The Diverse Tapestry of Africa’s Landforms
Related Articles: The Diverse Tapestry of Africa’s Landforms
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Diverse Tapestry of Africa’s Landforms. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Diverse Tapestry of Africa’s Landforms
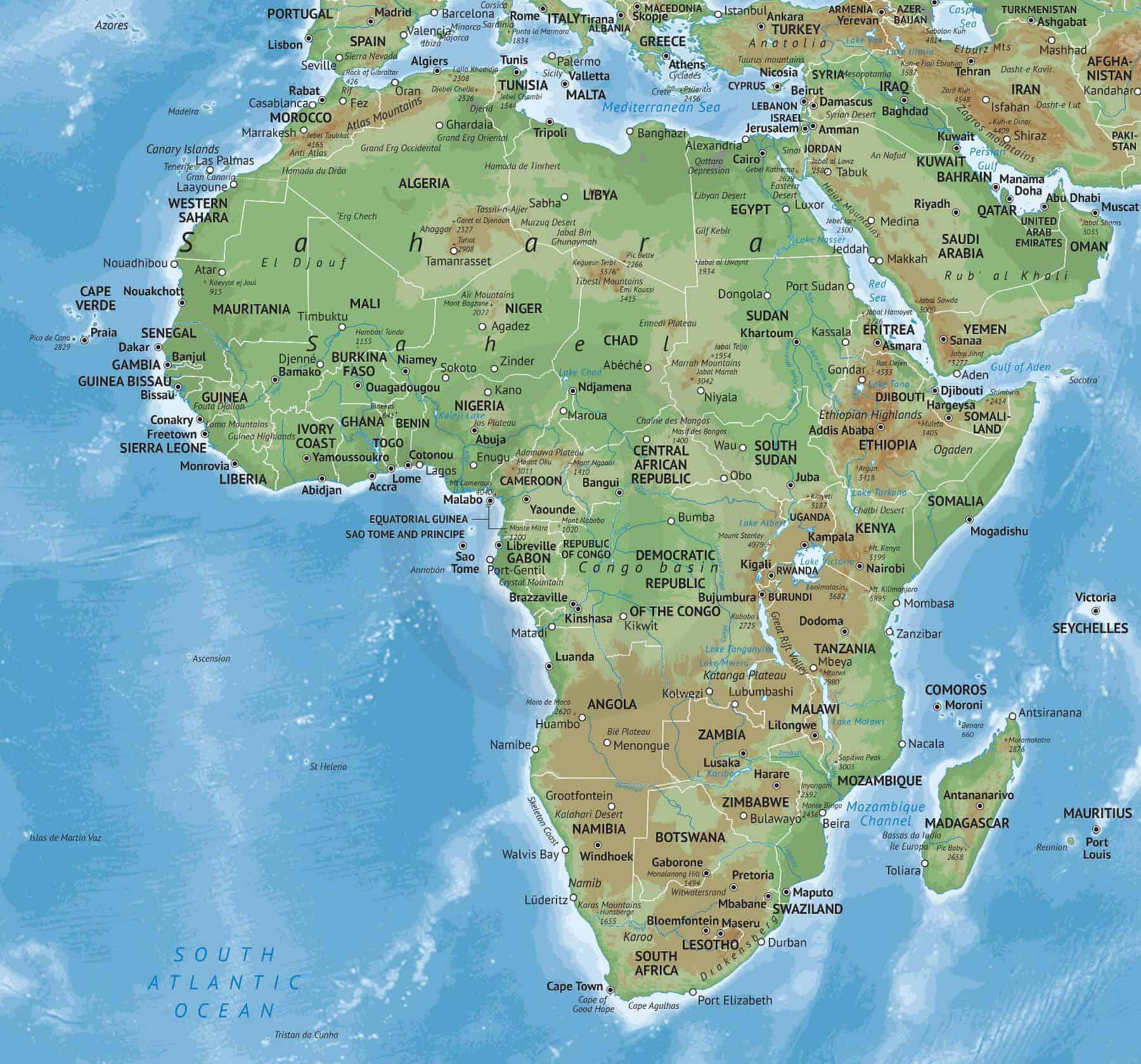
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a realm of breathtaking contrasts. From the towering peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the vast, arid expanse of the Sahara Desert, its landscape is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped its geological history. This diversity of landforms, each with its unique characteristics and ecological significance, contributes to the continent’s rich biodiversity and cultural tapestry.
The Great Rift Valley: A Geological Wonder
One of Africa’s most prominent and dramatic features is the Great Rift Valley, a vast geological formation stretching over 6,000 kilometers from the Red Sea in the north to Mozambique in the south. This massive fault system, formed by the slow but relentless movement of tectonic plates, has created a series of dramatic landscapes, including:
- Volcanic Mountains: The Rift Valley is home to several active volcanoes, including Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Kenya, and Mount Nyiragongo. These towering peaks have shaped the surrounding landscape and provide fertile volcanic soils, supporting diverse ecosystems.
- Rift Valley Lakes: The valley is punctuated by a series of lakes, some of which are among the deepest in the world. These lakes, including Lake Tanganyika, Lake Malawi, and Lake Victoria, are crucial habitats for diverse aquatic life and support significant fishing industries.
- Escarpments and Plateaus: The Rift Valley is bounded by steep escarpments and plateaus, which offer panoramic views and provide diverse habitats for wildlife. The East African Plateau, for example, is known for its unique flora and fauna, including the iconic African savanna.
The Sahara Desert: A Vast and Arid Landscape
The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, dominates North Africa, covering an area larger than the United States. This vast expanse of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and dry valleys is shaped by extreme temperatures and limited rainfall.
- Sand Dunes: The Sahara is known for its iconic sand dunes, some reaching hundreds of meters in height. These dunes, shaped by wind erosion, create a constantly shifting landscape that poses challenges to human settlement and transportation.
- Rock Plateaus: The desert also features vast rock plateaus, remnants of ancient geological formations. These plateaus, such as the Ennedi Massif in Chad, offer unique landscapes with canyons, arches, and rock shelters, providing evidence of past human habitation.
- Oases: Scattered throughout the desert are oases, small pockets of vegetation nourished by underground springs. These oases, vital for human survival and animal life, provide respite from the harsh desert environment and serve as important trading centers.
The Congo Basin: A Lush and Biodiverse Region
The Congo Basin, centered around the Congo River, is one of the largest tropical rainforest regions in the world. This dense and humid landscape is characterized by its rich biodiversity, abundant rainfall, and a vast network of rivers and swamps.
- Rainforests: The Congo Basin is home to a vast expanse of rainforest, teeming with life. This ecosystem is characterized by its dense canopy, high humidity, and diverse flora and fauna, including gorillas, chimpanzees, and okapi.
- Rivers and Swamps: The Congo River, the second-largest river in the world by volume, flows through the basin, creating a network of tributaries and swamps. These wetlands provide essential habitats for aquatic life and support communities relying on fishing and agriculture.
- Plateaus and Mountains: The Congo Basin is also characterized by plateaus and mountains, offering varied landscapes and microclimates. These areas support unique plant and animal species, contributing to the region’s exceptional biodiversity.
The Coastal Regions: A Tapestry of Landscapes
Africa’s coastal regions are as diverse as the continent itself. From the rocky shores of the Mediterranean Sea to the sandy beaches of the Indian Ocean, these areas offer a range of landscapes and ecosystems:
- Beaches and Lagoons: Africa’s coastlines are dotted with stunning beaches, lagoons, and estuaries. These areas provide important habitats for marine life, support tourism, and offer opportunities for fishing and recreation.
- Mangrove Forests: Mangrove forests thrive in sheltered coastal areas, providing vital habitats for fish, birds, and other wildlife. These unique ecosystems act as natural barriers against erosion and contribute to coastal protection.
- Cliffs and Headlands: Along Africa’s coast, dramatic cliffs and headlands rise from the sea, offering spectacular views and creating diverse habitats for birds and marine life. These features also play a role in coastal defense and shaping the coastline’s unique character.
The Importance of Africa’s Landforms
Africa’s diverse landforms are not just beautiful; they are essential to the continent’s natural and human systems.
- Biodiversity: The varied landscapes of Africa support a vast array of plant and animal life, contributing to the continent’s exceptional biodiversity. From the rainforests of the Congo Basin to the savannas of East Africa, each region harbors unique species that are crucial for maintaining ecological balance.
- Natural Resources: Africa’s landforms are rich in natural resources, including minerals, oil, gas, and fertile soils. These resources are essential for economic development and provide opportunities for employment and trade.
- Cultural Heritage: Africa’s landscapes have shaped its cultural heritage, influencing the traditions, beliefs, and livelihoods of its people. The vastness of the Sahara Desert, for example, has inspired nomadic cultures and storytelling traditions, while the fertile Nile Valley has supported ancient civilizations.
- Tourism: Africa’s dramatic landscapes attract tourists from around the world, contributing to economic growth and cultural exchange. From safaris in the savanna to trekking in the mountains, the continent’s diverse landforms offer unique experiences for travelers.
FAQs about Africa’s Landforms
Q: What are the major landforms of Africa?
A: Africa’s major landforms include the Great Rift Valley, the Sahara Desert, the Congo Basin, the coastal regions, and various plateaus, mountains, and highlands.
Q: How have Africa’s landforms been shaped?
A: Africa’s landforms have been shaped by a combination of tectonic plate movement, volcanic activity, erosion, and climate change over millions of years.
Q: What is the significance of the Great Rift Valley?
A: The Great Rift Valley is a significant geological feature that has created dramatic landscapes, including volcanic mountains, rift valley lakes, and escarpments. It plays a vital role in shaping the continent’s biodiversity and natural resources.
Q: What are the challenges of living in the Sahara Desert?
A: Living in the Sahara Desert presents challenges due to extreme temperatures, limited rainfall, and the harshness of the environment. Adaptations to these conditions have shaped the cultures and livelihoods of desert communities.
Q: What is the importance of the Congo Basin?
A: The Congo Basin is crucial for its rich biodiversity, abundant rainfall, and vast network of rivers and swamps. It plays a vital role in regulating global climate and providing essential resources for local communities.
Q: How are Africa’s coastal regions important?
A: Africa’s coastal regions are important for their diverse ecosystems, including beaches, lagoons, mangrove forests, and cliffs. These areas support marine life, provide opportunities for tourism and fishing, and contribute to coastal protection.
Tips for Understanding Africa’s Landforms
- Use a physical map: Studying a physical map of Africa can help you visualize the continent’s major landforms and their relative locations.
- Read about geological processes: Learning about the processes that have shaped Africa’s landforms, such as tectonic plate movement and erosion, can enhance your understanding of their formation.
- Explore online resources: Websites and documentaries dedicated to African geography and geology can provide detailed information and visual representations of the continent’s diverse landscapes.
- Travel to Africa: If possible, visiting Africa and experiencing its diverse landforms firsthand can deepen your appreciation for their beauty and significance.
Conclusion
Africa’s landforms are a testament to the planet’s dynamic geological history and a source of wonder and inspiration. From the towering peaks of the Rift Valley to the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, each landscape plays a vital role in shaping the continent’s biodiversity, natural resources, and cultural heritage. Understanding these landforms is essential for appreciating the richness and complexity of Africa’s natural world and for informing sustainable development strategies for the future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Diverse Tapestry of Africa’s Landforms. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!