Unraveling the Grid: Prime Meridian and Equator in Mapping
Related Articles: Unraveling the Grid: Prime Meridian and Equator in Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Grid: Prime Meridian and Equator in Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Grid: Prime Meridian and Equator in Mapping
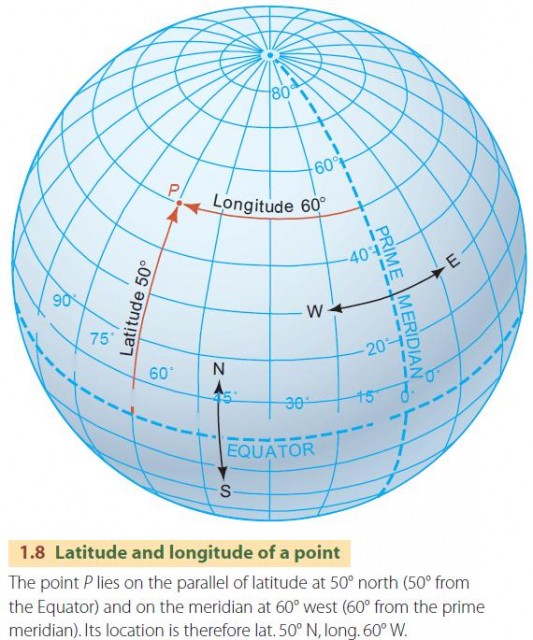
The Earth, a vast and dynamic sphere, presents a challenge for navigating its surface. To effectively chart locations and understand spatial relationships, a system of reference lines is essential. This system, known as the geographic coordinate system, relies on two fundamental lines: the prime meridian and the equator.
The Prime Meridian: Dividing the Earth Longitudinally
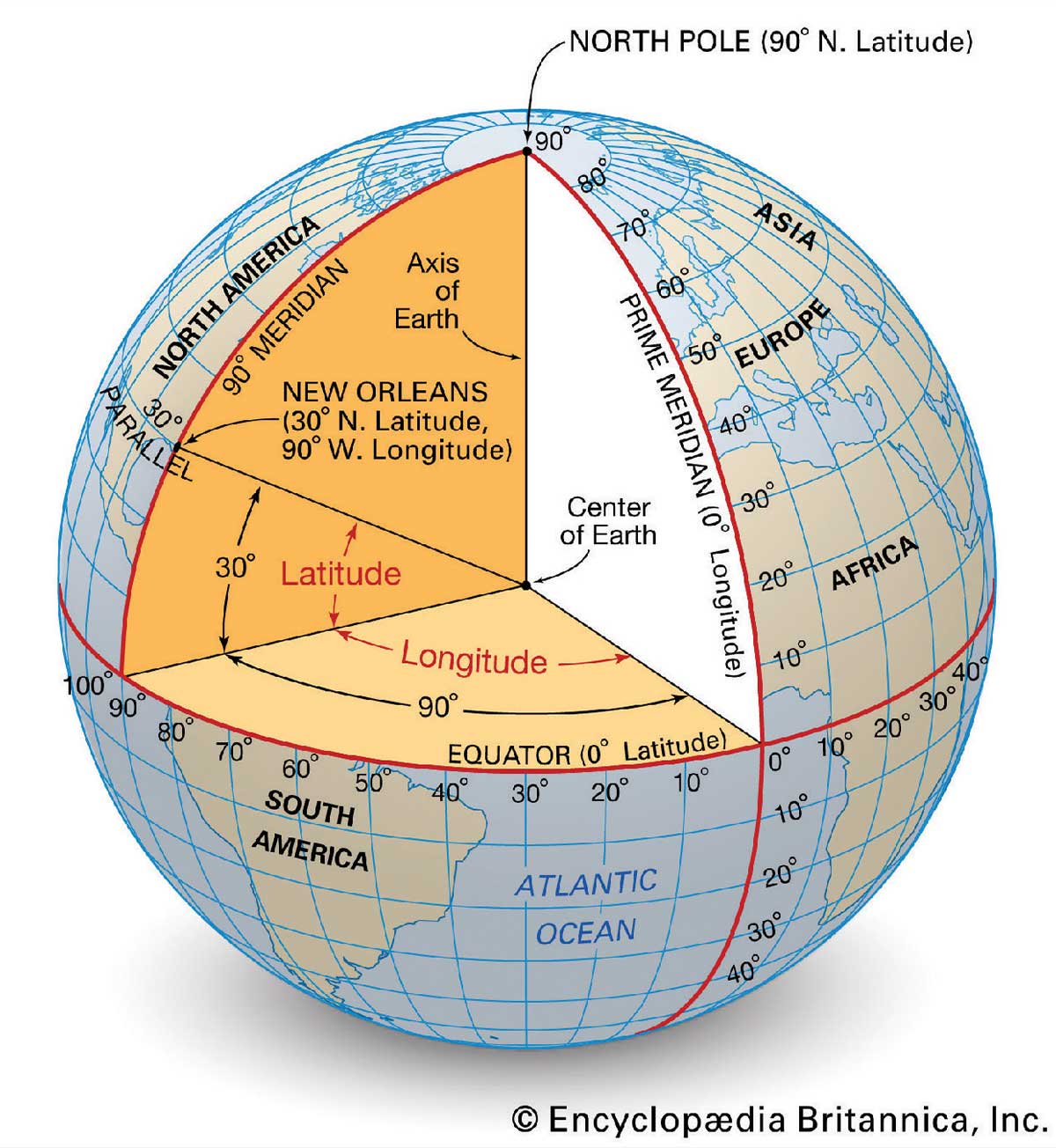
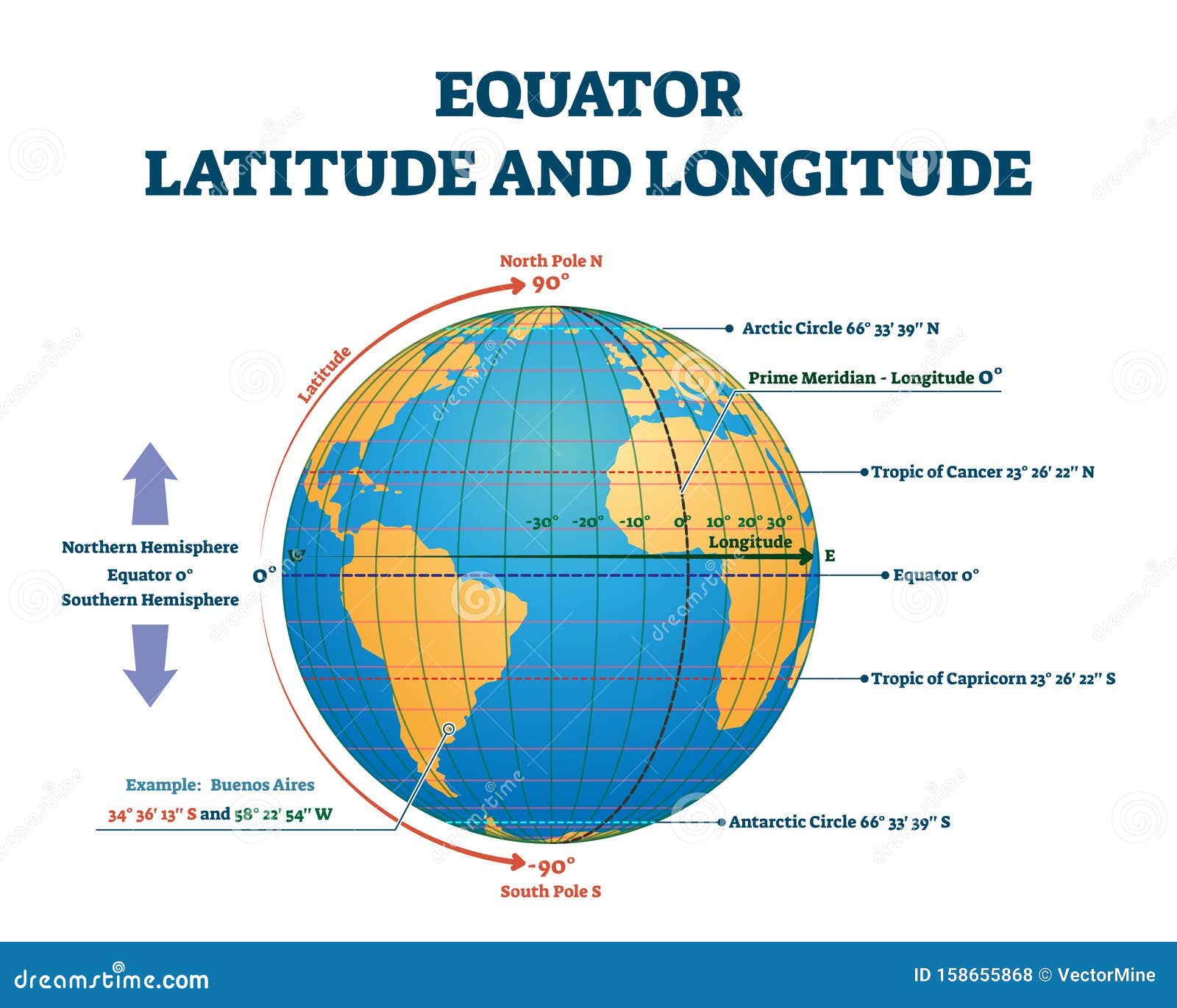
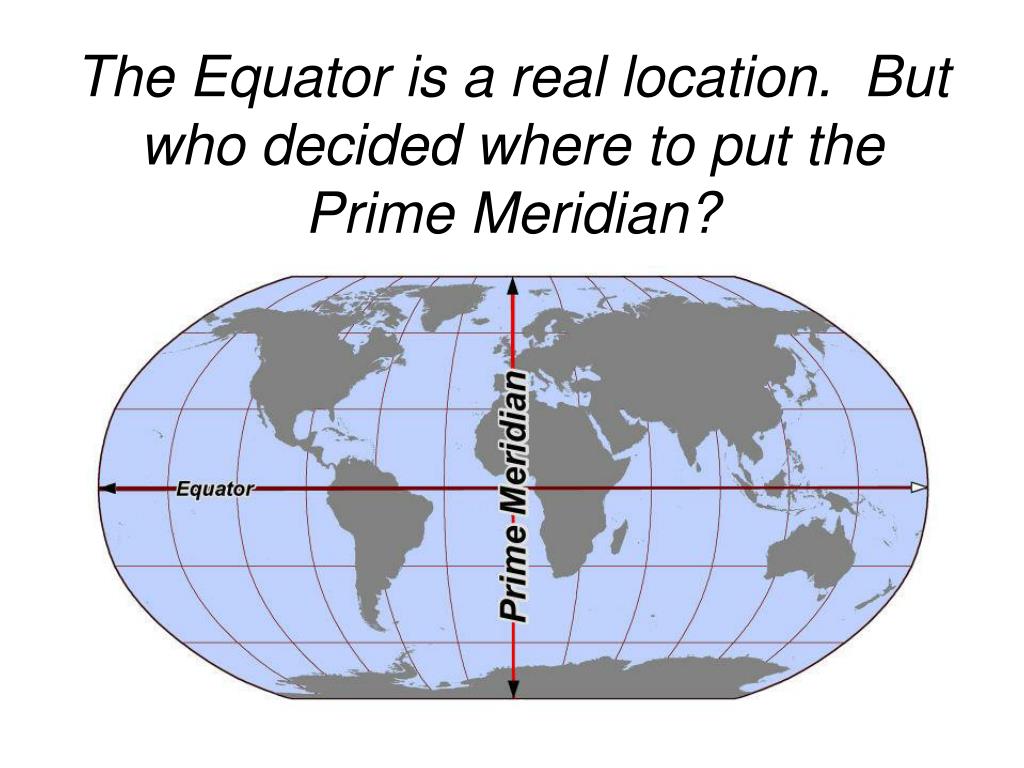
The prime meridian, often referred to as the zero meridian, is an imaginary line that circles the Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole, dividing the globe into two hemispheres: the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere. It serves as the starting point for measuring longitude, which is the angular distance, measured in degrees, east or west of the prime meridian.
The Equator: Dividing the Earth Latitudinally
The equator, another imaginary line, circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, equidistant from the North and South Poles. It divides the globe into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. This line is crucial for measuring latitude, the angular distance, measured in degrees, north or south of the equator.
The Interplay of Prime Meridian and Equator: A Grid for the World
Together, the prime meridian and equator form the foundation of a global grid system. This grid, composed of lines of longitude and latitude, enables the precise location of any point on Earth. Each point can be uniquely identified by its latitude and longitude coordinates, similar to an address on a map.
Historical Evolution of the Prime Meridian
The concept of a prime meridian predates modern cartography. Ancient civilizations, including the Greeks and Romans, recognized the need for a reference point for establishing direction and measuring distances. However, the location of the prime meridian varied throughout history.
In the 19th century, with the advent of global trade and communication, the need for a universally accepted prime meridian became increasingly important. In 1884, at the International Meridian Conference in Washington, D.C., delegates from 25 nations agreed to adopt the Greenwich Meridian as the prime meridian. This meridian passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, a significant center for astronomical observation at the time.
The Significance of the Prime Meridian and Equator
The prime meridian and equator play a pivotal role in various fields, including:
- Navigation: By providing a reference frame for measuring longitude and latitude, these lines are crucial for accurate navigation, both on land and at sea.
- Cartography: The grid system formed by these lines is the foundation of all maps, enabling the representation of the Earth’s surface on a two-dimensional plane.
- Time Zones: The prime meridian serves as the basis for the international system of time zones, with each time zone spanning 15 degrees of longitude.
- Scientific Research: The prime meridian and equator facilitate scientific research in fields like astronomy, geology, and meteorology, enabling the study of global phenomena.
FAQs on Prime Meridian and Equator
1. Why is the Greenwich Meridian the prime meridian?
The Greenwich Meridian was chosen as the prime meridian due to its historical significance as the location of the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. This observatory was a leading center for astronomical observation, and its meridian was widely used as a reference point for navigation.
2. Are there any other proposed prime meridians?
While the Greenwich Meridian is universally accepted, there have been alternative proposals throughout history. Some nations, such as France, initially advocated for using their own meridians as the prime meridian. However, the international consensus on the Greenwich Meridian remains strong.
3. How is the equator important for climate?
The equator plays a crucial role in shaping global climate patterns. Its location at 0 degrees latitude means it receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to high temperatures and significant rainfall. This region experiences the tropical climate characterized by high humidity, dense vegetation, and biodiversity.
4. Can the prime meridian and equator change their positions?
The prime meridian and equator are fixed lines based on the Earth’s rotation and its shape. Their positions are not subject to change, although the Earth’s crust experiences slow movements over geological time scales.
5. How do the prime meridian and equator impact satellite navigation?
The prime meridian and equator are fundamental to satellite navigation systems like GPS. Satellites orbit the Earth in specific paths determined by their latitude and longitude coordinates. This system enables accurate location tracking and navigation using satellite signals.
Tips for Understanding Prime Meridian and Equator
- Visualize the Earth as a globe: Understanding the three-dimensional nature of the Earth helps grasp the concept of lines of longitude and latitude.
- Use online tools: Interactive maps and globes can provide a dynamic visualization of the prime meridian, equator, and their relationship to locations on Earth.
- Explore historical maps: Examining historical maps can illustrate the evolution of prime meridian choices and their impact on cartography.
- Connect with real-world examples: Observe how the prime meridian and equator are used in everyday life, such as in news reports, weather maps, and travel itineraries.
Conclusion
The prime meridian and equator are fundamental elements of the geographic coordinate system, providing a framework for understanding the Earth’s spatial relationships. Their importance extends to various fields, including navigation, cartography, time zones, and scientific research. By recognizing the significance of these lines, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of our planet and the systems that enable us to navigate and understand its vastness.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Grid: Prime Meridian and Equator in Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!