Unveiling Mexico’s Diverse Terrain: A Journey Through Elevation
Related Articles: Unveiling Mexico’s Diverse Terrain: A Journey Through Elevation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Mexico’s Diverse Terrain: A Journey Through Elevation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Mexico’s Diverse Terrain: A Journey Through Elevation
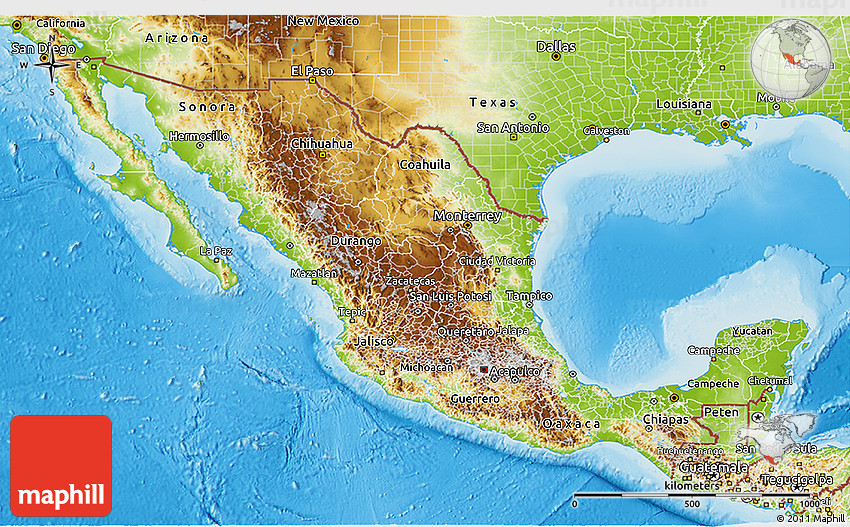
Mexico, a land of vibrant culture, rich history, and captivating landscapes, boasts a remarkable diversity in its topography. This diversity, evident in its elevation map, plays a crucial role in shaping the country’s climate, ecosystems, and human settlements. Examining this map allows us to understand the intricate relationship between elevation and the various facets of Mexico’s geographical identity.
A Tapestry of Elevation:
The Mexican elevation map showcases a dramatic spectrum of altitudes, ranging from the depths of the Pacific Ocean to the towering peaks of the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental. This varied terrain can be broadly categorized into distinct regions:
-
The Coastal Plains: These lowlands, hugging the Pacific and Atlantic coasts, are characterized by relatively low elevations, typically below 1,000 meters. They support a diverse range of ecosystems, including coastal forests, mangrove swamps, and sandy beaches.
-
The Central Plateau: A vast, elevated plateau situated in the heart of Mexico, this region is dominated by the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. This belt, a chain of volcanoes, includes the iconic Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl, which reach elevations exceeding 5,000 meters. The plateau’s high elevation contributes to its drier climate and unique vegetation, characterized by grasslands, scrublands, and pine forests.
-
The Sierra Madre Mountains: Encircling the Central Plateau are the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental, two prominent mountain ranges. The Sierra Madre Occidental, a rugged and arid range, stretches along the western coast, reaching elevations exceeding 3,000 meters. In contrast, the Sierra Madre Oriental, a more humid range, runs along the eastern coast, with peaks reaching over 4,000 meters.
-
The Yucatan Peninsula: This flat, low-lying peninsula, characterized by its karstic limestone formations, is a stark contrast to the mountainous regions of Mexico. Its elevation rarely exceeds 100 meters, resulting in a tropical climate and unique ecosystems, including cenotes, underground sinkholes filled with freshwater.
The Impact of Elevation:
Mexico’s elevation map is not merely a static representation of its topography; it actively influences the country’s climate, biodiversity, and human activity.
-
Climate Variations: Elevation plays a significant role in determining Mexico’s diverse climate patterns. As altitude increases, temperatures generally decrease, leading to a range of microclimates across the country. The high-elevation regions of the central plateau experience cooler temperatures and lower rainfall, while the coastal plains enjoy warmer temperatures and higher humidity.
-
Ecosystem Diversity: Mexico’s elevation map is intricately linked to its rich biodiversity. The different elevations support a wide array of ecosystems, from the arid deserts of the northern regions to the lush rainforests of the southern states. The Central Plateau, with its varied elevations, harbors a unique blend of vegetation, including grasslands, pine forests, and oak woodlands.
-
Human Settlements and Agriculture: Elevation influences human settlement patterns and agricultural practices. The fertile valleys and lowlands along the coasts are traditionally densely populated, supporting a diverse range of agricultural activities. In contrast, the high-elevation regions of the central plateau, with their cooler temperatures and limited rainfall, are less densely populated, with agriculture primarily focused on crops adapted to these conditions.
Understanding the Benefits:
The Mexican elevation map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s complex geography and its impact on various aspects of life. It provides valuable insights for:
-
Resource Management: The map helps identify areas with potential for water resources, mineral deposits, and agricultural production. It aids in planning sustainable resource management practices, considering the unique conditions at different elevations.
-
Disaster Preparedness: Understanding the elevation map is crucial for disaster preparedness, particularly for events like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. The map helps identify areas at higher risk and facilitates the development of effective disaster mitigation strategies.
-
Infrastructure Development: The elevation map guides infrastructure development, ensuring that roads, bridges, and other critical infrastructure are built to withstand the specific challenges posed by the terrain. It also aids in identifying suitable locations for hydroelectric power generation and other energy projects.
-
Tourism and Recreation: The elevation map highlights the diverse landscapes and natural wonders of Mexico, attracting tourists and outdoor enthusiasts. It guides the development of tourism infrastructure, ensuring access to hiking trails, ski resorts, and other recreational activities.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the highest point in Mexico?
A: The highest point in Mexico is Pico de Orizaba, an inactive volcano in the state of Veracruz, reaching an elevation of 5,636 meters.
Q: What are the main mountain ranges in Mexico?
A: The main mountain ranges in Mexico are the Sierra Madre Occidental, Sierra Madre Oriental, and Sierra Madre del Sur.
Q: How does elevation affect climate in Mexico?
A: Higher elevations generally experience cooler temperatures and lower rainfall due to the decreasing atmospheric pressure and density.
Q: What are the major agricultural regions in Mexico based on elevation?
A: The lowlands along the coasts are ideal for growing tropical fruits, vegetables, and grains. The central plateau, with its cooler temperatures, is suited for crops like potatoes, wheat, and barley.
Q: What are some of the challenges posed by Mexico’s varied terrain?
A: The rugged terrain poses challenges for infrastructure development, transportation, and communication. It also increases the risk of natural disasters like earthquakes, landslides, and floods.
Tips for Utilizing the Mexican Elevation Map:
- Explore Online Resources: Numerous online platforms offer interactive elevation maps of Mexico, allowing users to zoom in, explore specific areas, and analyze data.
- Identify Key Features: Focus on identifying the main mountain ranges, plateaus, and coastal plains. Understand their general elevations and associated ecosystems.
- Consider Human Impact: Analyze how elevation influences population distribution, agricultural practices, and infrastructure development.
- Connect to Climate Data: Utilize the elevation map in conjunction with climate data to understand how elevation affects temperature, rainfall, and other climatic variables.
Conclusion:
The Mexican elevation map is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s diverse geography and its impact on climate, ecosystems, and human activity. It provides valuable insights for resource management, disaster preparedness, infrastructure development, and tourism. By understanding the intricate relationship between elevation and the various facets of Mexico’s landscape, we gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s rich natural heritage and the challenges and opportunities it presents.
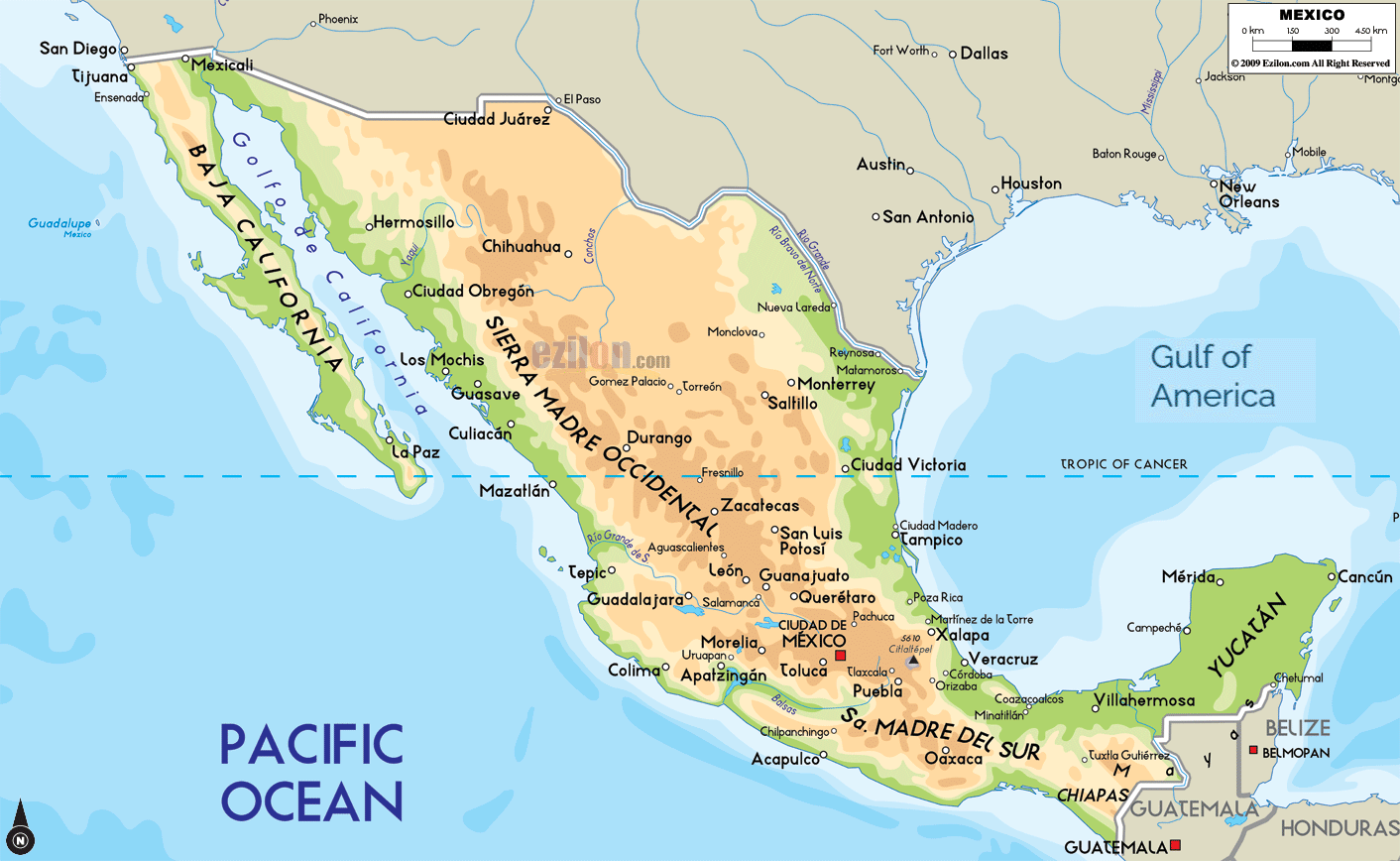







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Mexico’s Diverse Terrain: A Journey Through Elevation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!