Unveiling the Earth’s Canvas: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Types Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Canvas: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Types Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Canvas: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Types Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Canvas: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Types Maps
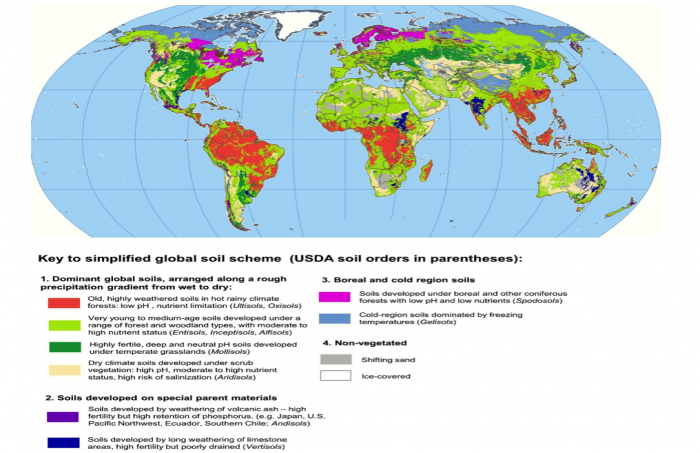
The Earth’s surface, while seemingly uniform, is a tapestry of diverse ecosystems, each with its own unique soil profile. These soils, the foundation of life on land, are not merely inert substances but complex, dynamic systems that influence everything from plant growth to water availability. A soil types map, a visual representation of these diverse soil profiles across a region, serves as a crucial tool for understanding and managing this vital resource.
A Journey Through the Earth’s Skin: Understanding Soil Types Maps
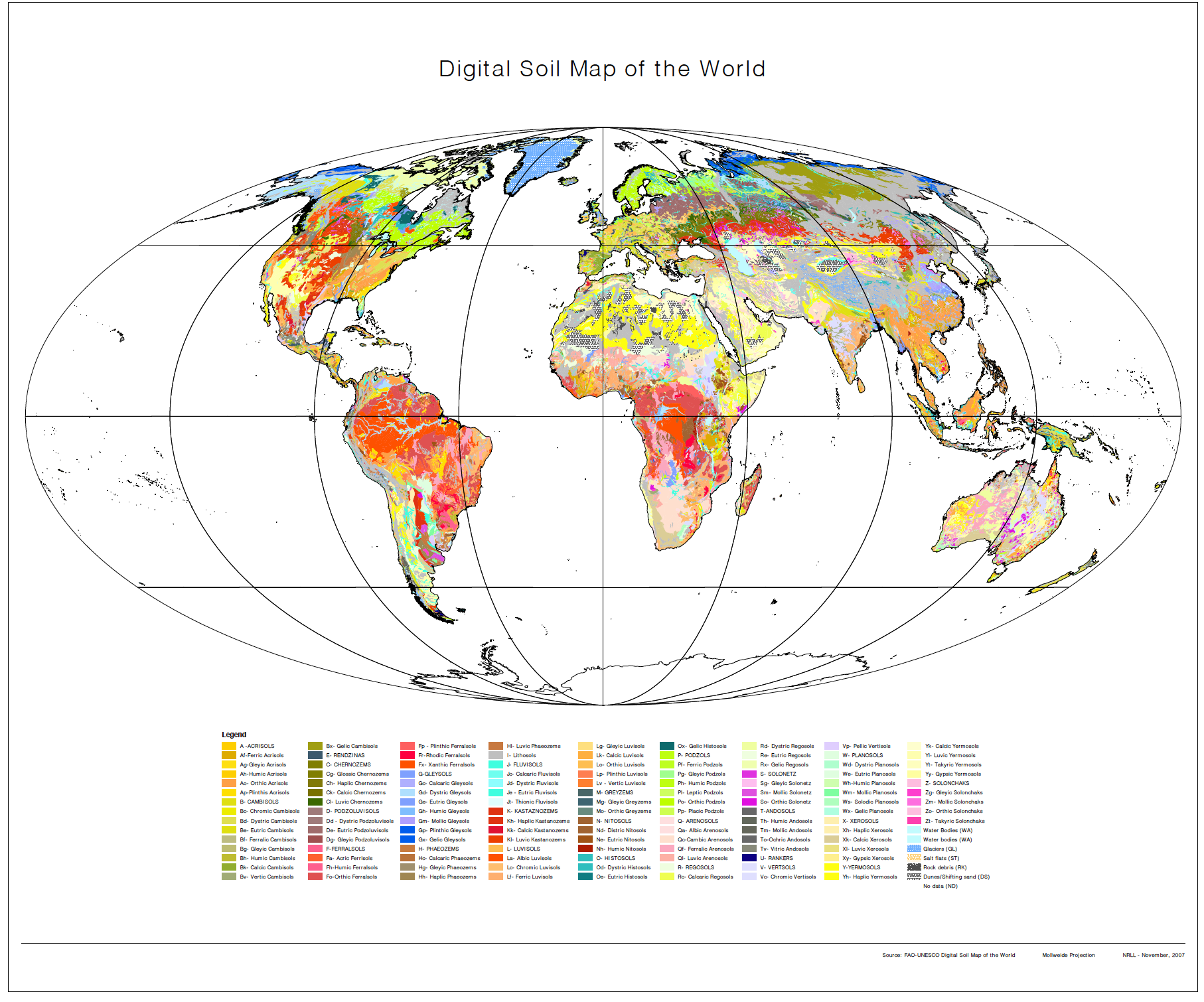
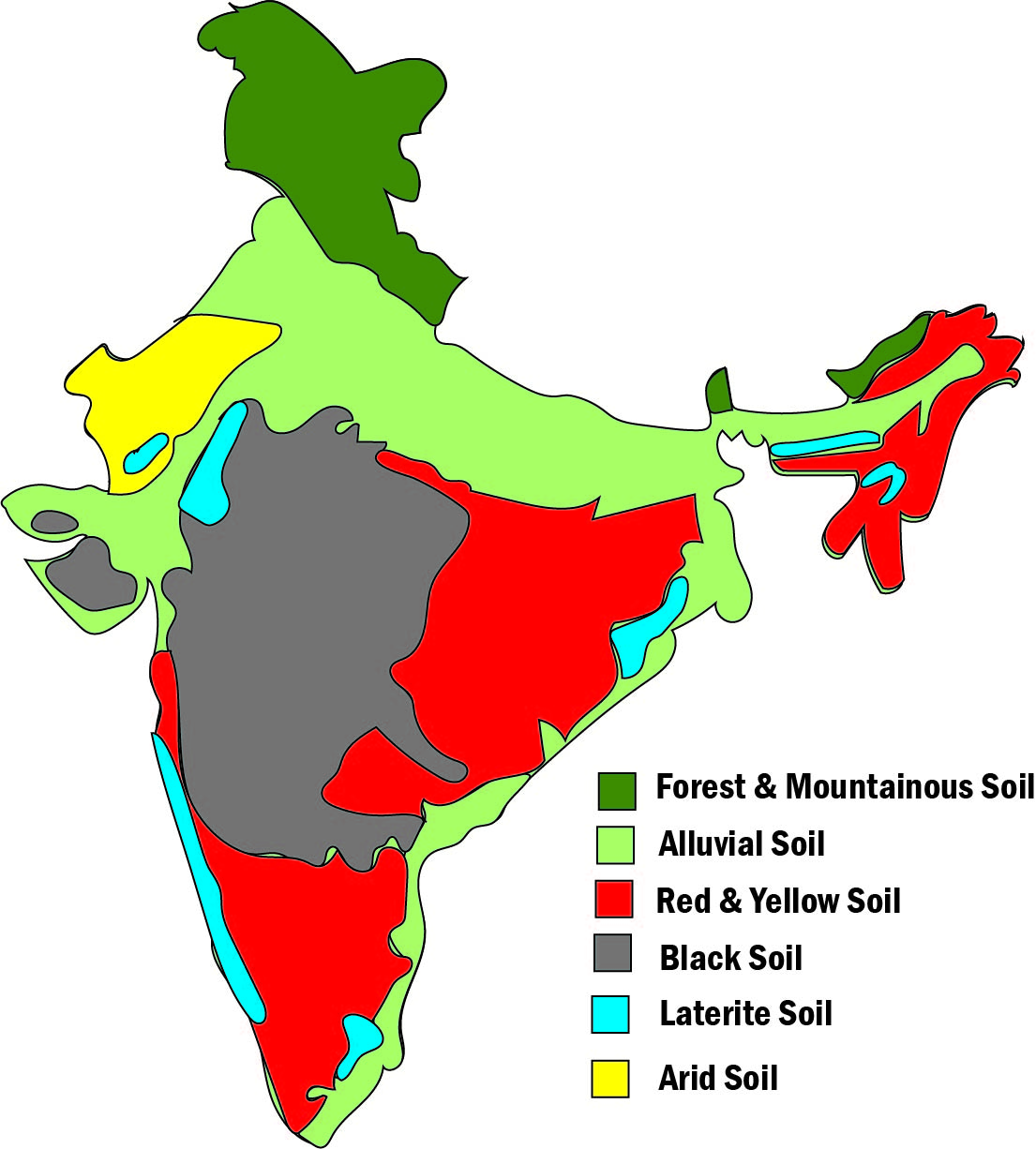
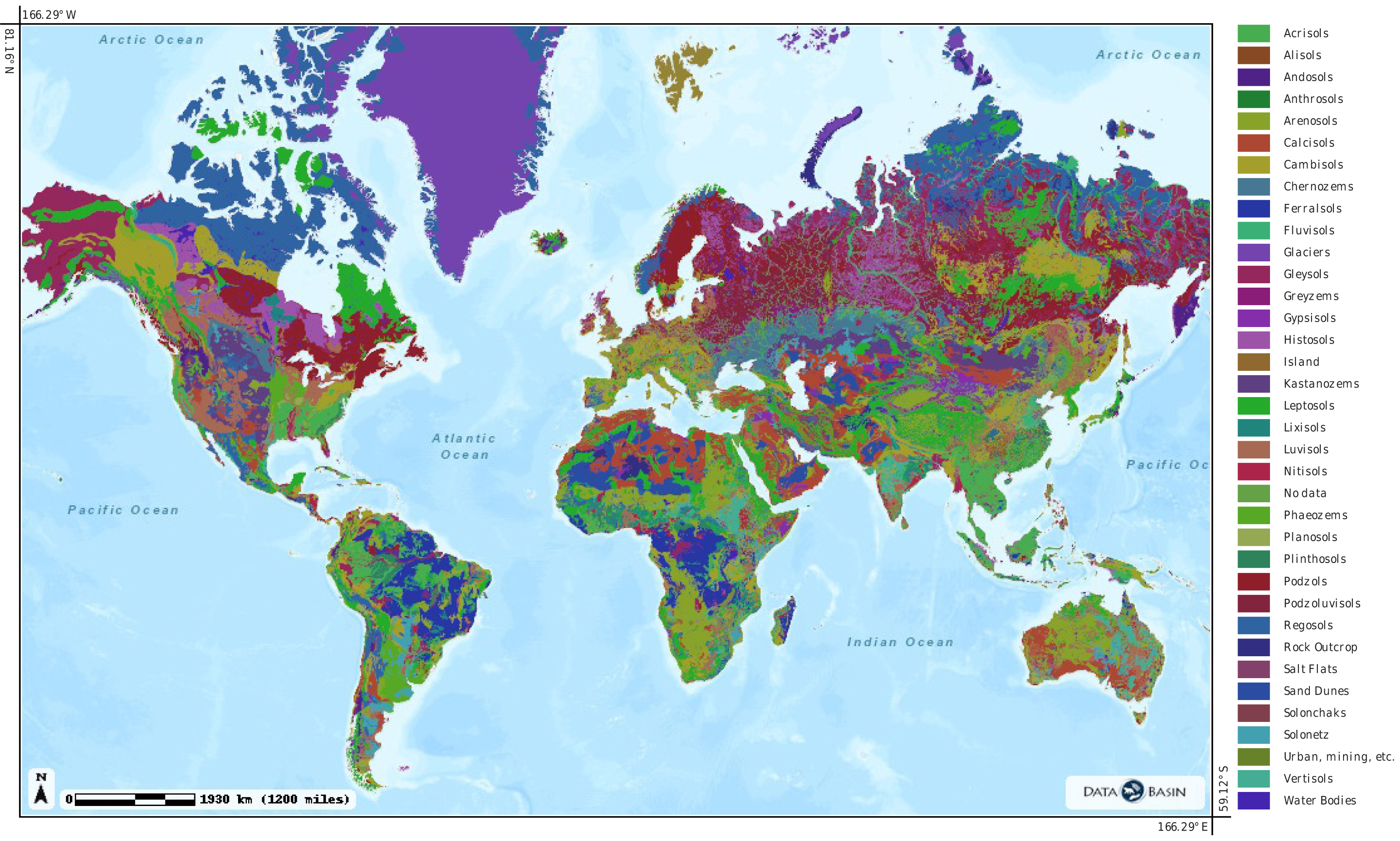
A soil types map, at its core, is a visual representation of the distribution of different soil types within a defined geographical area. Each color or symbol on the map corresponds to a specific soil type, characterized by its unique combination of physical, chemical, and biological properties. These properties, in turn, dictate the soil’s suitability for various purposes, including agriculture, forestry, and construction.
The Building Blocks of Soil: A Closer Look at Soil Properties
To comprehend the significance of a soil types map, it is crucial to understand the key properties that define soil types:
- Texture: Refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles in the soil. This determines the soil’s ability to retain water and nutrients, influencing plant growth and drainage patterns.
- Structure: Describes the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates, influencing aeration, water infiltration, and root penetration.
- Organic Matter: Composed of decaying plant and animal matter, organic matter enriches soil fertility, improves water retention, and enhances soil structure.
- pH: Indicates the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, influencing the availability of nutrients for plants.
- Nutrient Content: Refers to the presence of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, crucial for plant growth and overall soil health.
Deciphering the Colors and Symbols: Reading a Soil Types Map
A soil types map is a visual language, with each color or symbol representing a distinct soil type. Common conventions used in soil types maps include:
- Color: Different colors are often used to represent major soil groups, such as Alfisols (brown), Mollisols (black), and Aridisols (red).
- Symbols: Specific symbols may be used to denote specific soil properties, such as the presence of gravel, bedrock, or high organic matter content.
- Boundaries: Lines on the map delineate areas with different soil types, reflecting the influence of factors like topography, climate, and parent material.
Beyond the Visual: The Importance of Soil Types Maps
Understanding the distribution of soil types has profound implications for various aspects of human activity:
- Agriculture: Soil types maps guide farmers in selecting appropriate crops, optimizing fertilizer application, and managing irrigation, leading to increased productivity and sustainable farming practices.
- Forestry: Maps help foresters identify areas suitable for different tree species, promoting biodiversity and sustainable forest management.
- Urban Planning: Soil types maps inform urban planning decisions, ensuring suitable soil conditions for infrastructure development and minimizing environmental impacts.
- Environmental Management: Understanding soil types is crucial for managing water resources, mitigating soil erosion, and preserving biodiversity.
Frequently Asked Questions about Soil Types Maps
1. What is the difference between a soil survey and a soil types map?
A soil survey is a comprehensive investigation of soil properties across a specific area, often involving detailed field observations and laboratory analysis. A soil types map is a visual representation of the results of a soil survey, summarizing the distribution of different soil types.
2. How are soil types maps created?
Soil types maps are typically developed through a combination of field observations, laboratory analysis, and remote sensing techniques. Soil scientists conduct field surveys, collect soil samples, and analyze their properties. Remote sensing data, such as aerial photographs and satellite imagery, can also provide valuable information about soil characteristics.
3. Are soil types maps static or dynamic?
Soil types are not static entities but are influenced by various factors, including climate, vegetation, and human activities. Soil types maps can be updated periodically to reflect these changes, ensuring their relevance and accuracy.
4. How can I access soil types maps for my region?
Soil types maps are often available from government agencies responsible for natural resource management, such as the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) or the Canadian Soil Survey. Many universities and research institutions also maintain soil databases and maps.
5. What are some limitations of soil types maps?
Soil types maps are simplified representations of complex soil systems. They may not capture the full range of variability within a given soil type, and they are subject to limitations in data collection and interpretation.
Tips for Utilizing Soil Types Maps Effectively
- Consult with Experts: Collaborate with soil scientists or agricultural experts to interpret soil types maps and understand their implications for your specific needs.
- Consider Scale: Soil types maps are available at various scales, from regional to local. Choose the appropriate scale for your intended use.
- Integrate with Other Data: Combine soil types maps with other relevant data, such as climate maps, topography maps, and land use maps, for a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Stay Informed: Soil types can change over time, so stay informed about updates to soil types maps and consult with relevant authorities for the most current information.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Sustainable Land Management
Soil types maps are essential tools for understanding and managing our planet’s most vital resource. By visualizing the distribution of diverse soil types, these maps empower us to make informed decisions regarding agriculture, forestry, urban planning, and environmental conservation. By leveraging the knowledge provided by soil types maps, we can ensure the sustainable use of this precious resource for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Canvas: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Types Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!