Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Geography of Upper and Lower Egypt
Related Articles: Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Geography of Upper and Lower Egypt
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Geography of Upper and Lower Egypt. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Geography of Upper and Lower Egypt
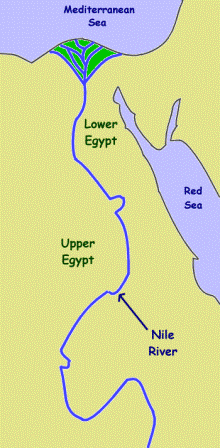
The ancient Egyptians, masters of harnessing the Nile’s power, divided their land into two distinct regions: Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. This division, based on the Nile’s flow, shaped their society, culture, and even their perception of the world. Understanding this geographical distinction is crucial for comprehending the history, mythology, and development of ancient Egypt.
The Nile’s Flow and the Ancient Divide:
The Nile River, the lifeblood of Egypt, flows from south to north, originating in the Ethiopian Highlands and emptying into the Mediterranean Sea. This southward-to-northward flow forms the basis for the distinction between Upper and Lower Egypt.
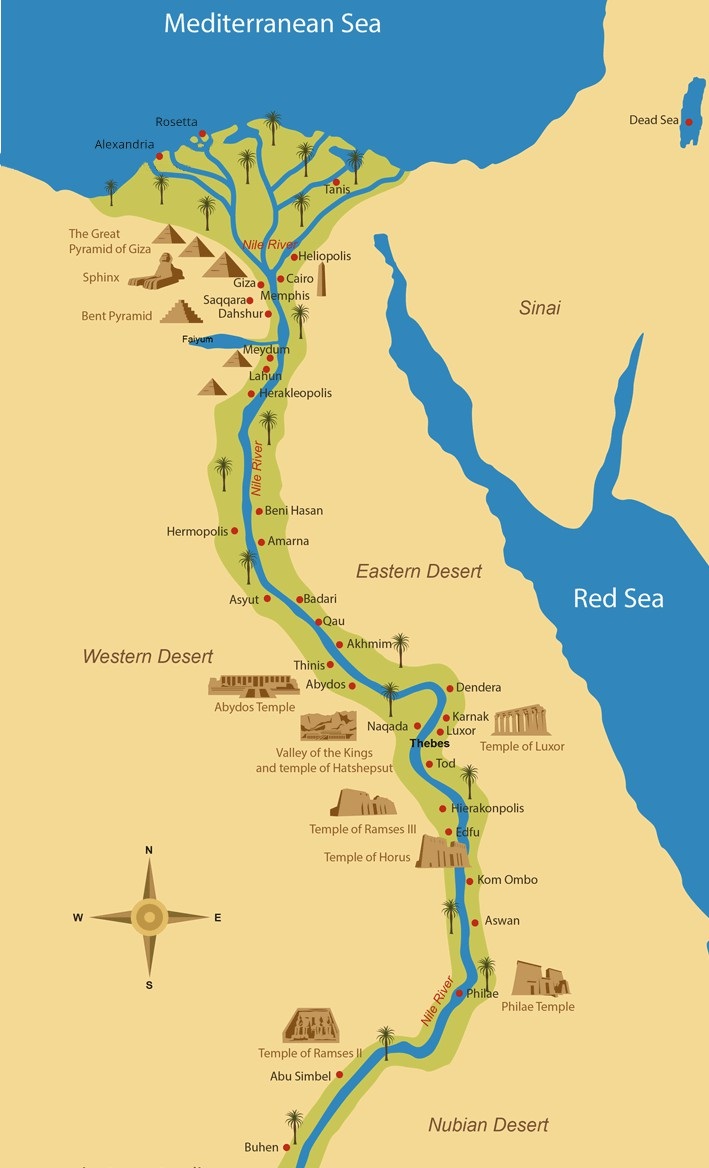
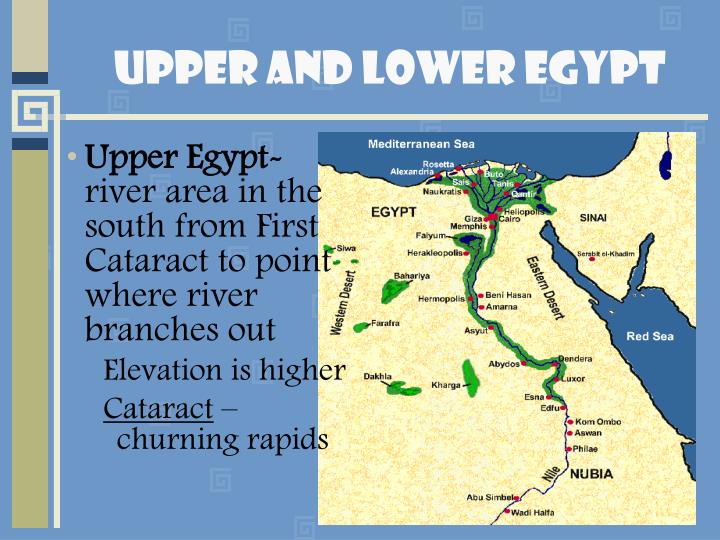
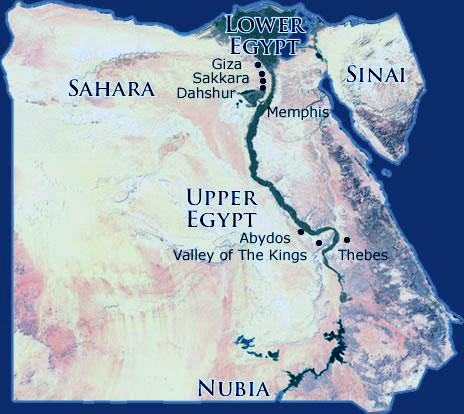
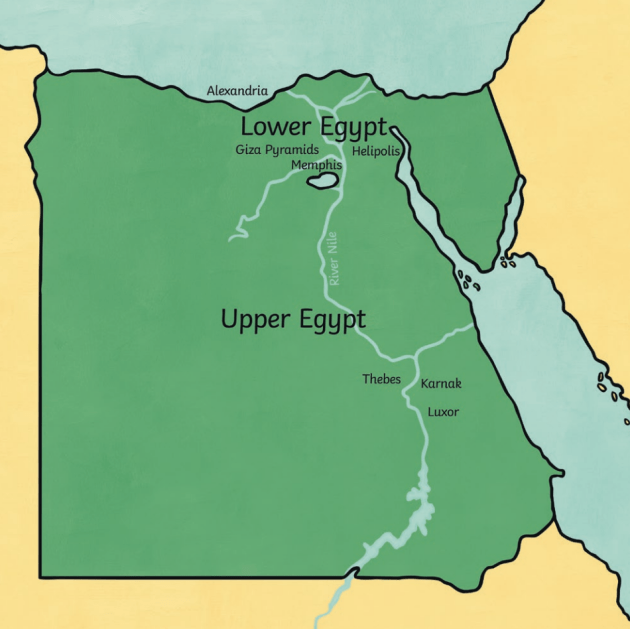
- Upper Egypt: This region encompasses the southern portion of the Nile Valley, stretching from the First Cataract (the southernmost point where the Nile is navigable) to the modern city of Cairo. Upper Egypt, despite its name, is geographically higher in elevation than Lower Egypt. It is characterized by a narrow, fertile valley bordered by rugged desert landscapes. This region was historically known for its rich agricultural lands and the abundance of natural resources, including gold, granite, and sandstone.
- Lower Egypt: Situated in the northern part of the Nile Delta, Lower Egypt extends from Cairo to the Mediterranean Sea. This region is defined by its vast, fertile delta, formed by the Nile’s sediment deposits over millennia. The delta’s rich soil and abundance of water made Lower Egypt a vital center for agriculture and trade, attracting a dense population.
Beyond Geography: Cultural and Historical Significance:
The division into Upper and Lower Egypt was not merely a geographical distinction. It held deep cultural and historical significance, influencing the development of ancient Egyptian society, religion, and political structures.
- Symbolic Representation: The ancient Egyptians often depicted Upper Egypt as a red crown, representing the strength and power of the south, while Lower Egypt was represented by a white crown, symbolizing the fertility and abundance of the north. The unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under King Menes, marked by the merging of the red and white crowns into a single symbol, the Double Crown, signified the creation of a unified Egyptian kingdom.
- Political and Economic Centers: Upper Egypt, with its abundance of natural resources, served as a source of wealth and power, while Lower Egypt, with its fertile delta and access to the Mediterranean Sea, became a vital hub for trade and commerce. This dynamic interplay between the two regions shaped the political landscape and economic development of ancient Egypt.
- Religious and Mythological Significance: The division between Upper and Lower Egypt is reflected in Egyptian mythology and religious beliefs. The god Horus, associated with the Upper Egyptian red crown, was often depicted as a falcon, symbolizing strength and power. On the other hand, the god Osiris, linked to the Lower Egyptian white crown, was associated with fertility and rebirth, reflecting the life-giving nature of the delta.
Mapping the Ancient World:
Maps of Upper and Lower Egypt provide a valuable tool for understanding the ancient world. They reveal the geographical relationship between the two regions, the locations of important cities, and the strategic importance of the Nile River.
- Ancient Maps: While no complete maps of ancient Egypt have been found, surviving fragments and hieroglyphic texts provide glimpses into how the ancient Egyptians visualized their land. These maps, often etched onto temple walls or inscribed on papyrus scrolls, reveal their understanding of the Nile’s flow, the location of key settlements, and the boundaries between Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Modern Maps: Modern maps, based on archaeological evidence and historical texts, offer a more detailed and accurate representation of ancient Egypt. They depict the boundaries between Upper and Lower Egypt, the locations of important cities like Thebes (in Upper Egypt) and Memphis (in Lower Egypt), and the intricate network of canals that connected the two regions.
The Enduring Legacy of the Divide:
The division between Upper and Lower Egypt, while a product of ancient geography, continues to influence our understanding of Egyptian civilization. It serves as a reminder of the complex interplay between geography, culture, and history, shaping the development of one of the world’s most enduring civilizations.
FAQs about Upper and Lower Egypt:
Q: Why was Upper Egypt called "Upper" despite being lower in elevation?
A: The term "Upper" and "Lower" refer to the Nile’s flow, not elevation. Upper Egypt, being located further south, is considered "upper" because the Nile flows from south to north.
Q: What were the major cities of Upper and Lower Egypt?
A: Some major cities in Upper Egypt included Thebes (modern Luxor), Abydos, and Dendera. In Lower Egypt, key cities included Memphis, Saqqara, and Alexandria.
Q: How did the division between Upper and Lower Egypt affect the political structure of ancient Egypt?
A: The two regions often had distinct political identities, with Upper Egypt sometimes wielding greater power. The unification of the two regions under a single ruler, as achieved by King Menes, was a significant milestone in Egyptian history.
Q: What are some examples of the cultural and religious differences between Upper and Lower Egypt?
A: Upper Egypt was associated with the god Horus, representing strength and power, while Lower Egypt was linked to the god Osiris, representing fertility and rebirth. This distinction reflected the different identities and values of the two regions.
Tips for Understanding Upper and Lower Egypt:
- Study a map: Familiarize yourself with the geographical location of Upper and Lower Egypt, the Nile’s flow, and the locations of key cities.
- Explore ancient Egyptian mythology: Understanding the gods and goddesses associated with each region can provide insights into their cultural and religious beliefs.
- Visit archaeological sites: Exploring ancient cities like Thebes, Memphis, and Saqqara can provide a tangible connection to the history and culture of Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Read about the unification of Egypt: Learning about the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under King Menes sheds light on the significance of this division in shaping Egyptian history.
Conclusion:
The division between Upper and Lower Egypt, based on the Nile’s flow, played a fundamental role in shaping the history, culture, and development of ancient Egypt. Understanding this distinction provides a crucial framework for comprehending the complex interplay between geography, society, and civilization. While the ancient Egyptians have long since passed, their legacy continues to resonate through the enduring presence of their magnificent monuments, intricate mythology, and a civilization that left an indelible mark on the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Nile: Understanding the Geography of Upper and Lower Egypt. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!