The Township Map of Wisconsin: A Guide to Understanding Land Division and History
Related Articles: The Township Map of Wisconsin: A Guide to Understanding Land Division and History
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Township Map of Wisconsin: A Guide to Understanding Land Division and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Township Map of Wisconsin: A Guide to Understanding Land Division and History

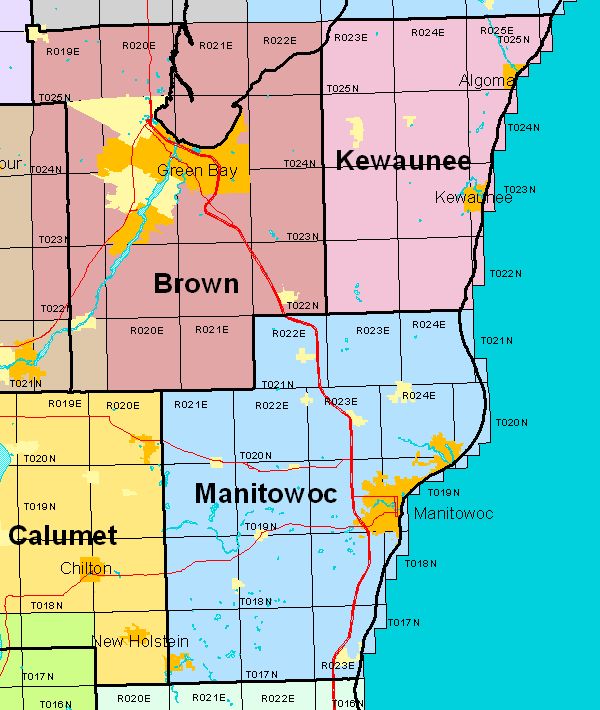
Wisconsin, known for its rolling hills, sparkling lakes, and rich history, is also a state with a unique and enduring system of land division: the township system. This system, established by the federal government in the 19th century, continues to play a significant role in land ownership, property identification, and even local governance in the state. Understanding the township map of Wisconsin is key to navigating the state’s land records, appreciating its historical development, and even appreciating the unique character of its landscape.
A Grid System of Land Division
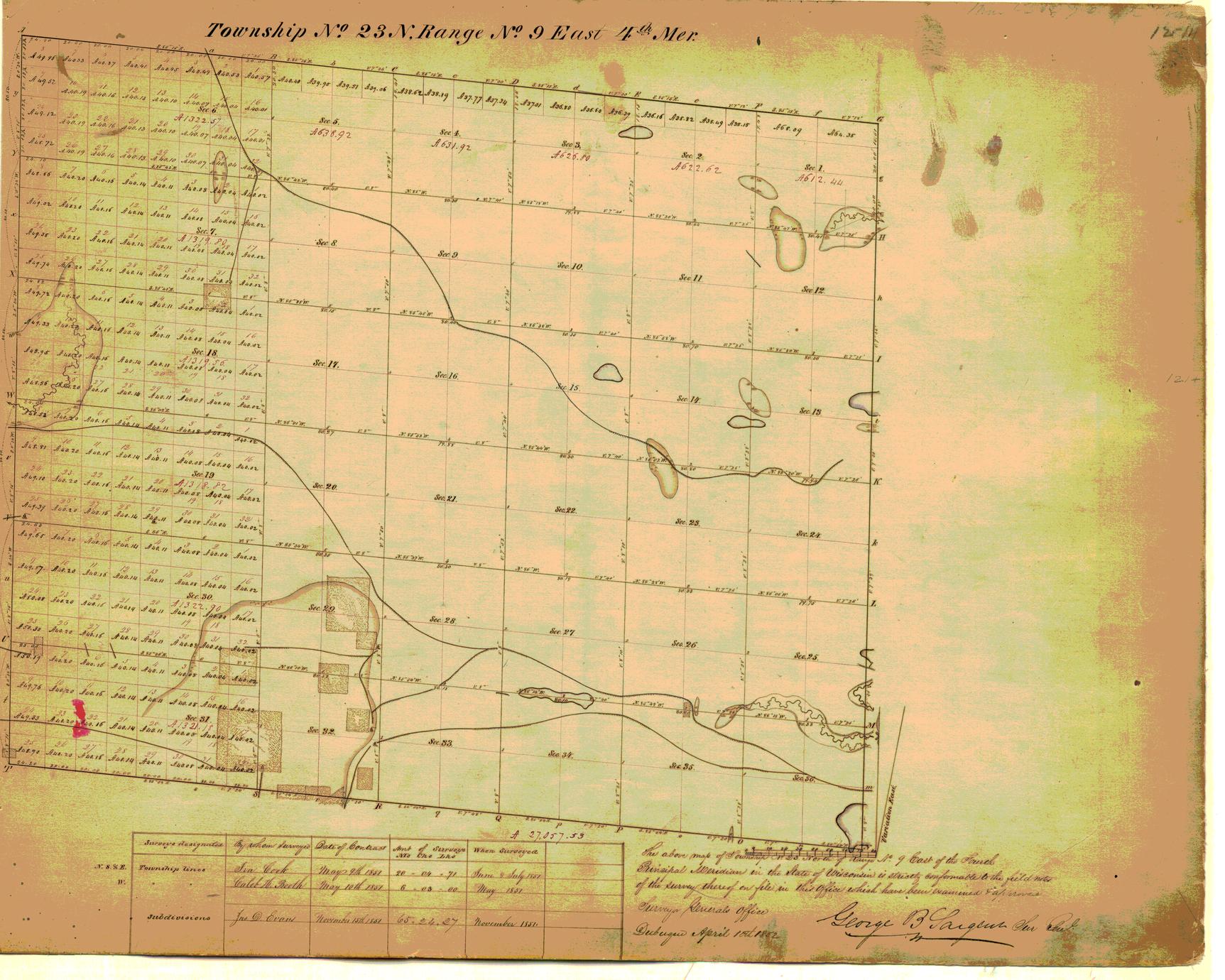
The township system is based on a grid pattern, dividing land into square sections, each measuring one mile by one mile. These sections are further divided into smaller units, creating a hierarchical structure that allows for precise identification of individual parcels of land.
The Basics of Township and Range
- Township: A township is a square area six miles by six miles, encompassing 36 square miles.
- Range: Ranges run north-south, parallel to the meridian lines, and are numbered east or west of the principal meridian.
- Section: Each township is divided into 36 sections, numbered in a specific pattern, starting in the northeast corner and moving in a serpentine pattern.
- Quarter Section: Each section can be further divided into quarter sections, with each quarter section encompassing 160 acres.
The Wisconsin Meridian and Base Line
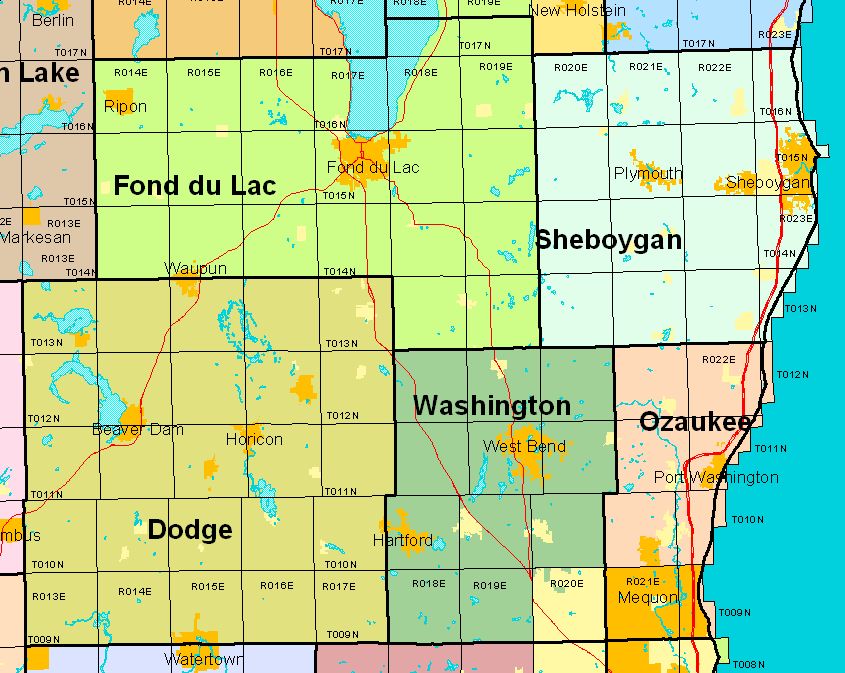
Wisconsin’s township and range system is based on the Fourth Principal Meridian and the Baseline. The Fourth Principal Meridian runs north-south through the center of Wisconsin, while the Baseline runs east-west, intersecting the meridian in the central part of the state. This intersection serves as the reference point for all townships and ranges in Wisconsin.
Navigating the Township Map
To locate a specific township on the map, one must identify the corresponding township and range numbers. For example, T2N R1E refers to Township 2 North, Range 1 East. This means the township is two townships north of the Baseline and one range east of the Fourth Principal Meridian.
The Importance of Township Maps
The township map of Wisconsin is essential for various reasons:
- Land Ownership and Property Identification: The system provides a clear and standardized way to identify and delineate property boundaries, simplifying land ownership records and transactions.
- Historical Understanding: The township system reflects the process of settlement and land allocation in Wisconsin, revealing the history of land use and development.
- Local Governance: Townships often serve as units of local government, with elected officials and administrative responsibilities. Understanding the township system helps citizens engage in local governance and understand the structure of their community.
- Property Taxes: Township maps are used to determine property tax assessments, ensuring equitable distribution of tax burdens.
- Natural Resource Management: The system provides a framework for managing and monitoring natural resources, including forests, wetlands, and wildlife habitats.
- Emergency Response: Township maps are crucial for emergency responders, enabling them to navigate effectively and locate specific locations during emergencies.
The Evolution of Township Maps
With advancements in technology, township maps have evolved from traditional paper maps to digital platforms, offering enhanced functionality and accessibility. Online mapping services provide interactive maps, allowing users to zoom in, explore specific areas, and access detailed information about each township and its sections.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of using a township map?
The township map offers a standardized and comprehensive way to identify land parcels, understand property boundaries, and navigate the state’s land records. It also provides insights into the historical development of land use and local governance.
2. How can I find the township and range of my property?
You can consult online mapping services, county records, or local land surveyors to determine the township and range of your property.
3. Are township maps still relevant in the digital age?
While digital maps offer enhanced features, the township system remains a fundamental framework for land management and identification in Wisconsin. Understanding the township map is essential for navigating land records and engaging in local governance.
4. What are some common uses of township maps?
Township maps are used for property transactions, property tax assessments, emergency response, natural resource management, and historical research.
5. How are township maps used for property transactions?
Township maps provide precise identification of property boundaries, facilitating accurate descriptions and legal transactions.
6. What are the limitations of the township system?
The township system can be rigid and may not always accurately reflect the current landscape, particularly in areas with complex land ownership patterns or significant changes in land use.
Tips
- Consult online mapping services: Explore interactive maps that allow you to zoom in, explore specific areas, and access detailed information about each township.
- Visit your local county clerk’s office: County records often contain detailed township maps and information about land ownership.
- Contact a land surveyor: A professional surveyor can help you accurately identify the township and range of your property and provide detailed property boundary information.
- Learn about the history of your township: Research the history of land use and settlement in your township to gain a deeper understanding of its development and unique characteristics.
- Engage in local governance: Attend township meetings, participate in community activities, and stay informed about local issues to contribute to the development and well-being of your community.
Conclusion
The township map of Wisconsin is a powerful tool for navigating land ownership, understanding local history, and engaging in community affairs. It offers a unique perspective on the state’s land division, revealing the intricate patterns of land use, settlement, and development that have shaped Wisconsin’s landscape and its people. By understanding the township system, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the state’s history, navigate land records with greater ease, and engage more effectively in local governance. The township map is not merely a grid of squares; it is a map that connects the past, present, and future of Wisconsin’s land and its people.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Township Map of Wisconsin: A Guide to Understanding Land Division and History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!