The Steppes: A Vast Tapestry of History and Ecology
Related Articles: The Steppes: A Vast Tapestry of History and Ecology
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Steppes: A Vast Tapestry of History and Ecology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Steppes: A Vast Tapestry of History and Ecology
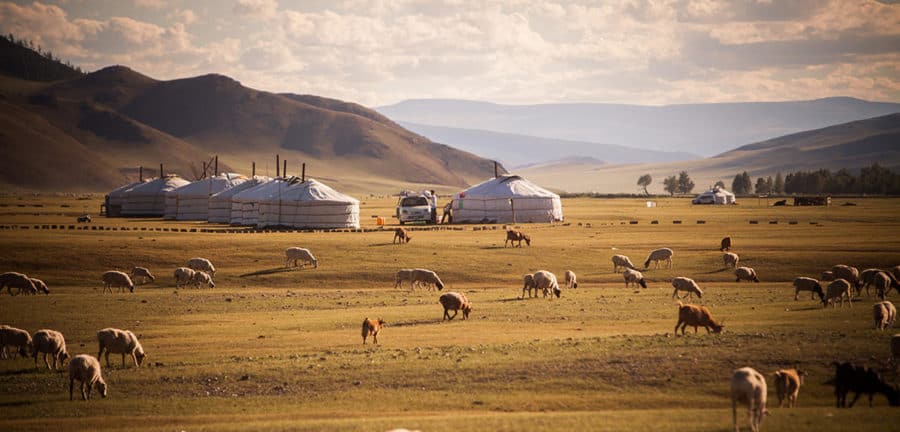

The term "steppes" evokes images of vast, open grasslands stretching towards the horizon, a landscape synonymous with nomadic cultures and the echoes of ancient empires. This expansive ecosystem, found across the Northern Hemisphere, holds a unique position in the global landscape, encompassing a rich history, diverse flora and fauna, and profound cultural significance. Understanding the steppes requires appreciating their geographical expanse, their environmental characteristics, and the human societies that have thrived within them for millennia.
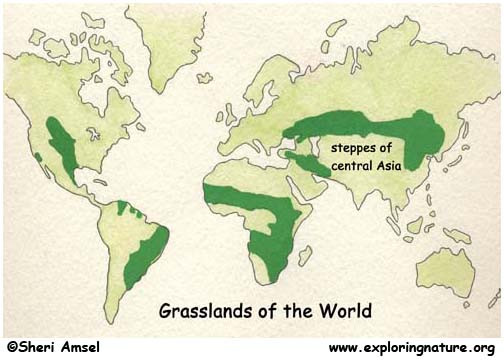
A Geographical Overview
The steppes, also known as prairies or pampas depending on the region, are characterized by their vast, flat, and treeless plains. These grasslands are primarily found in the temperate zones of the world, with significant steppes present in Eurasia, North America, and South America.
- Eurasian Steppes: This vast expanse stretches from the Black Sea in the west to the Altai Mountains in the east, encompassing regions of Ukraine, Russia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China. This region is characterized by its arid climate, cold winters, and hot, dry summers.
- North American Great Plains: This region, stretching from the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River, boasts a diverse range of grasses, from tallgrass prairies to shortgrass steppes. This area experiences significant variations in temperature and precipitation, with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- South American Pampas: Located in Argentina and Uruguay, the pampas are known for their fertile soils and lush grasslands, supporting a vast agricultural industry. The climate is characterized by moderate temperatures and ample rainfall.
Environmental Characteristics
The steppes are defined by their unique environmental characteristics, which have shaped the evolution of life within these ecosystems.
- Climate: The steppes are typically characterized by a semi-arid to arid climate, with low precipitation and high evaporation rates. This leads to a distinct lack of trees, with grasses dominating the vegetation.
- Soils: Steppes are characterized by fertile, deep soils, often rich in organic matter. These soils are well-suited for agriculture, but can be prone to erosion due to the lack of tree cover and the presence of strong winds.
- Flora: The steppes are home to a diverse range of grasses, including fescue, wheatgrass, and blue grama. These grasses have adapted to the harsh conditions, developing deep root systems and drought-resistant mechanisms.
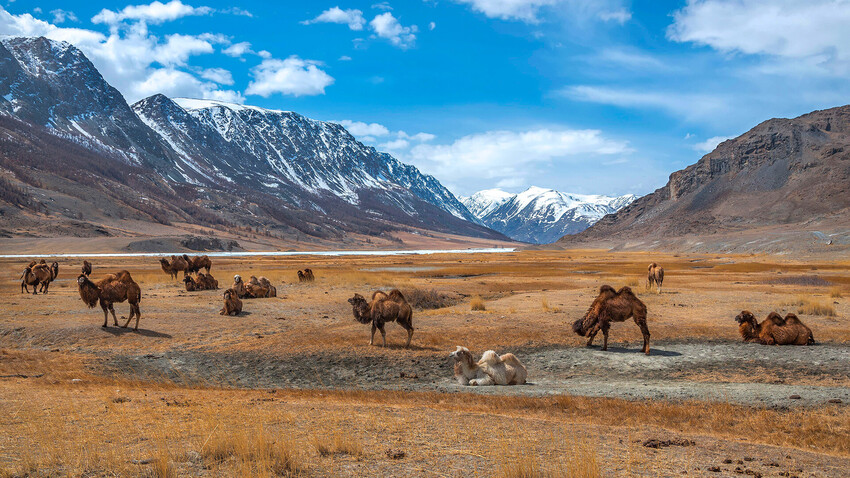
- Fauna: The steppes are home to a variety of animals, including large herbivores such as bison, horses, and antelope, as well as predators like wolves, coyotes, and foxes. The fauna of the steppes has adapted to the open landscapes and harsh climate, developing specialized survival strategies.
Human Societies and the Steppes
For millennia, the steppes have been home to nomadic cultures, their lives intricately intertwined with the rhythms of the grasslands.
- Nomadic Pastoralism: The steppes have been a cradle of nomadic pastoralism, with cultures such as the Scythians, Huns, Mongols, and others, adapting their lives to the seasonal availability of grazing lands. Nomadic societies relied on livestock for sustenance and transportation, developing unique social structures and cultural practices.
- Agriculture and Settlement: While nomadic pastoralism dominated for centuries, the steppes have also witnessed the development of agricultural societies. The fertile soils of the steppes have supported the development of farming communities, leading to the rise of empires and the development of trade routes.
- Cultural Influence: The steppes have exerted a profound influence on the history and culture of the surrounding regions. The nomadic cultures of the steppes have contributed to the development of language, art, and warfare, shaping the destinies of empires and societies.
The Importance of the Steppes
The steppes hold immense ecological and cultural significance, highlighting the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The steppes are home to a wide range of biodiversity, with unique species adapted to the harsh conditions. Protecting these ecosystems is crucial for maintaining global biodiversity and ensuring the survival of countless species.
- Carbon Sequestration: The vast grasslands of the steppes play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigating climate change.
- Cultural Heritage: The steppes are a treasure trove of cultural heritage, representing the legacy of nomadic cultures and their unique way of life. Preserving these traditions is essential for understanding the diverse tapestry of human history.
Challenges Facing the Steppes
Despite their importance, the steppes face numerous challenges, threatening their ecological integrity and cultural heritage.
- Climate Change: Climate change is impacting the steppes, leading to increased drought, desertification, and changes in vegetation patterns. These changes threaten the livelihoods of nomadic communities and the survival of unique species.
- Overgrazing: Unsustainable grazing practices can lead to land degradation, reducing the carrying capacity of the steppes and impacting biodiversity.
- Agricultural Expansion: The expansion of agriculture into the steppes can lead to habitat loss, fragmentation, and the displacement of nomadic cultures.
- Pollution: Industrial activities, including mining and oil extraction, can pollute the steppes, harming wildlife and impacting water resources.
Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the importance of the steppes, various conservation efforts are underway to protect these ecosystems and their cultural heritage.
- Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, is crucial for safeguarding the biodiversity of the steppes.
- Sustainable Land Management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as rotational grazing and controlled burning, can help to restore degraded lands and ensure the long-term health of the steppes.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential for ensuring the success of any conservation program. This includes promoting traditional knowledge and empowering communities to manage their resources sustainably.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is crucial for addressing the transboundary challenges facing the steppes, including climate change and land degradation.
FAQs about the Steppes
1. What is the difference between a steppe and a prairie?
While often used interchangeably, "steppe" and "prairie" can have slightly different connotations. "Steppe" generally refers to the Eurasian grasslands, while "prairie" often refers to the North American grasslands. However, both terms refer to vast, treeless grasslands with similar ecological characteristics.
2. Are the steppes a fragile ecosystem?
The steppes are resilient ecosystems, having evolved to withstand harsh conditions. However, they are also vulnerable to human activities and climate change. Overgrazing, agricultural expansion, and pollution can have significant impacts on the health of the steppes.
3. What are the benefits of protecting the steppes?
Protecting the steppes is essential for maintaining biodiversity, mitigating climate change, and preserving cultural heritage. The steppes provide valuable ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, water filtration, and habitat for countless species. They also represent a unique cultural landscape, embodying the history and traditions of nomadic cultures.
4. What are the challenges facing the steppes today?
The steppes face numerous challenges, including climate change, overgrazing, agricultural expansion, and pollution. These threats can lead to land degradation, biodiversity loss, and the displacement of nomadic communities.
5. What can be done to protect the steppes?
Protecting the steppes requires a multi-faceted approach, including establishing protected areas, implementing sustainable land management practices, engaging local communities, and promoting international cooperation. These efforts are essential for safeguarding the ecological integrity and cultural heritage of the steppes.
Tips for Understanding the Steppes
- Explore Maps: Use maps to visualize the vast expanse of the steppes and the different regions they encompass.
- Read Historical Accounts: Delve into historical accounts of nomadic cultures and their interactions with the steppes, gaining insight into their unique way of life.
- Visit a Steppe Ecosystem: If possible, visit a steppe ecosystem to witness firsthand the beauty and resilience of these grasslands.
- Support Conservation Organizations: Donate to or volunteer with organizations working to protect the steppes and their biodiversity.
Conclusion
The steppes, with their vast expanse, unique biodiversity, and rich cultural heritage, stand as a testament to the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Understanding the ecological and cultural significance of the steppes is crucial for appreciating the importance of preserving these ecosystems for future generations. By addressing the challenges facing the steppes, we can ensure the continued existence of these vital landscapes and the rich tapestry of life they support.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Steppes: A Vast Tapestry of History and Ecology. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!