Unraveling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar Maps
Weather, an ever-present force shaping our lives, is a complex and dynamic system. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for ensuring safety, planning activities, and making informed decisions. One of the most powerful tools for deciphering the atmospheric puzzle is weather radar. This sophisticated technology, using radio waves to detect precipitation, has revolutionized our ability to predict and track storms, providing invaluable insights into the ever-changing skies above.
The Power of Radar: Unveiling the Invisible
Radar, an acronym for Radio Detection and Ranging, works by emitting radio waves that bounce off objects in their path. Weather radars specifically target precipitation, such as rain, snow, hail, and even dust storms. The reflected signals, known as echoes, are then analyzed to determine the location, intensity, and type of precipitation.
Deciphering the Map: A Visual Guide to Weather Events
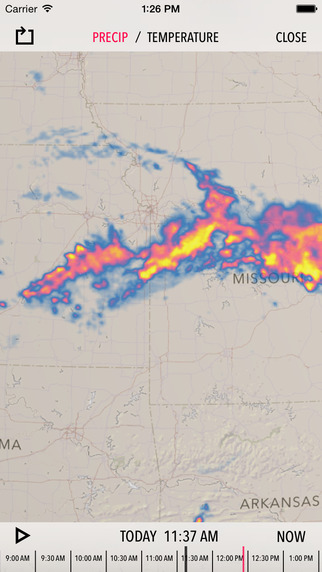
Weather radar maps, often displayed on television screens, websites, and mobile apps, offer a visual representation of precipitation across a specific region. These maps are typically color-coded, with different shades representing varying levels of precipitation intensity. The intensity is often measured in terms of reflectivity, a measure of how strongly the radio waves are reflected back to the radar. Higher reflectivity values indicate heavier precipitation.
Dissecting the Details: Understanding Key Features
1. Location and Movement: Weather radar maps clearly depict the location of precipitation, allowing users to identify areas currently experiencing rain, snow, or other weather events. Furthermore, the movement of precipitation patterns can be tracked over time, providing insights into storm progression and potential impacts.
2. Intensity and Type: Color variations on the map represent different levels of precipitation intensity. This information is crucial for assessing the severity of a storm and its potential hazards. Additionally, some radar systems can differentiate between rain, snow, hail, and other precipitation types, enhancing the accuracy of weather forecasts.
3. Storm Cells and Fronts: Radar maps often display individual storm cells, areas of concentrated precipitation, and weather fronts, boundaries between air masses with different temperatures and moisture content. These features provide vital information about storm structure and potential for severe weather events.
4. Doppler Radar and Wind Velocity: Doppler radar, a specialized type of weather radar, can detect the movement of precipitation particles and calculate wind speeds. This information is critical for identifying potentially dangerous weather phenomena, such as tornadoes and strong winds.
Benefits of Weather Radar: Empowering Informed Decisions
Weather radar maps provide a wealth of information that empowers individuals and organizations to make informed decisions in a variety of contexts:
1. Public Safety: Radar data is vital for issuing timely warnings of severe weather events, such as tornadoes, flash floods, and heavy snowfall. This allows emergency responders and the public to take necessary precautions, minimizing potential risks.
2. Transportation: Weather radar maps help airlines, shipping companies, and road transportation agencies plan routes, avoid hazardous weather conditions, and ensure the safety of passengers and cargo.
3. Agriculture: Farmers rely on radar data to monitor rainfall patterns and make informed decisions about irrigation, planting, and harvesting. This helps optimize crop yields and protect against weather-related losses.
4. Energy Production: Weather radar maps are crucial for utilities, particularly those involved in renewable energy sources like wind and solar power. They provide insights into wind patterns and cloud cover, optimizing energy generation and ensuring grid stability.
5. Research and Forecasting: Scientists use weather radar data to study atmospheric processes, improve weather forecasting models, and develop innovative technologies for weather prediction and mitigation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the limitations of weather radar?
A: Weather radar has limitations, primarily due to its reliance on radio waves. It may struggle to detect very light precipitation or precipitation in areas with heavy clutter, such as mountains or dense urban environments. Additionally, radar signals can be affected by atmospheric conditions, leading to potential inaccuracies in data interpretation.
Q: How accurate are weather radar maps?
A: Weather radar maps provide a valuable tool for understanding weather patterns, but they are not perfect. Accuracy is influenced by factors such as radar technology, data processing, and the complexity of atmospheric conditions. However, advancements in radar technology and data analysis have significantly improved accuracy over time.
Q: What are the different types of weather radar?
A: There are various types of weather radar, including:
- Traditional Radar: This type of radar measures precipitation intensity and location.
- Doppler Radar: Doppler radar measures the movement of precipitation particles, providing information about wind speed and direction.
- Dual-Polarization Radar: This advanced technology can differentiate between different types of precipitation, such as rain, snow, and hail, enhancing the accuracy of weather forecasts.
Tips for Utilizing Weather Radar Maps Effectively
- Understand the color scale: Familiarize yourself with the color-coding system used by your chosen weather radar map provider. Different shades represent different levels of precipitation intensity.
- Consider the time delay: Radar data is typically displayed with a slight time delay, as it takes time for the signals to travel back to the radar and be processed.
- Cross-reference with other data sources: Combine radar data with other weather information, such as satellite imagery, surface observations, and weather forecasts, for a more comprehensive understanding of weather conditions.
- Be aware of limitations: Recognize that weather radar has limitations and may not always provide a completely accurate picture of weather events.
- Stay informed: Keep up to date on weather forecasts and warnings issued by reputable sources, such as the National Weather Service.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Weather Awareness
Weather radar technology has revolutionized our ability to understand and predict weather events. By providing real-time information on precipitation location, intensity, and movement, weather radar maps empower individuals, organizations, and researchers to make informed decisions, enhancing safety, planning, and preparedness. As technology continues to advance, weather radar is poised to play an even more significant role in our understanding and management of the ever-changing world of weather.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/radsfcus_exp_new21-58b740193df78c060e192d43.gif)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Radar Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!