The Andes: A Mountainous Spine Across South America
Related Articles: The Andes: A Mountainous Spine Across South America
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Andes: A Mountainous Spine Across South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Andes: A Mountainous Spine Across South America
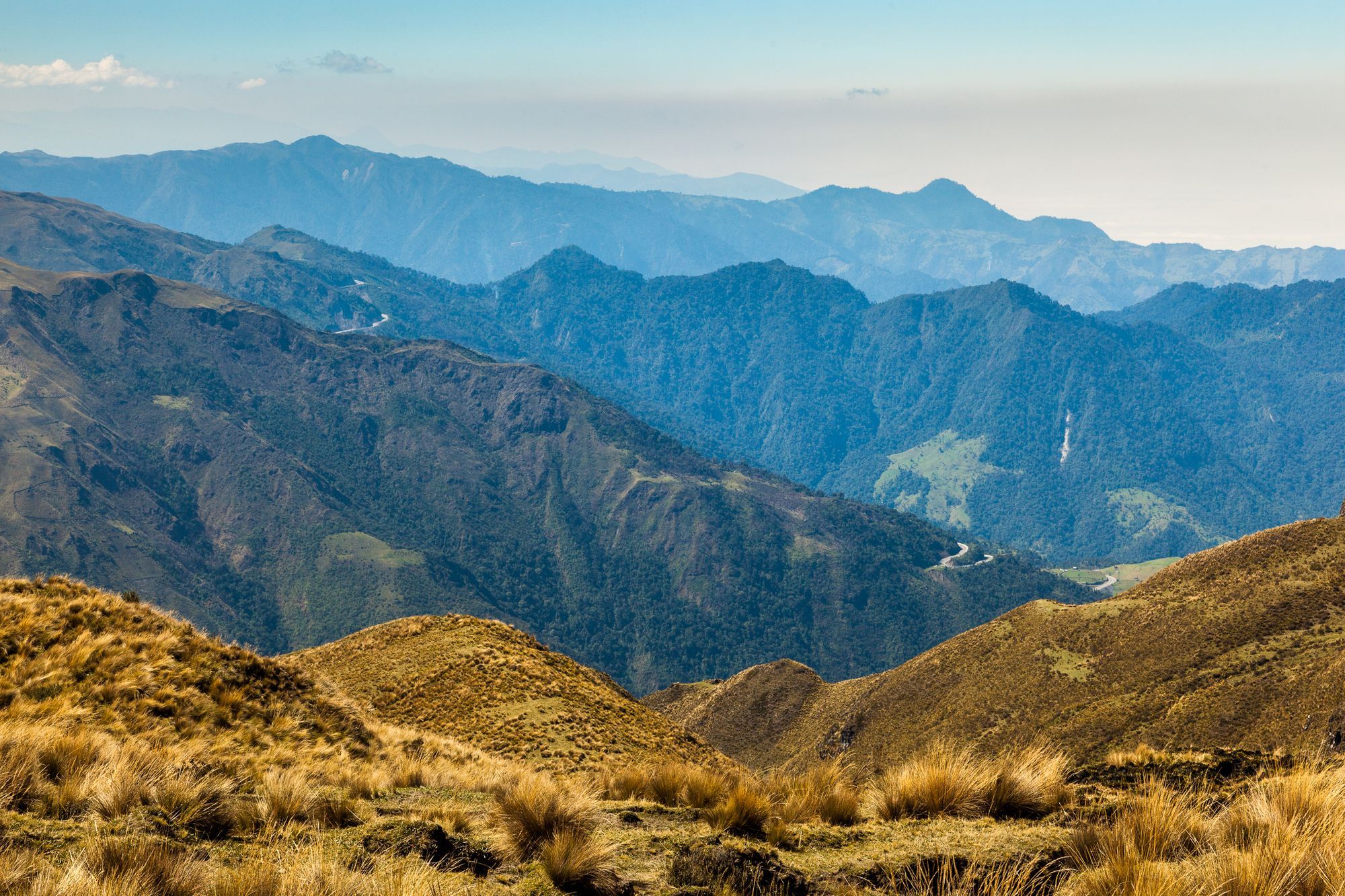

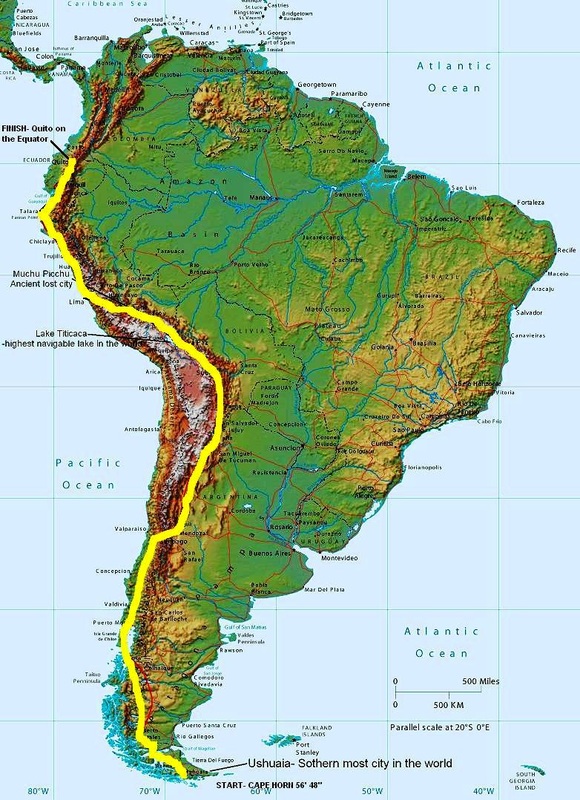
The Andes mountain range, a colossal geological formation stretching over 7,000 kilometers along the western edge of South America, is a testament to the dynamic forces shaping our planet. Its imposing peaks, expansive plateaus, and deep valleys create a dramatic landscape of immense beauty and ecological diversity. This article delves into the Andes, exploring its geographical features, geological origins, ecological significance, and cultural impact.
A Tapestry of Mountains:
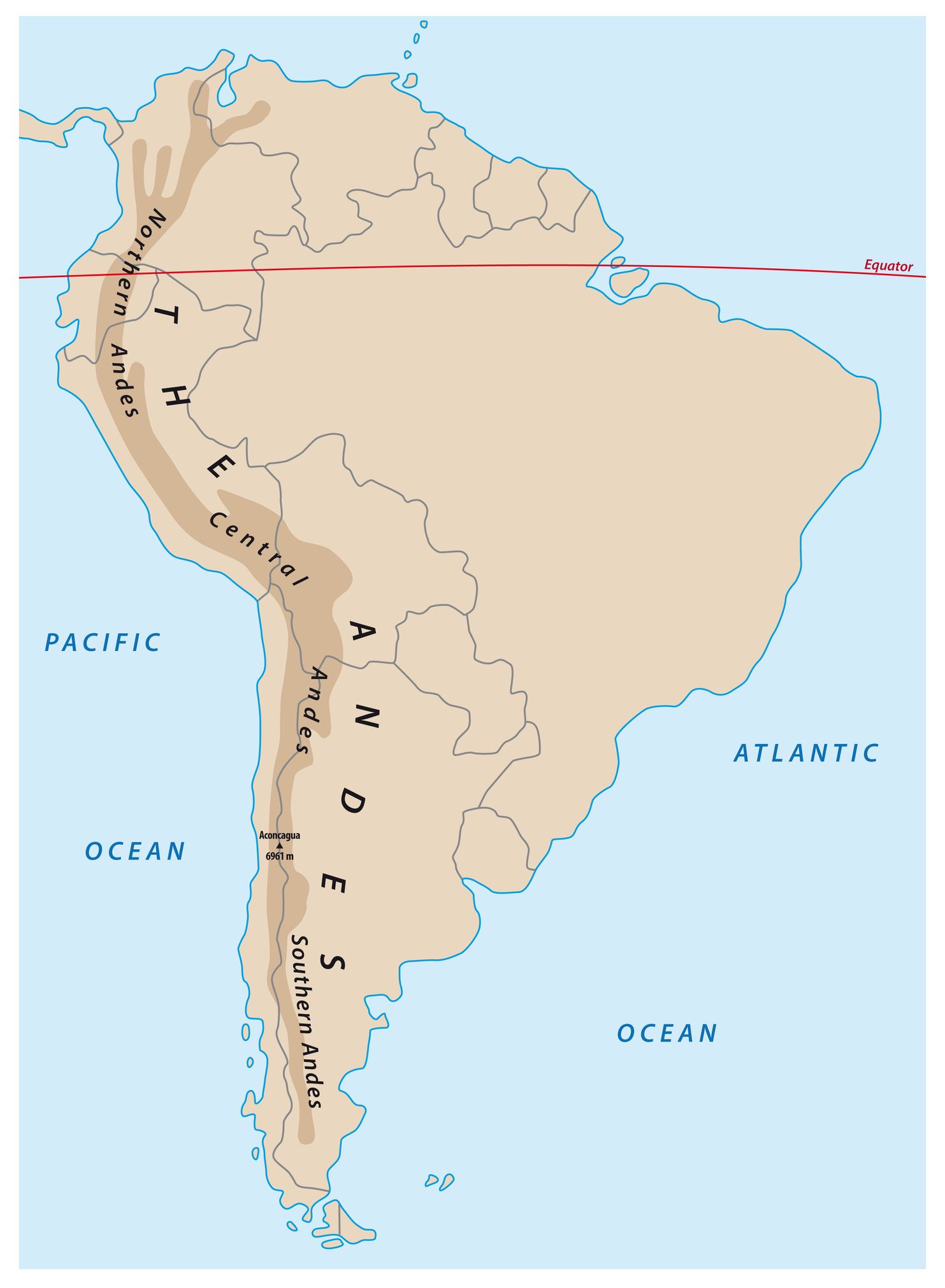
The Andes are not a monolithic entity but rather a complex system of interconnected mountain ranges, plateaus, and valleys. They can be broadly divided into three sections:
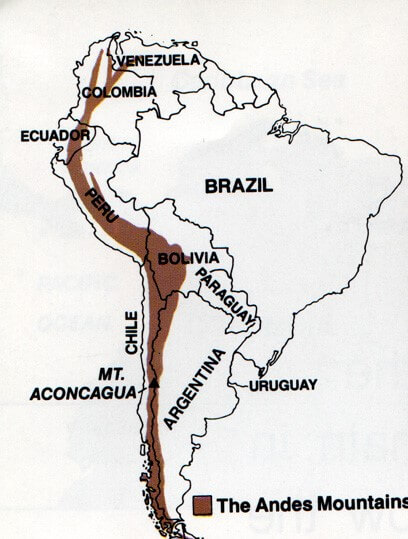
- Northern Andes: This section encompasses the mountains of Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador. Characterized by a series of parallel ranges, it features towering peaks like the Pico Cristóbal Colón (5,775 meters) in Venezuela and the active volcano Cotopaxi (5,897 meters) in Ecuador.
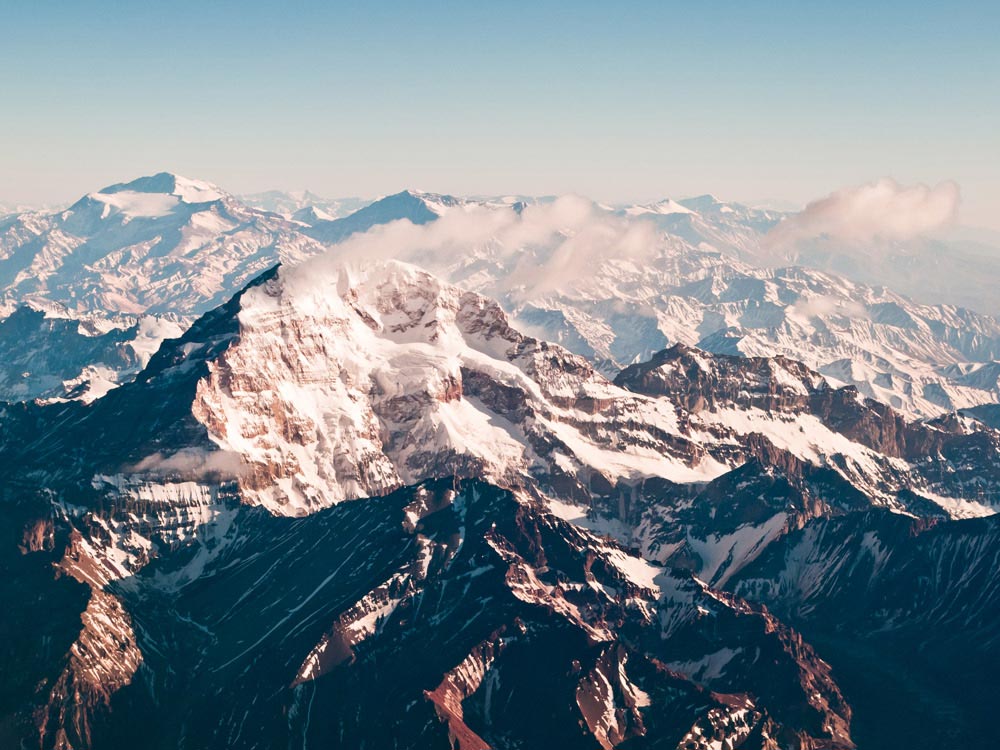
- Central Andes: This segment, spanning Peru and Bolivia, is home to the highest peaks in the Andes, including the iconic Mount Aconcagua (6,961 meters) in Argentina, the highest mountain outside Asia. The Central Andes also feature the vast altiplano, a high plateau home to unique ecosystems and indigenous cultures.
- Southern Andes: Extending through Chile and Argentina, this section is marked by a more rugged and fragmented landscape. It features volcanic peaks like the Ojos del Salado (6,893 meters) and the iconic Torres del Paine National Park in Chile, renowned for its dramatic granite peaks.
Geological Origins:
The Andes are the product of a complex geological process known as plate tectonics. The Nazca Plate, a dense oceanic plate, is subducting beneath the South American Plate. This process, where one plate slides beneath another, generates intense pressure and heat, leading to the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. The Andes are a prime example of this tectonic activity, with numerous active volcanoes and frequent seismic events.
Ecological Significance:
The Andes are a biodiversity hotspot, home to a staggering array of plant and animal life. The diverse elevations, climates, and geological formations create a unique mosaic of ecosystems, ranging from snow-capped peaks to lush rainforests and arid deserts. The Andes are home to a remarkable array of endemic species, including the iconic Andean condor, the vicuña, and the giant hummingbird.
Cultural Significance:
The Andes have played a pivotal role in the history and culture of South America. Indigenous cultures have thrived in this region for millennia, adapting to the challenging environment and developing unique traditions, languages, and belief systems. The Inca Empire, one of the most powerful pre-Columbian civilizations, originated in the Andes, leaving behind a legacy of impressive architectural and agricultural achievements. Today, the Andes remain a vibrant cultural landscape, with indigenous communities maintaining their traditions and contributing to the region’s rich cultural tapestry.
Economic Importance:
The Andes are a vital resource for South America, providing important resources and supporting various industries. The region is rich in mineral deposits, including copper, silver, gold, and tin, making it a significant contributor to the global mining industry. The Andes also play a crucial role in agriculture, with vast areas dedicated to the cultivation of crops like potatoes, quinoa, and coffee. Additionally, the mountains serve as a source of hydropower, providing electricity to surrounding regions.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Andes face numerous challenges, including climate change, deforestation, mining pollution, and the threat of biodiversity loss. Climate change is particularly concerning, with rising temperatures impacting glaciers and water resources, threatening the livelihoods of communities dependent on these resources. Deforestation is another major concern, as it leads to habitat loss and soil erosion, impacting both biodiversity and human populations.
Despite these challenges, the Andes also present opportunities for sustainable development and conservation. The region’s rich biodiversity and cultural heritage attract tourism, providing economic benefits and raising awareness about the importance of conservation. Efforts to promote sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and ecotourism can help mitigate environmental impacts and promote economic growth.
FAQs by Andes Mountain Range Map:
1. What is the highest peak in the Andes?
The highest peak in the Andes is Mount Aconcagua, located in Argentina, reaching a height of 6,961 meters.
2. How many countries does the Andes Mountain Range span?
The Andes stretch across seven countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina.
3. What are the main geographical features of the Andes?
The Andes feature a diverse landscape, including towering peaks, expansive plateaus, deep valleys, and numerous active volcanoes.
4. What is the ecological significance of the Andes?
The Andes are a biodiversity hotspot, home to a vast array of endemic species and unique ecosystems.
5. What are the cultural influences in the Andes?
The Andes are home to a rich tapestry of indigenous cultures, with a long history of adaptation to the challenging environment.
6. What are the economic benefits of the Andes?
The Andes provide essential resources, including minerals, agricultural products, and hydropower, contributing significantly to the economies of South American countries.
7. What are the major threats to the Andes?
The Andes face challenges such as climate change, deforestation, mining pollution, and the loss of biodiversity.
8. What are the opportunities for sustainable development in the Andes?
The Andes present opportunities for sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, ecotourism, and conservation efforts.
Tips by Andes Mountain Range Map:
- Use a detailed map to explore the diverse landscapes and geographic features of the Andes.
- Consult resources on the history, culture, and ecology of the Andes to gain a deeper understanding of this remarkable region.
- Consider visiting the Andes to experience its breathtaking beauty firsthand and learn about the challenges and opportunities facing this vital ecosystem.
- Support organizations working to conserve the Andes and promote sustainable development in the region.
Conclusion by Andes Mountain Range Map:
The Andes Mountain Range, a geological marvel spanning thousands of kilometers, stands as a testament to the Earth’s dynamic processes and the resilience of life. Its towering peaks, vast plateaus, and unique ecosystems have shaped the history and culture of South America, providing essential resources and inspiring awe in those who witness its grandeur. As we face the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, understanding and protecting the Andes is crucial for the future of this vital region and the planet as a whole.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Andes: A Mountainous Spine Across South America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!