Navigating the Landscape of Lyme Disease: A Guide to Understanding the Tick-Borne Threat
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Lyme Disease: A Guide to Understanding the Tick-Borne Threat
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Lyme Disease: A Guide to Understanding the Tick-Borne Threat. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Lyme Disease: A Guide to Understanding the Tick-Borne Threat
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Lyme Disease: A Guide to Understanding the Tick-Borne Threat
- 3.1 The Lyme Disease Map: A Visual Representation of Risk
- 3.2 Understanding the Factors Influencing Lyme Disease Spread
- 3.3 Navigating the Lyme Disease Map: A Closer Look
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.5 Tips for Preventing Lyme Disease
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Call for Vigilance
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Lyme Disease: A Guide to Understanding the Tick-Borne Threat

Lyme disease, a debilitating illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, is a growing concern across the globe. Its transmission primarily occurs through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks, commonly known as deer ticks. These tiny arachnids, often no larger than a poppy seed, are prevalent in wooded and grassy areas, posing a significant threat to humans and animals alike. Understanding the geographic distribution of Lyme disease and the factors influencing its spread is crucial for effective prevention and management.
The Lyme Disease Map: A Visual Representation of Risk
The Lyme disease map, often depicted as a color-coded representation of risk levels, serves as a valuable tool for visualizing the geographical prevalence of the disease. Areas with high incidence of Lyme disease are typically shaded in darker colors, while regions with lower risk are represented in lighter hues. These maps are generated using data collected from various sources, including:
- Surveillance data: Reports from healthcare providers, laboratories, and public health agencies provide valuable insights into the number of Lyme disease cases in specific regions.
- Tick surveillance: Monitoring tick populations and their infection rates with Borrelia burgdorferi allows for a better understanding of the potential for Lyme disease transmission in different areas.
- Environmental factors: Factors such as climate, vegetation, and wildlife populations can influence tick populations and the spread of Lyme disease.
The Lyme disease map is a dynamic tool, constantly evolving as new data becomes available. It serves several important purposes:
- Public awareness: By visualizing the distribution of Lyme disease, the map raises awareness of the potential risk in specific areas, encouraging individuals to take preventive measures.
- Risk assessment: The map allows healthcare professionals and public health officials to identify high-risk areas and target preventive interventions accordingly.
- Research and monitoring: The map provides valuable data for researchers studying the epidemiology and transmission of Lyme disease, aiding in the development of effective control strategies.
Understanding the Factors Influencing Lyme Disease Spread
The spread of Lyme disease is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Tick populations: The abundance of blacklegged ticks in a region is directly correlated with the risk of Lyme disease transmission. Factors like habitat suitability, climate, and host availability influence tick populations.
- Infection rates: The percentage of ticks carrying Borrelia burgdorferi varies geographically. This infection rate is influenced by factors like the presence of infected animal reservoirs, such as white-footed mice.
- Human activity: The frequency of human exposure to tick-infested areas, particularly during peak tick activity seasons, significantly influences the risk of Lyme disease.
Navigating the Lyme Disease Map: A Closer Look
The Lyme disease map is not a definitive predictor of individual risk. While areas with higher incidence may indicate a greater likelihood of encountering infected ticks, individual behaviors and precautions play a crucial role in mitigating risk.
Factors to Consider:
- Time of year: Tick activity peaks during spring and summer months, coinciding with warmer temperatures and increased outdoor activity.
- Location: Wooded and grassy areas with high vegetation provide suitable habitats for ticks.
- Host availability: The presence of deer and other suitable hosts for ticks can contribute to higher tick populations.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
1. How accurate are Lyme disease maps?
Lyme disease maps are based on available data, which can vary in quality and completeness. The accuracy of the map is dependent on the reliability and comprehensiveness of the data sources.
2. Can Lyme disease be found in areas not shown on the map?
While Lyme disease maps provide a general overview of risk areas, it is important to note that the disease can occur in areas not depicted on the map, particularly if conditions are suitable for tick populations and transmission.
3. What should I do if I live in a high-risk area?
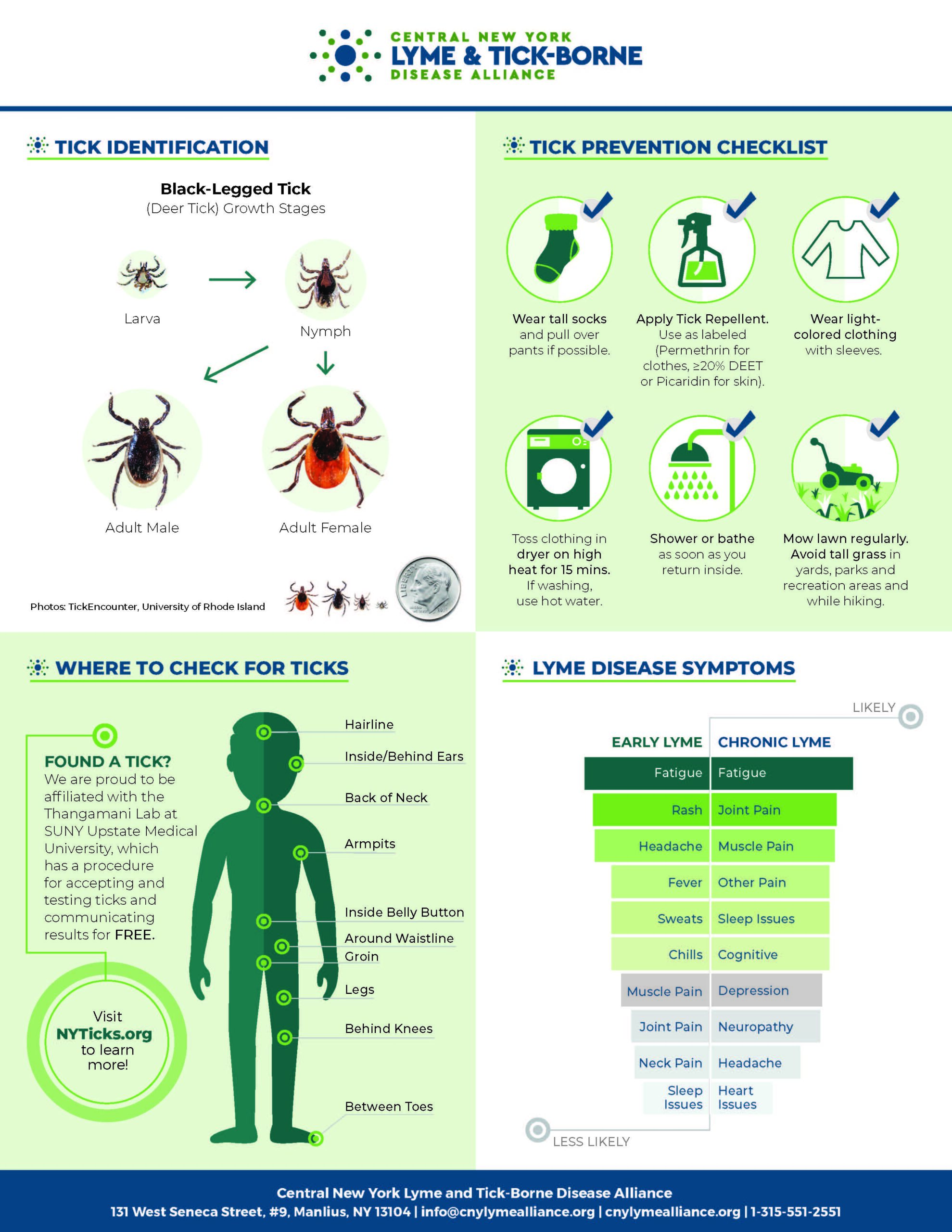
Individuals living in high-risk areas should take extra precautions to prevent tick bites, including wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, and performing thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors.
4. What should I do if I get bitten by a tick?
If bitten by a tick, it is important to remove it promptly and correctly. Seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of Lyme disease, such as fever, rash, fatigue, or joint pain.
Tips for Preventing Lyme Disease
- Wear light-colored clothing: This allows for easier detection of ticks.
- Tuck pants into socks: This prevents ticks from crawling up legs.
- Use insect repellent: DEET-containing repellents are effective against ticks.
- Check for ticks regularly: Perform thorough checks on yourself and pets after spending time outdoors.
- Remove ticks promptly and correctly: Use tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible and pull upward with steady pressure.
Conclusion: A Call for Vigilance
The Lyme disease map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the geographical distribution of this debilitating illness. While the map provides valuable insights, it is crucial to remember that individual behavior and precautions play a significant role in mitigating the risk of Lyme disease. By understanding the factors influencing Lyme disease spread and implementing preventative measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting this potentially debilitating infection. Continued research, surveillance, and public awareness are essential for effectively managing the Lyme disease threat and ensuring the health and well-being of communities.



![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Lyme Disease: A Guide to Understanding the Tick-Borne Threat. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!