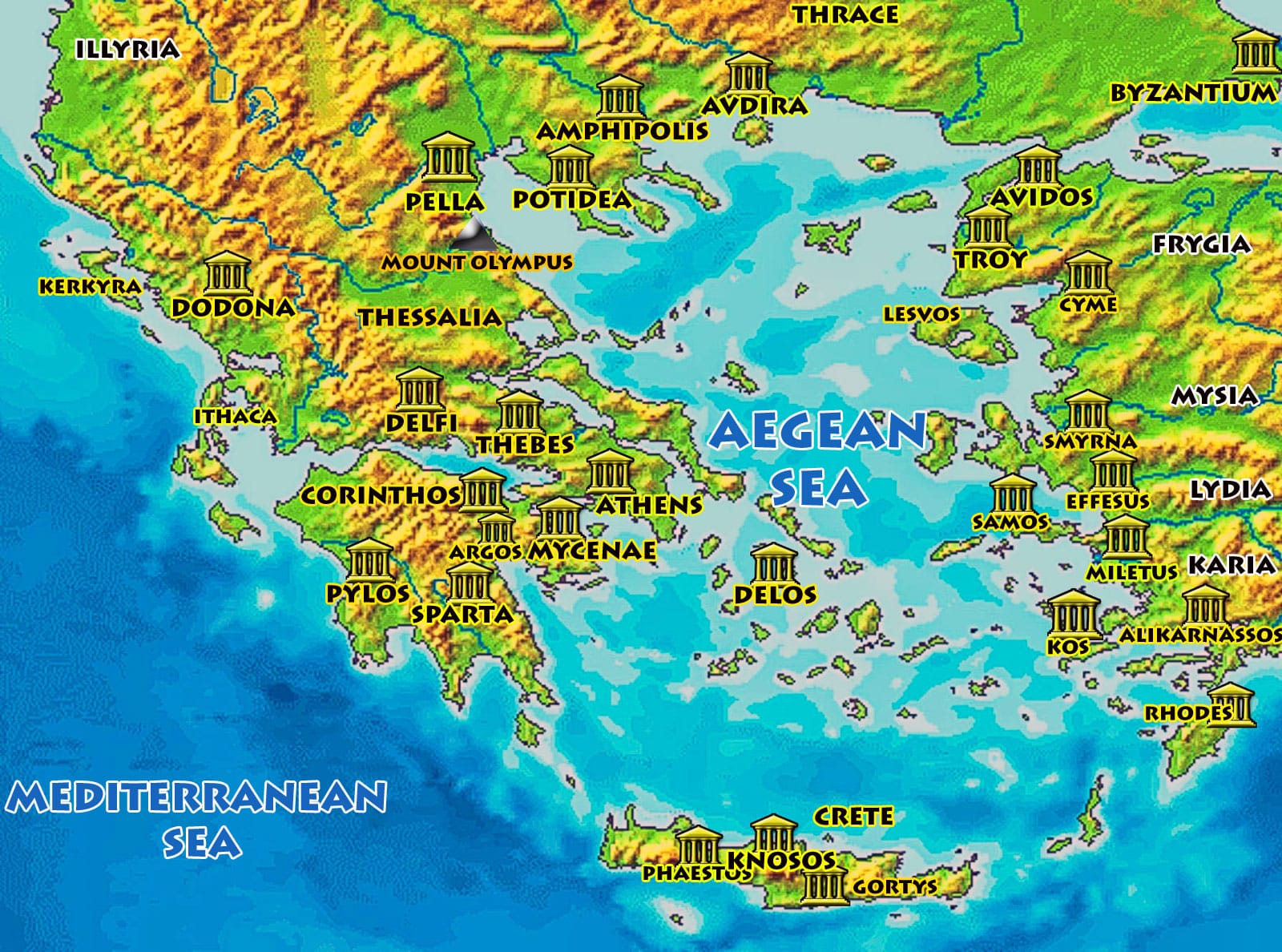
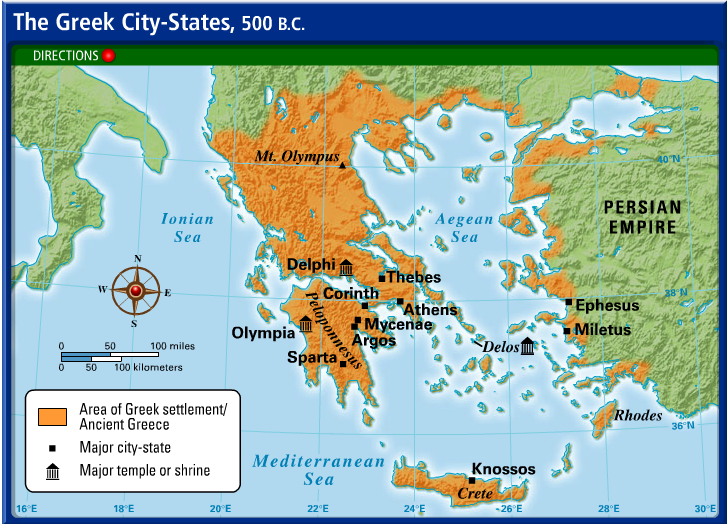
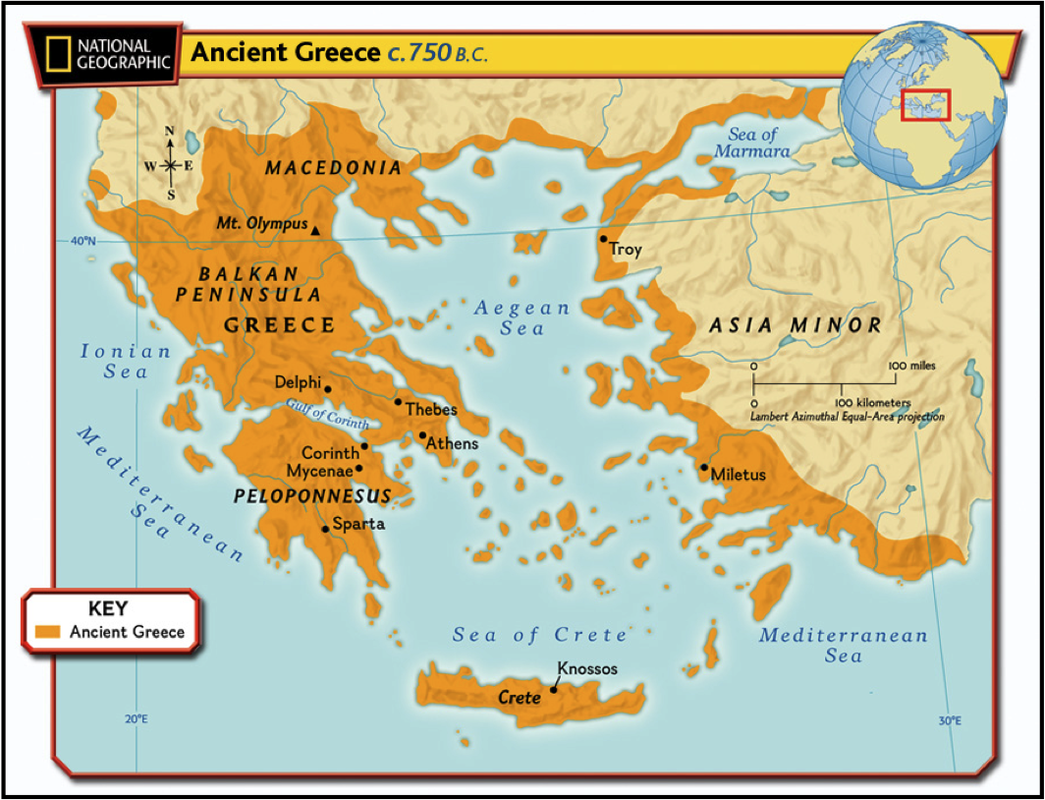
The ancient Greek world was a tapestry of vibrant city-states, each with its unique character and contribution to the broader civilization. Understanding the geographical distribution of these cities is crucial for appreciating the complexities of their interactions, their political dynamics, and their cultural achievements. A map of ancient Greece serves as a powerful tool for navigating this rich and dynamic landscape.
The Importance of a Geographical Perspective
A map of ancient Greece provides a visual framework for understanding the spatial relationships between different city-states. It reveals the strategic importance of geographic features like mountains, valleys, and coastlines, which influenced trade routes, military campaigns, and the spread of ideas. For example, the mountainous terrain of Greece fostered the development of independent city-states, while the numerous islands facilitated maritime trade and cultural exchange.
Key Cities and Their Contributions
The map highlights the major city-states of ancient Greece, each with its own distinct legacy:
-
Athens: Situated on the Attic peninsula, Athens rose to prominence as a center of democracy, philosophy, and the arts. Its iconic Acropolis, adorned with the Parthenon, stands as a testament to its cultural achievements.
-
Sparta: Located in the Peloponnese, Sparta was a militaristic society known for its strict discipline and warrior ethos. Its military prowess shaped the course of Greek history, particularly during the Peloponnesian War.
-
Corinth: Strategically positioned at the Isthmus of Corinth, connecting the Peloponnese to mainland Greece, Corinth flourished as a major trading hub and naval power. Its influence extended across the Mediterranean, fostering cultural exchange and economic growth.
-
Thebes: Located in Boeotia, Thebes played a significant role in Greek mythology and warfare. Its legendary king, Oedipus, and its military victories during the Theban Wars cemented its place in history.
-
Delphi: Situated on Mount Parnassus, Delphi was renowned for its oracle, a religious sanctuary that attracted pilgrims and rulers from across the Greek world. Its pronouncements shaped political decisions and influenced the course of history.
-
Olympia: Located in Elis, Olympia was the site of the ancient Olympic Games, a pan-Hellenic festival that celebrated athletic excellence and fostered unity among the Greek city-states. The games were held in honor of Zeus, the king of the gods, and symbolized the ideals of peace and competition.
Understanding the Interplay of City-States
The map showcases the complex relationships between these cities, ranging from alliances and cooperation to rivalries and conflicts. The Peloponnesian War, a devastating conflict between Athens and Sparta, highlights the tensions that could arise between powerful city-states. The map also reveals the interconnectedness of the Greek world, as trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of ideas transcended political boundaries.
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Cities
The map of ancient Greece serves as a reminder of the enduring legacy of these cities. Their contributions to philosophy, democracy, art, literature, and architecture continue to shape our world today. The principles of democracy developed in Athens, the philosophical insights of Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, and the artistic achievements of the classical period all have profound implications for modern society.
FAQs about the Map of Ancient Greece
Q: What are the main geographical features of ancient Greece?
A: Ancient Greece is characterized by mountainous terrain, numerous islands, and a long coastline. The rugged landscape fostered the development of independent city-states, while the islands facilitated maritime trade and cultural exchange.
Q: How did the geography of ancient Greece influence the development of its cities?
A: The mountainous terrain of Greece promoted the development of independent city-states, as it made communication and travel difficult. The numerous islands provided opportunities for maritime trade and cultural exchange.
Q: What were the main political structures of the ancient Greek city-states?
A: The ancient Greek city-states had diverse political structures, ranging from monarchies to oligarchies to democracies. Athens was famous for its direct democracy, while Sparta was ruled by an oligarchy of wealthy landowners.
Q: What were the main cultural achievements of the ancient Greek city-states?
A: The ancient Greek city-states made significant contributions to philosophy, art, literature, and architecture. Athens was a center of philosophical inquiry, while Sparta was known for its military prowess.
Q: How did the ancient Greek city-states interact with each other?
A: The ancient Greek city-states engaged in both cooperation and conflict. They formed alliances, participated in trade, and competed in athletic contests. However, they also fought wars, such as the Peloponnesian War, which devastated the Greek world.
Tips for Using the Map of Ancient Greece
- Study the geographical features: Pay attention to the mountains, valleys, rivers, and coastlines, as they played a significant role in the development of ancient Greek civilization.
- Locate the major cities: Identify the key city-states and their locations, understanding their strategic importance and their contributions to Greek culture.
- Trace trade routes: Analyze the routes of trade and communication, understanding how they connected different parts of the Greek world.
- Explore historical events: Use the map to visualize the locations of major battles, political alliances, and cultural developments.
- Engage in research: Use the map as a starting point for further exploration of ancient Greek history and civilization.
Conclusion
The map of ancient Greece is a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of this vibrant civilization. It reveals the spatial relationships between city-states, the influence of geography, and the interconnectedness of the Greek world. By using this map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the achievements of ancient Greece and its lasting legacy on our world today.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/History_of_Greece_for_High_Schools_and_Academies_1899_14576880059-9b79528371d3443089862b67a1fbc002.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Greecemap4g-56aaa0193df78cf772b458a4.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Ancient Greek Civilization: A Map-Based Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!