The Maya Territory Map: A Window into a Complex and Enduring Civilization
Related Articles: The Maya Territory Map: A Window into a Complex and Enduring Civilization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Maya Territory Map: A Window into a Complex and Enduring Civilization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Maya Territory Map: A Window into a Complex and Enduring Civilization
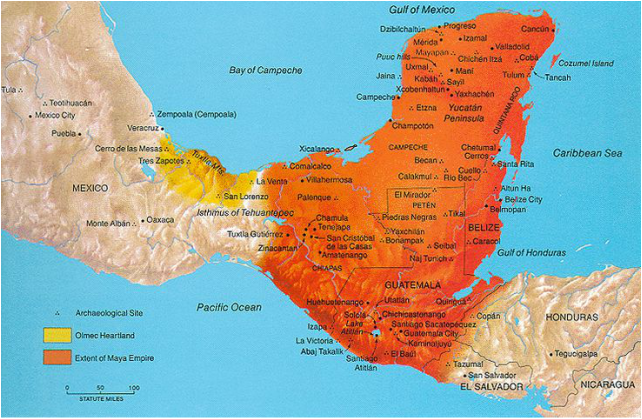
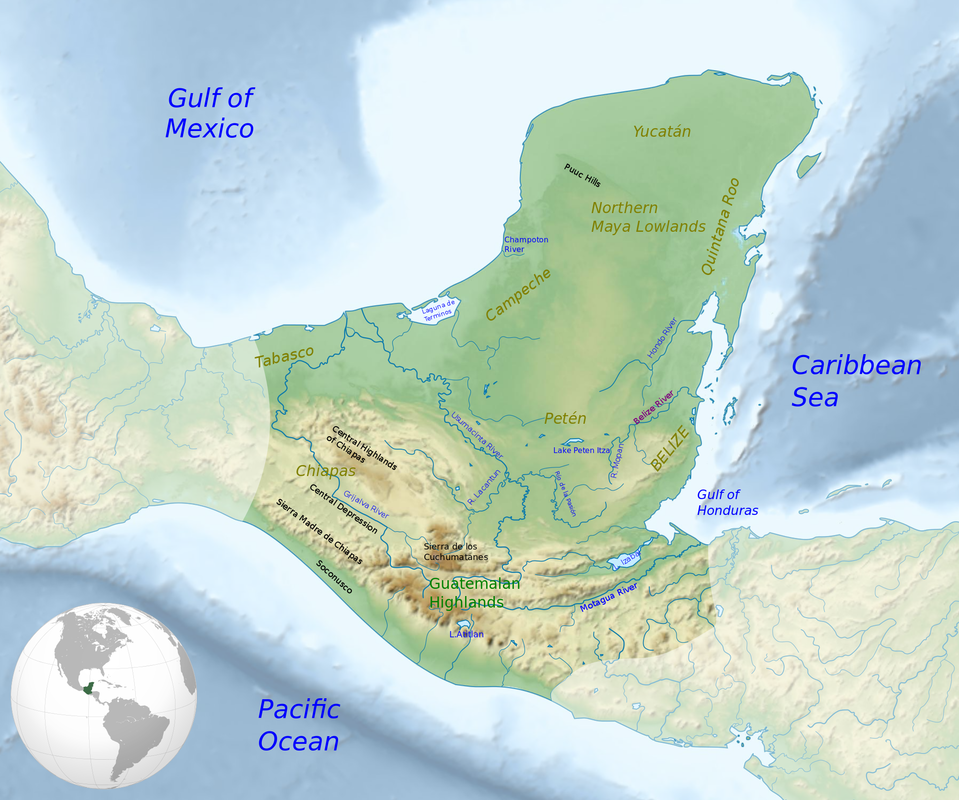
The Maya civilization, renowned for its intricate calendar systems, stunning architecture, and sophisticated writing system, flourished across a vast region of Mesoamerica for over 2,000 years. Understanding the geographic extent of this civilization requires examining the Maya territory map, a crucial tool for scholars and researchers.
This map is not merely a static representation of physical boundaries. It is a dynamic and evolving landscape that reflects the ebb and flow of political power, cultural exchange, and economic activity. Its intricacies reveal the complex tapestry of Maya society, highlighting the interconnectedness of its numerous city-states and the vast network of trade routes that linked them.
Delving into the Depths of the Maya Territory Map
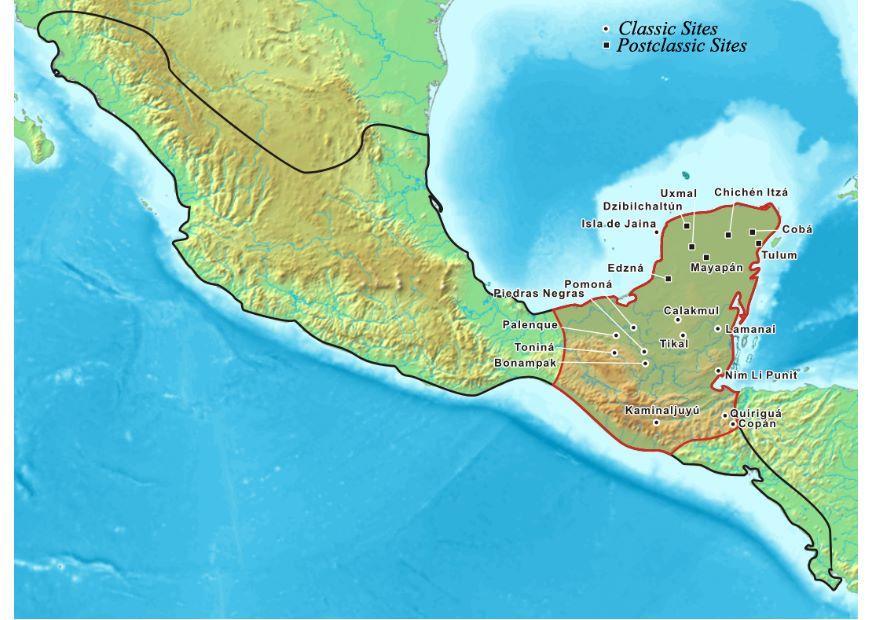
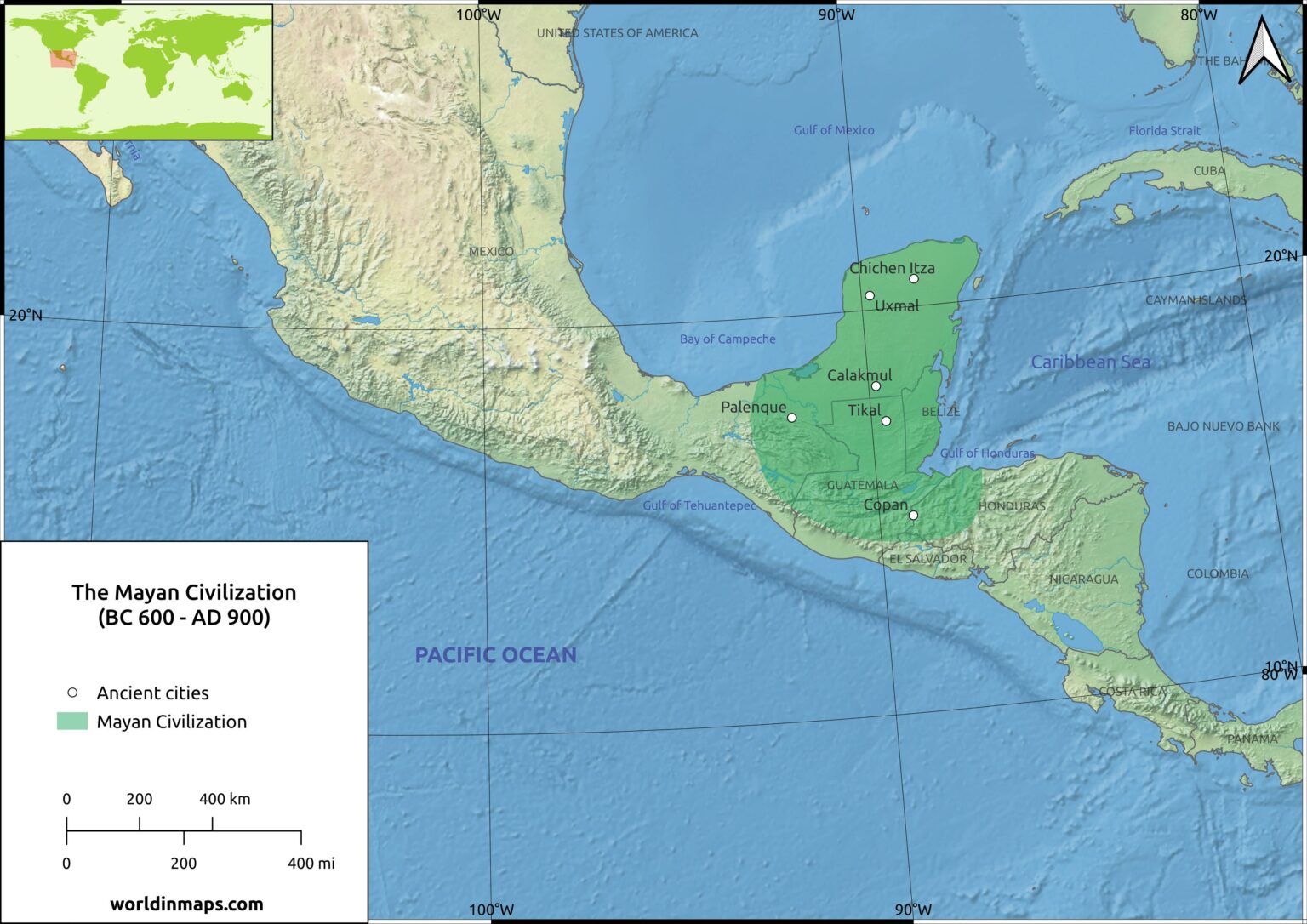
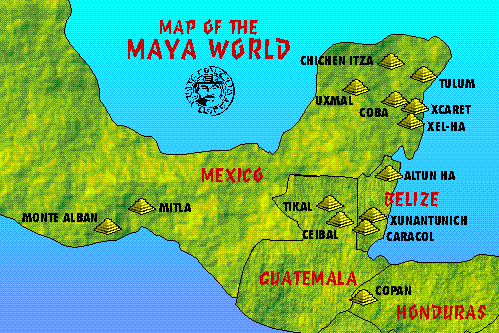
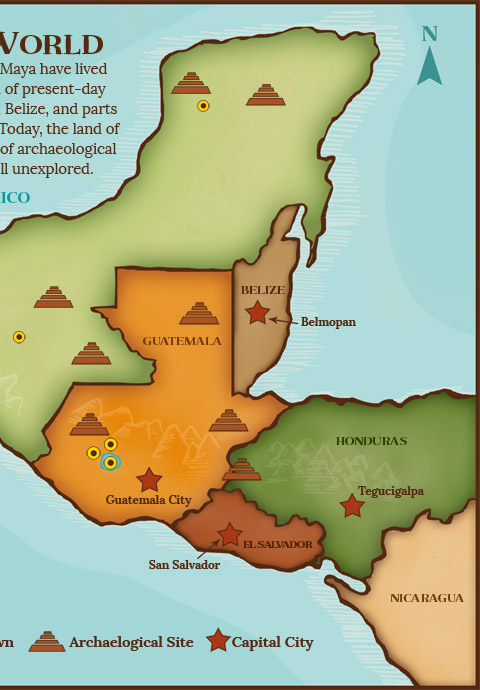
The Maya territory map encompasses a diverse geographical area, stretching from present-day southern Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador. Within this vast region, the Maya civilization thrived in a variety of ecological zones, from lush rainforests to rugged highlands and fertile lowlands. This diversity shaped their agricultural practices, their social structures, and even their artistic expressions.
The map reveals the distinct characteristics of each Maya region:
- The Yucatan Peninsula: Characterized by its vast, flat limestone plain, this region was home to some of the most iconic Maya cities, including Chichén Itzá and Uxmal. Its dry climate and limited water resources led to the development of sophisticated water management systems and a focus on agriculture.
- The Petén Basin: Located in northern Guatemala, this dense rainforest region was a hub of political power and cultural innovation. Its fertile soils and abundant rainfall supported a thriving agricultural economy, fostering the growth of major cities like Tikal and Caracol.
- The Highlands: This mountainous region, encompassing parts of Guatemala and Chiapas, Mexico, was characterized by its diverse terrain and cooler climate. Its inhabitants adapted to the challenging environment, developing unique agricultural techniques and cultivating crops like maize, beans, and squash.
- The Pacific Coast: This region, extending from Chiapas, Mexico to El Salvador, was influenced by trade and interaction with other Mesoamerican cultures. Its coastal location facilitated maritime trade and the development of unique artistic styles.
Understanding the Interconnectedness of Maya City-States
The Maya territory map is not just a collection of isolated city-states. It reveals a complex network of interactions and dependencies between these political entities. Trade routes crisscrossed the region, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices. The map illustrates how Maya cities collaborated and competed for resources, territory, and political dominance.
For example, the monumental city of Tikal in the Petén Basin exerted considerable influence over surrounding regions. Its political power extended beyond its immediate boundaries, forming alliances with other cities and engaging in conflict with rivals. This dynamic interplay between cooperation and competition is evident throughout the Maya territory map, highlighting the intricate political landscape of this ancient civilization.
Exploring the Legacy of the Maya Territory Map
The Maya territory map continues to be a valuable tool for understanding the history, culture, and legacy of the Maya civilization. Its insights contribute to various fields of study, including:
- Archaeology: By mapping the location of Maya cities and archaeological sites, researchers can reconstruct the spatial distribution of Maya settlements and trace their evolution over time.
- Anthropology: The map helps to analyze the social, political, and economic structures of Maya society, shedding light on their cultural diversity and the interconnectedness of their various city-states.
- Linguistics: The distribution of Maya languages on the map provides insights into the linguistic diversity of the region and the historical relationships between different Maya groups.
- Environmental studies: The map highlights the diverse ecosystems inhabited by the Maya and the impact of their agricultural practices on the environment.
FAQs about the Maya Territory Map
Q: How accurate are the existing Maya territory maps?
A: The accuracy of Maya territory maps is constantly evolving as new archaeological discoveries are made. However, the current maps are based on extensive research and provide a reasonably accurate representation of the known Maya territory.
Q: What are the limitations of the Maya territory map?
A: The map reflects only the known settlements and trade routes. It is likely that many smaller settlements and pathways remain undiscovered. Furthermore, the map does not fully capture the fluidity of Maya political boundaries and the shifting alliances between city-states.
Q: What are the benefits of studying the Maya territory map?
A: Studying the Maya territory map offers a deeper understanding of the complexities of Maya civilization, its cultural diversity, its political dynamics, and its interconnectedness. This knowledge can be used to inform conservation efforts, promote cultural heritage, and foster a greater appreciation for the legacy of the Maya people.
Tips for Using the Maya Territory Map
- Consult multiple sources: Different maps may depict the Maya territory in slightly different ways. Refer to various sources for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Consider the historical context: The map reflects the state of the Maya territory at a specific point in time. Understanding the historical context is crucial for interpreting its data.
- Look beyond the physical boundaries: The map is more than just a geographical representation. It offers insights into the cultural, political, and economic dynamics of Maya society.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Scholars from various disciplines, including archaeology, anthropology, and linguistics, offer unique perspectives on the Maya territory map.
Conclusion
The Maya territory map is a powerful tool for exploring the rich history and culture of the Maya civilization. It provides a valuable framework for understanding the spatial distribution of Maya settlements, their political relationships, and their cultural interactions. By studying this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of this ancient civilization and its lasting legacy.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Maya Territory Map: A Window into a Complex and Enduring Civilization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!