Unraveling the Tapestry of Australia’s Physical Features
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Australia’s Physical Features
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Australia’s Physical Features. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Australia’s Physical Features

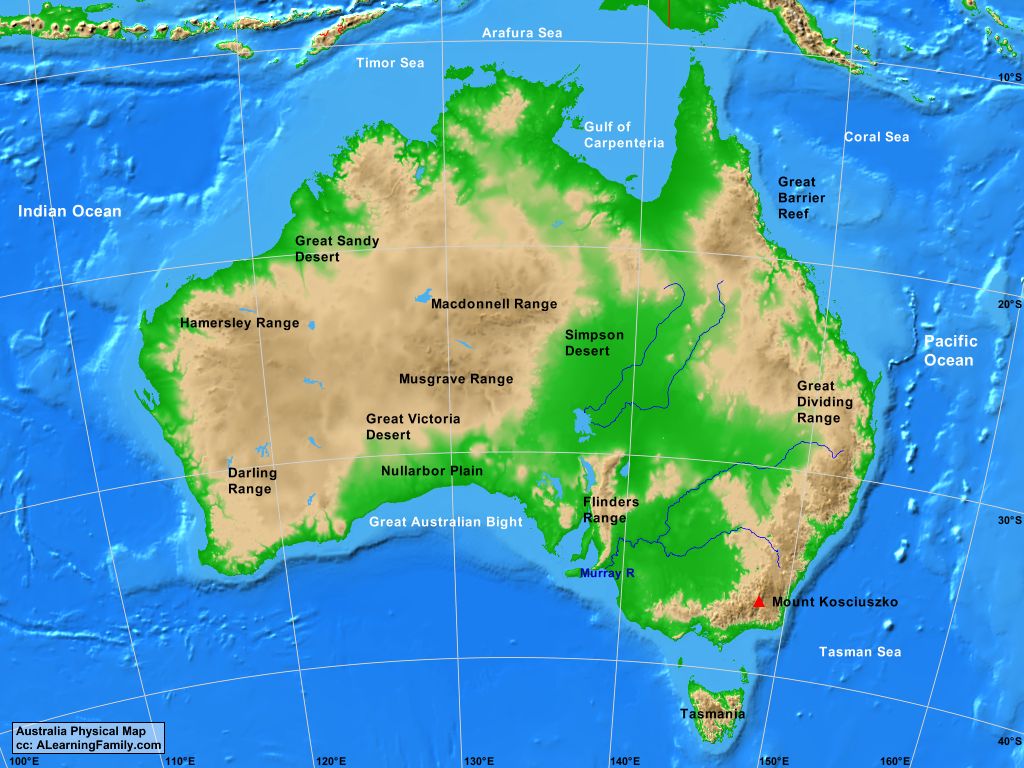
Australia, the world’s largest island and smallest continent, boasts a landscape of remarkable diversity. From the rugged peaks of the Great Dividing Range to the vast, arid expanse of the Outback, the Australian continent reveals a captivating tapestry of physical features. Understanding these features is crucial for appreciating the country’s unique natural heritage, its diverse ecosystems, and the challenges and opportunities they present.
A Mosaic of Landforms:
The Australian landscape is a mosaic of diverse landforms, shaped by a complex interplay of geological forces and climatic influences.
-
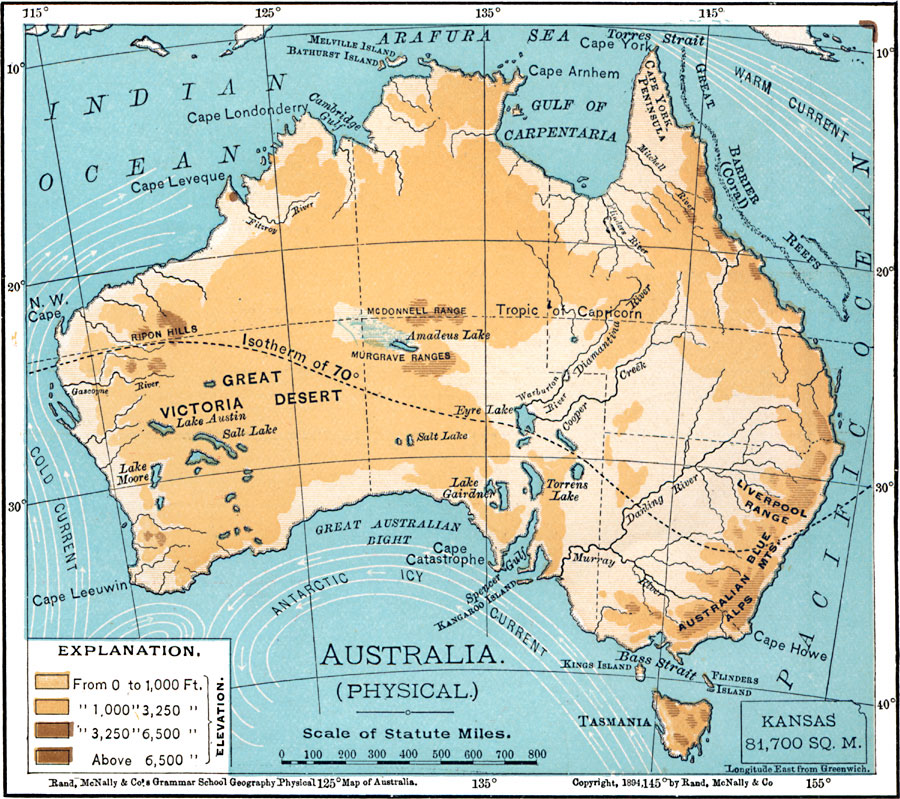
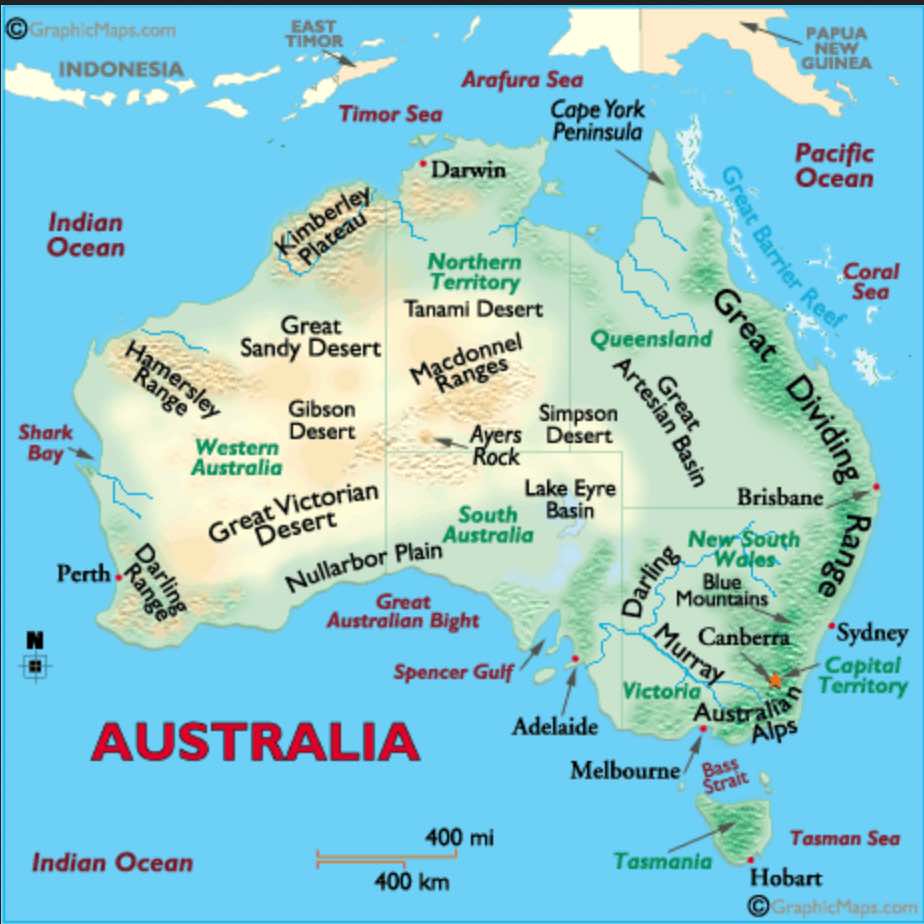
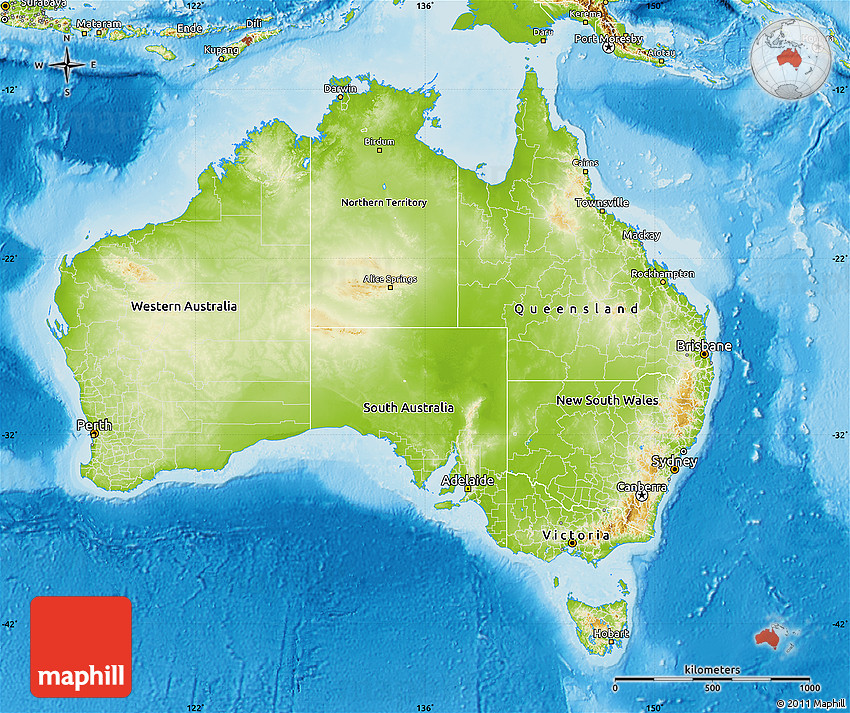
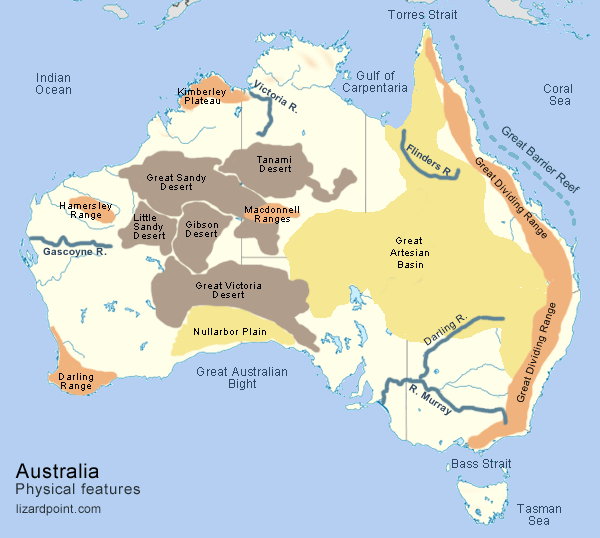
The Great Dividing Range: This ancient mountain range, stretching over 3,500 kilometers along the eastern coast, is the backbone of Australia’s physical geography. Its peaks, including Mount Kosciuszko, the highest point in mainland Australia, capture moisture from the Pacific Ocean, creating fertile slopes and lush rainforests.
-
The Outback: This vast, arid interior covers over 70% of the continent, characterized by vast plains, rugged desert ranges, and ancient rock formations. The Outback’s harsh climate, with extreme temperatures and low rainfall, poses significant challenges to human habitation and development.
-
The Western Plateau: A vast, elevated plateau covering much of Western Australia, it is marked by ancient, eroded landscapes, including the striking sandstone formations of the Bungle Bungle Range and the iconic Uluru (Ayers Rock).
-
The Coastal Plains: Narrow strips of fertile land along the eastern, southern, and western coasts provide vital agricultural land and urban centers. The eastern coastal plains are characterized by fertile soils, lush rainforests, and a network of rivers, while the southern and western plains are more arid and support diverse plant and animal life.
A Spectrum of Climates:
Australia’s vast size and diverse landforms create a wide range of climates, from tropical to temperate, arid to humid.
-
Tropical: The northernmost regions experience a tropical climate, characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and heavy rainfall during the wet season. This region is home to diverse rainforests, savannas, and wetlands.
-
Temperate: The southern and eastern coastal regions enjoy a temperate climate with mild to warm summers and cool winters. This area supports a diverse range of plant and animal life, including eucalyptus forests, grasslands, and alpine meadows.
-
Arid: The vast interior experiences a hot, dry climate, with low rainfall and extreme temperatures. This region is dominated by desert landscapes, including sand dunes, spinifex grasslands, and salt lakes.
Waterways and Basins:
Australia’s water resources are unevenly distributed, with significant variations in rainfall and river systems.
-
The Murray-Darling Basin: This vast inland drainage system is the largest in Australia, encompassing a network of rivers, wetlands, and floodplains. It is a vital source of water for agriculture and urban centers, but faces increasing pressure from drought and water extraction.
-
The Great Artesian Basin: This vast underground reservoir, covering over 1.7 million square kilometers, provides a valuable source of water for livestock and communities in the arid interior. However, over-extraction and salinity pose significant challenges to its sustainability.
Significance and Benefits:
Understanding Australia’s physical features is essential for:
-
Conservation and Management: Recognizing the diverse ecosystems and their fragility is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies and managing natural resources sustainably.
-
Economic Development: Understanding the distribution of water resources, land suitability for agriculture, and the potential for mineral resources guides economic development initiatives.
-
Infrastructure Development: Knowledge of terrain, climate, and water availability is essential for planning and constructing infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and dams.
-
Tourism: Australia’s diverse physical features attract millions of tourists each year, contributing significantly to the country’s economy.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the major physical features of Australia?
A: The major physical features of Australia include the Great Dividing Range, the Outback, the Western Plateau, the coastal plains, and a diverse array of rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
Q: What are the different climate zones in Australia?
A: Australia has a wide range of climates, including tropical, temperate, and arid. The northern regions experience a tropical climate, the southern and eastern coasts are temperate, and the vast interior is arid.
Q: What are the major challenges faced by Australia’s physical features?
A: Australia faces challenges such as drought, salinity, land degradation, and climate change, which threaten its diverse ecosystems and water resources.
Q: How does Australia’s physical geography impact its biodiversity?
A: Australia’s unique physical features have led to the evolution of a diverse range of plant and animal life, including many endemic species. However, these ecosystems are vulnerable to human activities and climate change.
Tips for Exploring Australia’s Physical Features:
-
Embrace the Outback: Experience the vastness and beauty of the Australian Outback by embarking on a 4WD adventure, visiting Uluru, or exploring the iconic red earth of the Simpson Desert.
-
Discover the Great Dividing Range: Hike through lush rainforests, visit scenic waterfalls, and explore alpine meadows in the Great Dividing Range.
-
Explore the Coastal Regions: Discover the diverse coastal landscapes, from the sandy beaches of the Gold Coast to the rugged cliffs of Tasmania.
-
Experience the Diverse Wildlife: Observe unique Australian animals in their natural habitat, from kangaroos and koalas to wombats and echidnas.
Conclusion:
Australia’s physical features are a testament to the continent’s ancient history and dynamic geological processes. From the towering peaks of the Great Dividing Range to the vast expanse of the Outback, each feature contributes to the country’s unique natural heritage and presents both challenges and opportunities. Understanding these features is crucial for appreciating the beauty and fragility of Australia’s landscapes and for ensuring their sustainable management for future generations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Australia’s Physical Features. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!