Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Rich Culture
Related Articles: Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Rich Culture
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Rich Culture. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Rich Culture
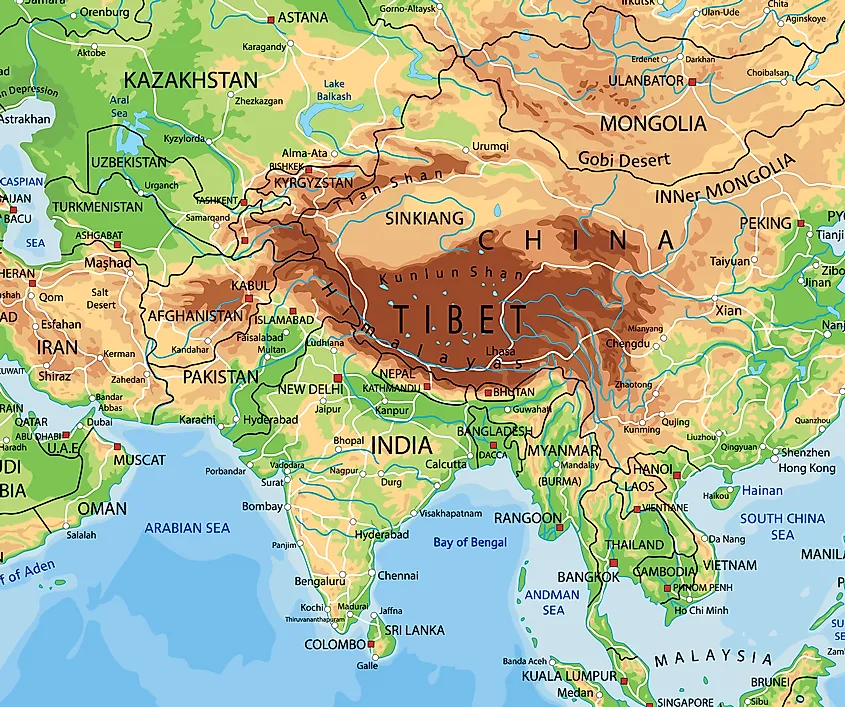
Tibet, often referred to as the "Roof of the World," occupies a prominent position on the world map, situated in the heart of Asia. Its vast and rugged terrain, characterized by towering Himalayan peaks and expansive plateaus, has shaped its unique culture, history, and ecological significance. Understanding Tibet’s geographical location and its role in the broader Asian context is crucial for appreciating its cultural, political, and environmental importance.
A Land of Extremes:
Tibet’s geographical location dictates its unique physical characteristics. It is a land of extremes, with the majority of its territory exceeding 4,000 meters (13,123 feet) in elevation. This high altitude, coupled with the harsh continental climate, creates a challenging environment for human habitation. However, it also contributes to the region’s distinctive beauty and biodiversity.
The Roof of the World:
The Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, form the southern boundary of Tibet, with Mount Everest, the tallest peak on Earth, standing proudly on the border with Nepal. This towering mountain range plays a significant role in shaping Tibet’s climate, acting as a natural barrier that blocks moisture-laden winds from the south. This creates a dry, arid environment in the Tibetan Plateau.
The Tibetan Plateau:
The Tibetan Plateau, the largest and highest plateau on Earth, covers the majority of Tibet’s territory. Its vast expanse, characterized by rolling grasslands, alpine meadows, and sparse vegetation, supports a unique ecosystem adapted to the extreme conditions. The plateau’s elevation and its unique geological features make it a crucial water source for major rivers in Asia, including the Yangtze, Yellow, Indus, Mekong, and Brahmaputra.
Cultural Significance:
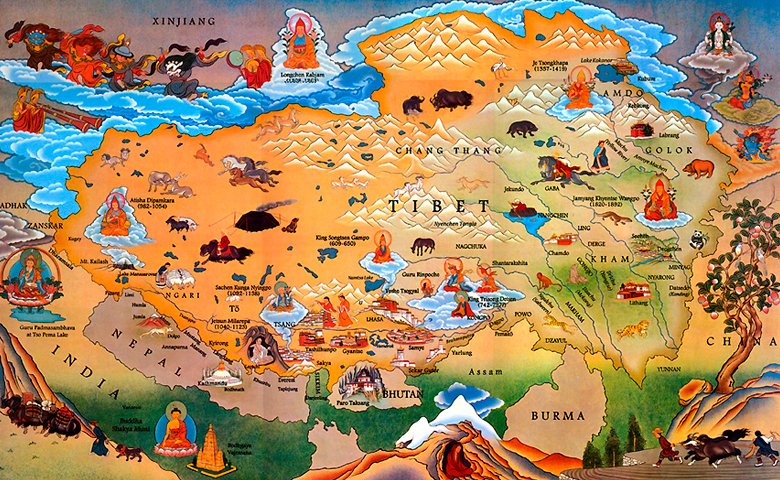
Tibet’s cultural significance extends far beyond its geographical boundaries. Tibetan Buddhism, a major branch of Buddhism that originated in Tibet, has a profound influence on the spiritual lives of millions of people across Asia. The region is also renowned for its rich artistic traditions, including intricate Thangka paintings, powerful prayer flags, and vibrant religious ceremonies.
Historical Importance:
Tibet’s history is intertwined with the histories of its neighboring countries, including China, India, and Nepal. The region has played a crucial role in trade and cultural exchange throughout the centuries, serving as a bridge between these powerful civilizations. Tibet’s strategic location has also made it a focal point of geopolitical tension, particularly in the 20th and 21st centuries.
Ecological Importance:
Tibet’s ecological significance is immense. The Tibetan Plateau acts as a "water tower" for Asia, providing water for millions of people downstream. Its unique ecosystem supports a diverse range of plant and animal species, including the endangered snow leopard, Tibetan antelope, and red panda. However, climate change and environmental degradation threaten this delicate ecosystem, highlighting the need for sustainable development practices in the region.
Geopolitical Context:
Tibet’s geopolitical context is complex and often contentious. The region is currently administered by China, which asserts its sovereignty over Tibet. However, many Tibetans advocate for greater autonomy or independence, leading to ongoing political tensions. The international community has expressed concerns about human rights and cultural preservation in Tibet, adding further complexity to the region’s political landscape.
Understanding Tibet’s Importance:
Tibet’s significance extends beyond its geographical location and physical characteristics. It is a region of immense cultural, historical, and ecological importance, playing a vital role in the broader Asian context. Its unique culture, rich history, and fragile ecosystem demand global attention and understanding.
FAQs about Tibet:
1. What is the geographical location of Tibet?
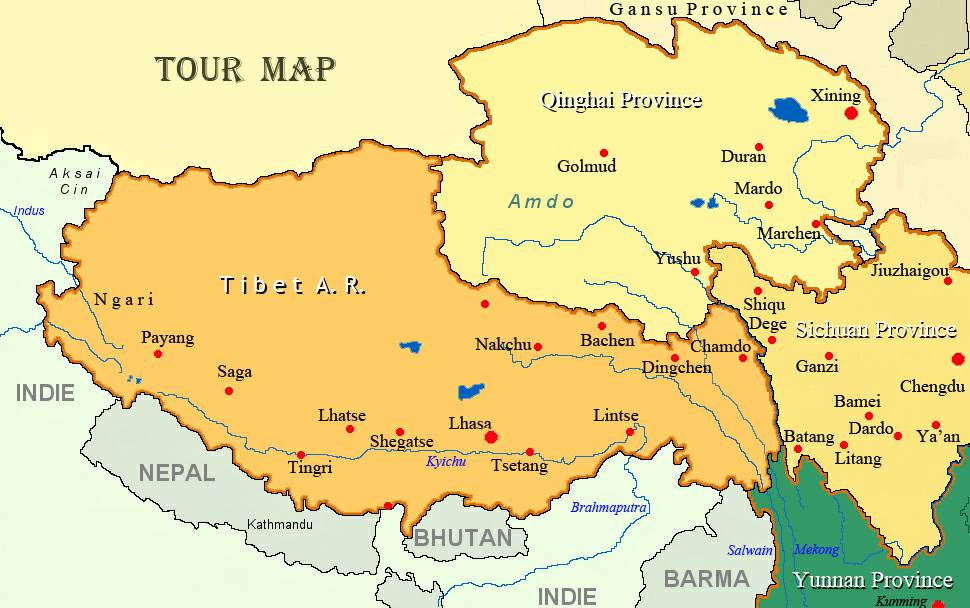
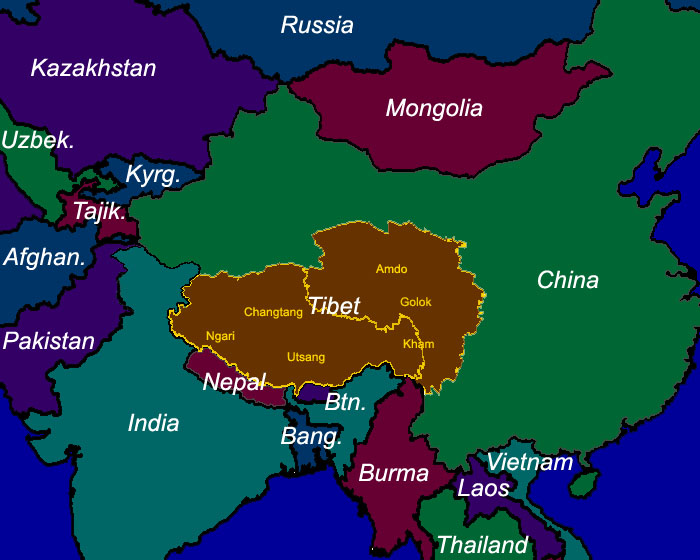
Tibet is located in the southwest of China, bordering Nepal, India, Bhutan, and Myanmar. It is situated on the Tibetan Plateau, the largest and highest plateau on Earth.
2. What are the major geographical features of Tibet?
Tibet is characterized by the towering Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, and the vast Tibetan Plateau. Its high altitude and harsh climate create a unique environment for human habitation and biodiversity.
3. What is the cultural significance of Tibet?
Tibet is the birthplace of Tibetan Buddhism, a major branch of Buddhism with a profound influence on the spiritual lives of millions of people across Asia. The region is also renowned for its rich artistic traditions, including intricate Thangka paintings and powerful prayer flags.
4. What is the historical significance of Tibet?
Tibet has a rich history, playing a crucial role in trade and cultural exchange between China, India, and Nepal. Its strategic location has also made it a focal point of geopolitical tension throughout history.
5. What is the ecological significance of Tibet?
The Tibetan Plateau acts as a "water tower" for Asia, providing water for major rivers like the Yangtze, Yellow, and Indus. Its unique ecosystem supports a diverse range of plant and animal species, highlighting its crucial role in regional biodiversity.
6. What are the current geopolitical issues surrounding Tibet?
Tibet is currently administered by China, which asserts its sovereignty over the region. However, many Tibetans advocate for greater autonomy or independence, leading to ongoing political tensions. The international community has expressed concerns about human rights and cultural preservation in Tibet.
7. What is the future of Tibet?
The future of Tibet remains uncertain, with ongoing political tensions and concerns about environmental sustainability. However, understanding the region’s cultural, historical, and ecological importance is crucial for finding sustainable solutions that benefit both the Tibetan people and the broader Asian region.
Tips for Understanding Tibet:
- Learn about Tibetan Buddhism: Explore the teachings and practices of Tibetan Buddhism to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s spiritual and cultural heritage.
- Read about Tibetan history: Delve into the rich history of Tibet, exploring its interactions with neighboring civilizations and its unique cultural development.
- Learn about the Tibetan Plateau: Understand the unique environmental challenges and ecological importance of the Tibetan Plateau, recognizing its role in regional water resources and biodiversity.
- Engage with Tibetan culture: Explore Tibetan art, music, and literature to gain a deeper appreciation for the region’s cultural richness and diversity.
- Stay informed about current events: Follow news and developments regarding Tibet to understand the ongoing political and social challenges facing the region.
Conclusion:
Tibet’s position on the world map is not merely a geographical marker; it signifies a region of immense cultural, historical, and ecological significance. Understanding the unique challenges and opportunities facing Tibet is crucial for navigating the complexities of the region and contributing to its sustainable development. By recognizing its importance and engaging with its diverse culture, we can foster a deeper understanding of this remarkable land and its vital role in the broader Asian context.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Rich Culture. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!