Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Look at the Political Map of Eastern Europe
Related Articles: Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Look at the Political Map of Eastern Europe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Look at the Political Map of Eastern Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Look at the Political Map of Eastern Europe
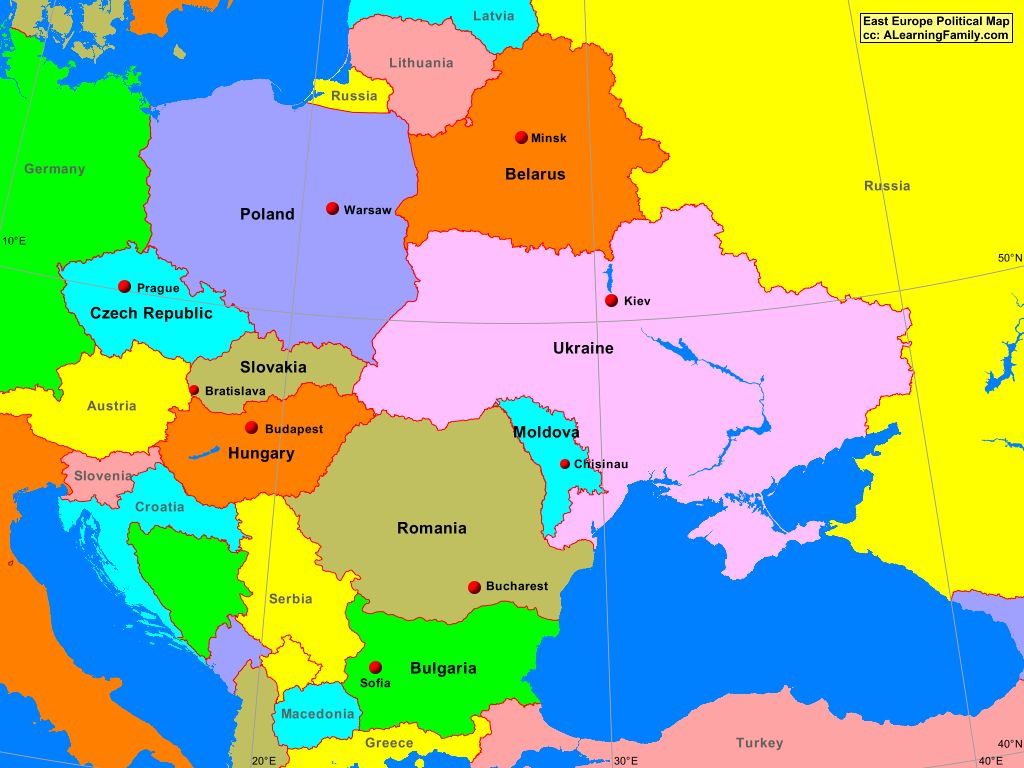
Eastern Europe, a region historically defined by its cultural, linguistic, and political ties to Russia, has undergone significant transformations in the past few decades. The fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 ushered in a new era, characterized by the emergence of independent states and the redefinition of regional power dynamics. Examining the political map of Eastern Europe offers a valuable lens through which to understand these changes and their lasting impact on the region.
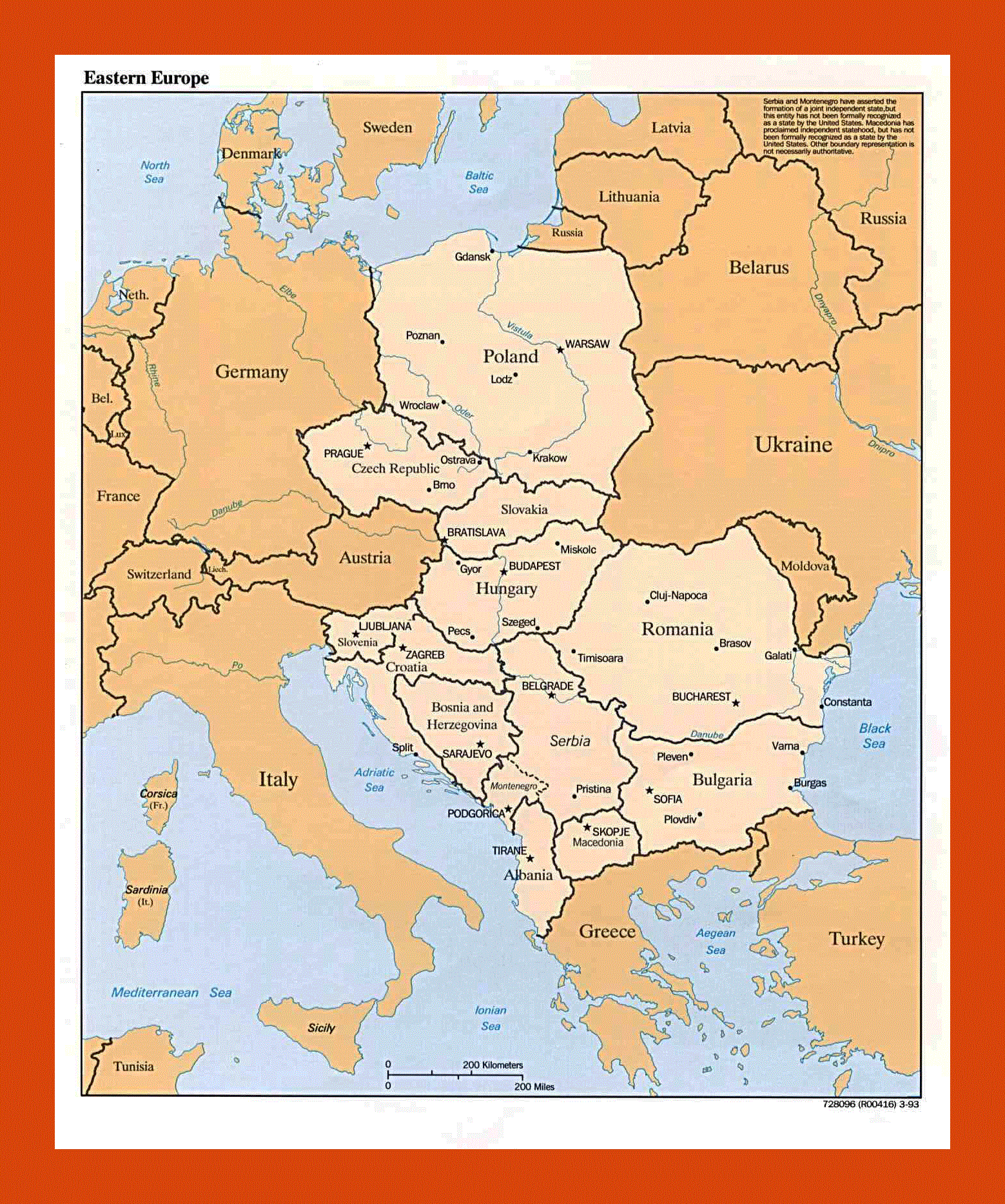
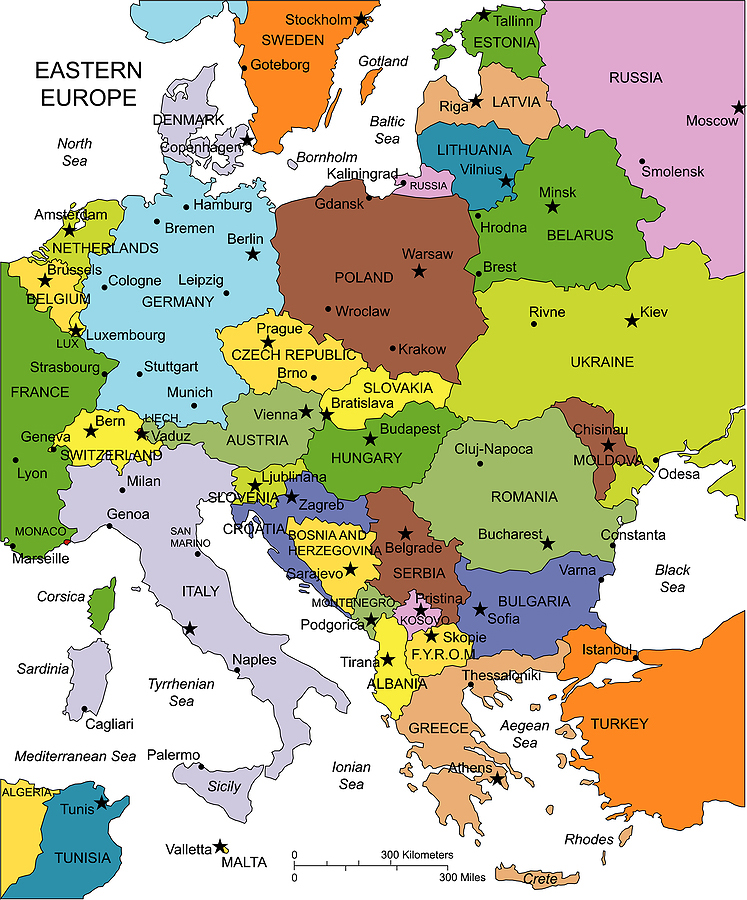
Defining Eastern Europe: A Complex Geography
The geographical boundaries of Eastern Europe are fluid and subject to debate. While traditionally encompassing countries like Poland, Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria, and the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania), the inclusion of countries like Slovakia, Czech Republic, Hungary, and even parts of Germany, depending on the context, further complicates the definition.
The Legacy of the Soviet Union:
The Soviet Union’s influence on the political landscape of Eastern Europe was profound. The region was largely integrated into a centralized system, with Moscow exercising significant control over political, economic, and social life. This resulted in a homogenous political structure dominated by communist parties and a standardized economic system based on central planning.
The Collapse and its Aftermath:
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to a rapid transformation of the region’s political map. The once monolithic Soviet bloc fragmented into independent states, each embarking on its own path of political and economic development.
The Emergence of New Political Systems:
The post-Soviet era witnessed the rise of diverse political systems in Eastern Europe. While many countries transitioned to democratic models, the process was not without challenges. Some states experienced periods of instability and political upheaval, while others struggled to establish strong democratic institutions and a free market economy.
The European Union’s Influence:
The European Union (EU) played a significant role in shaping the political landscape of Eastern Europe. The prospect of EU membership incentivized democratic reforms and economic liberalization in many countries. EU membership provided access to a larger market, financial assistance, and political stability, attracting several Eastern European states to join the bloc.
The Role of Russia:
Despite the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia continued to exert significant influence on the region. Its economic and military power, coupled with historical and cultural ties, allowed Russia to maintain influence over its former satellite states. This influence, however, has been met with resistance from the West, leading to ongoing tensions and geopolitical competition.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Eastern Europe faces numerous challenges, including economic disparities, corruption, social inequality, and the enduring legacy of Soviet-era infrastructure. However, the region also presents significant opportunities for growth and development. The integration of Eastern European economies into the global market has fueled economic growth, while the region’s young and increasingly educated population offers a source of innovation and talent.
The Political Map Today: A Diverse Landscape
The political map of Eastern Europe today reflects a diverse landscape of political systems, economic structures, and social realities.
- The European Union: Countries like Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania are members of the EU, benefiting from its economic and political integration.
- The Post-Soviet Bloc: Countries like Ukraine, Belarus, and Moldova remain outside the EU and continue to grapple with the legacy of Soviet rule.
- Russia’s Influence: Russia continues to exert influence on the region, particularly in Belarus and Ukraine, through political and economic ties.
Navigating the Future:
The political map of Eastern Europe is constantly evolving, shaped by internal and external factors. The region’s future will depend on its ability to address its challenges, leverage its opportunities, and navigate the complex geopolitical landscape.
Understanding the Political Map: Importance and Benefits
Analyzing the political map of Eastern Europe provides valuable insights into:
- Regional Dynamics: It reveals the interplay of political forces, economic interests, and historical legacies that shape the region’s development.
- Geopolitical Significance: The region’s strategic location between Russia and the West makes it a key player in global affairs.
- Economic Opportunities: Understanding the region’s political landscape is crucial for businesses looking to invest and expand into the Eastern European market.
- Social and Cultural Developments: The political map reflects the diverse social and cultural identities that shape the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the key factors that influence the political map of Eastern Europe?
The political map of Eastern Europe is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Historical Legacy: The region’s history under Soviet rule and its subsequent transition to independence have shaped its political landscape.
- Geopolitical Location: Eastern Europe’s strategic location between Russia and the West makes it a focal point of geopolitical competition.
- Economic Development: The region’s economic performance, particularly its integration into the global market, influences its political stability and direction.
- Social and Cultural Factors: The diverse social and cultural identities within the region contribute to its political dynamics.
2. How does the European Union influence the political map of Eastern Europe?
The European Union has played a significant role in shaping the political landscape of Eastern Europe by:
- Promoting Democracy: EU membership incentivizes democratic reforms and the establishment of strong institutions.
- Enhancing Economic Integration: EU membership provides access to a larger market, financial assistance, and economic stability.
- Strengthening Political Stability: EU membership strengthens political stability by promoting cooperation and dialogue between member states.
3. What are the challenges faced by Eastern European countries?
Eastern European countries face numerous challenges, including:
- Economic Disparities: The region experiences significant economic disparities, with some countries struggling to achieve sustainable economic growth.
- Corruption: Corruption remains a significant problem in many countries, hindering economic development and undermining public trust in institutions.
- Social Inequality: Social inequality persists in many countries, with disparities in income, access to healthcare, and education.
- The Legacy of Soviet Rule: The region continues to grapple with the legacy of Soviet-era infrastructure, political systems, and social norms.
4. What are the opportunities for growth and development in Eastern Europe?
Eastern Europe presents significant opportunities for growth and development, including:
- Economic Integration: The region’s integration into the global market has fueled economic growth and attracted foreign investment.
- Young and Educated Population: The region has a young and increasingly educated population, offering a source of innovation and talent.
- Technological Advancements: Eastern European countries are increasingly embracing technological advancements, driving innovation and economic growth.
5. What are the implications of Russia’s influence on the political map of Eastern Europe?
Russia’s influence on the political map of Eastern Europe is a complex and contentious issue. It has led to:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Russia’s influence in the region has created tensions with the West, particularly over Ukraine and other former Soviet republics.
- Economic Leverage: Russia uses its economic power to influence political decisions in countries like Belarus and Ukraine.
- Cultural and Historical Ties: Russia maintains strong cultural and historical ties with many Eastern European countries, which it uses to exert influence.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of Eastern Europe
- Stay Informed: Follow news and developments in the region through reputable sources.
- Learn about History: Understanding the region’s history, particularly the Soviet era, is crucial to understanding its current political landscape.
- Consider Geopolitical Factors: Analyze the region’s location and its strategic importance in global affairs.
- Examine Economic Trends: Pay attention to economic developments, including trade patterns, investment flows, and growth rates.
- Engage with Diverse Perspectives: Seek out different perspectives on the region’s political issues to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
The political map of Eastern Europe is a dynamic and evolving landscape shaped by a complex interplay of historical, geopolitical, economic, and social factors. Understanding the region’s political dynamics is essential for comprehending its current challenges and opportunities, navigating its complex geopolitical landscape, and engaging with its diverse social and cultural identities.
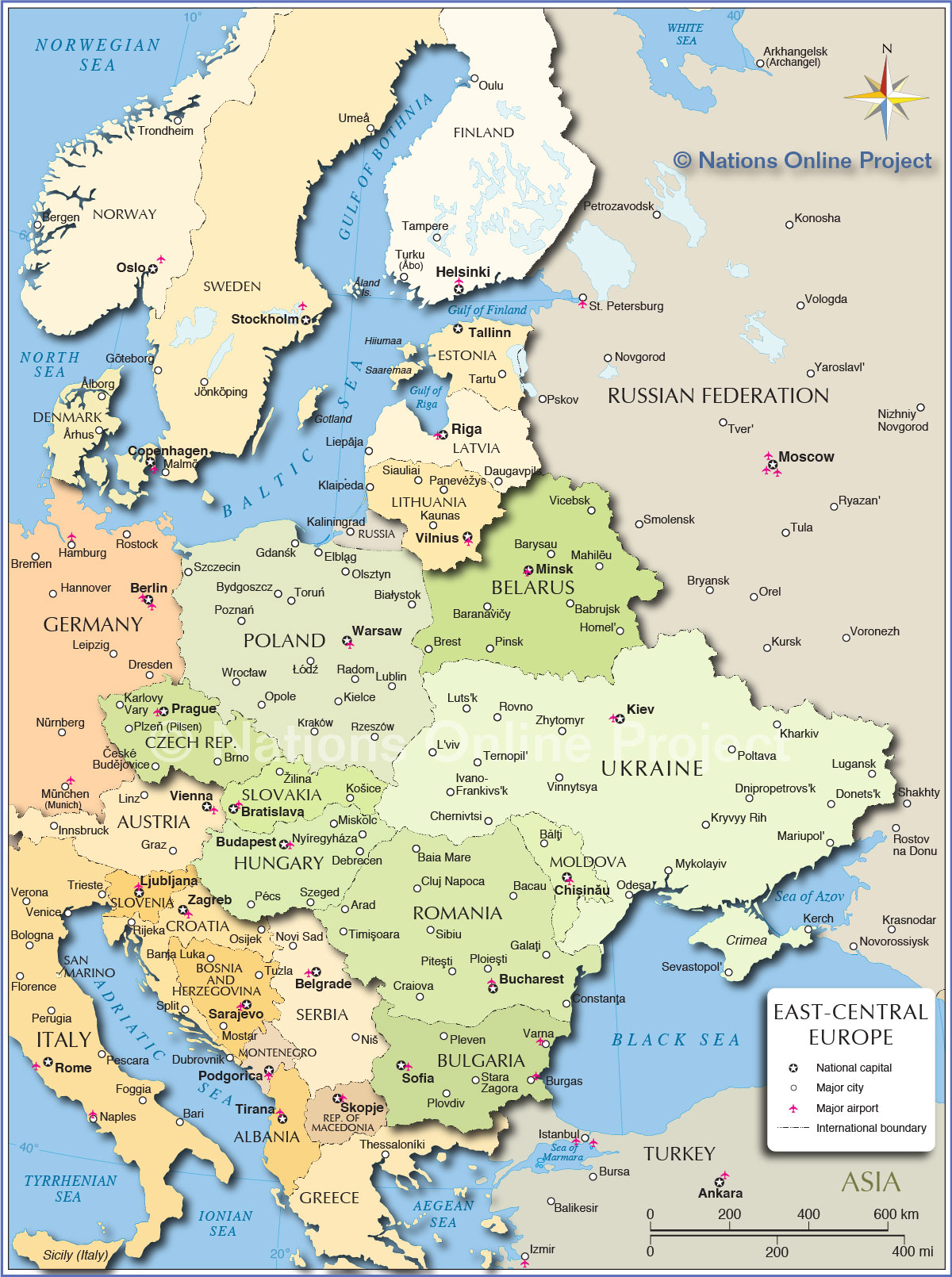
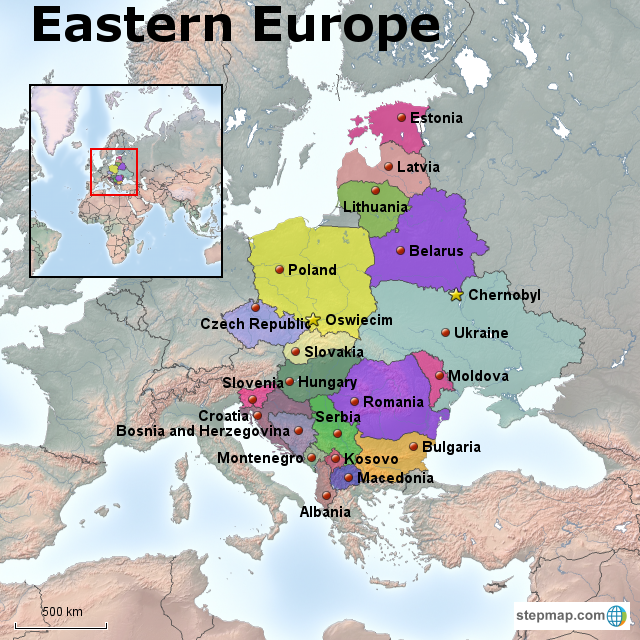
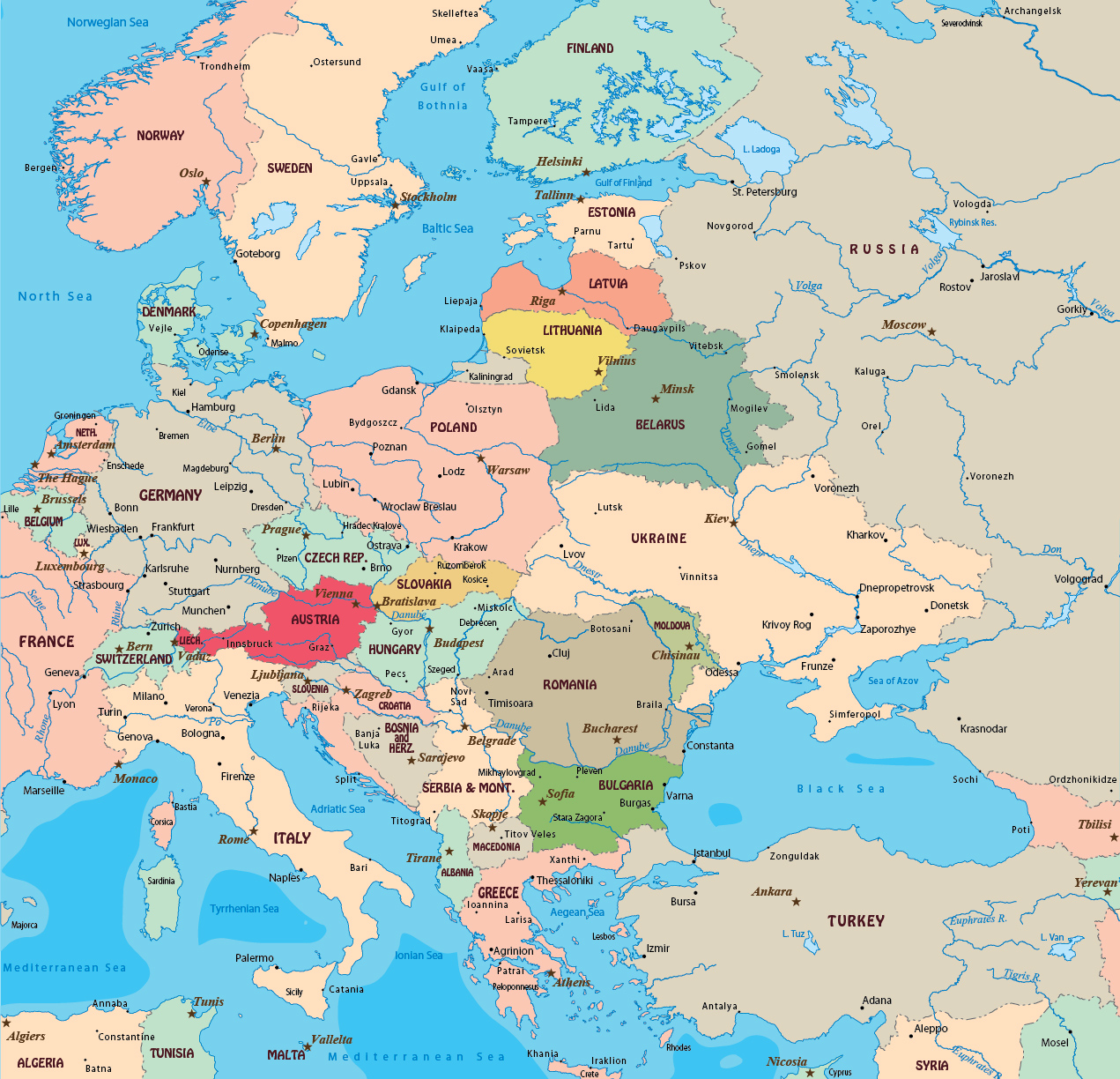


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Look at the Political Map of Eastern Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!