Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topography Map of New York State
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topography Map of New York State
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topography Map of New York State. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topography Map of New York State
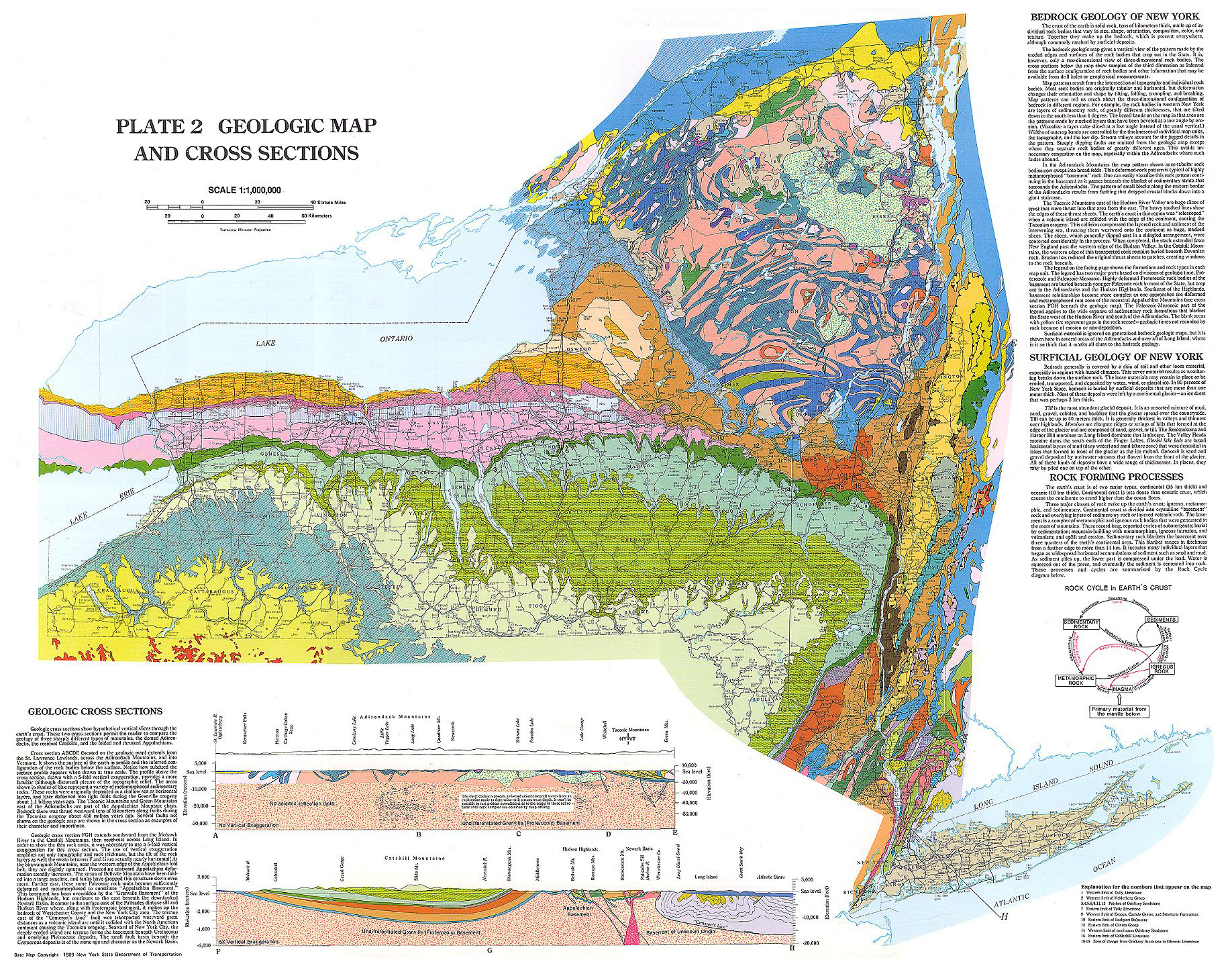
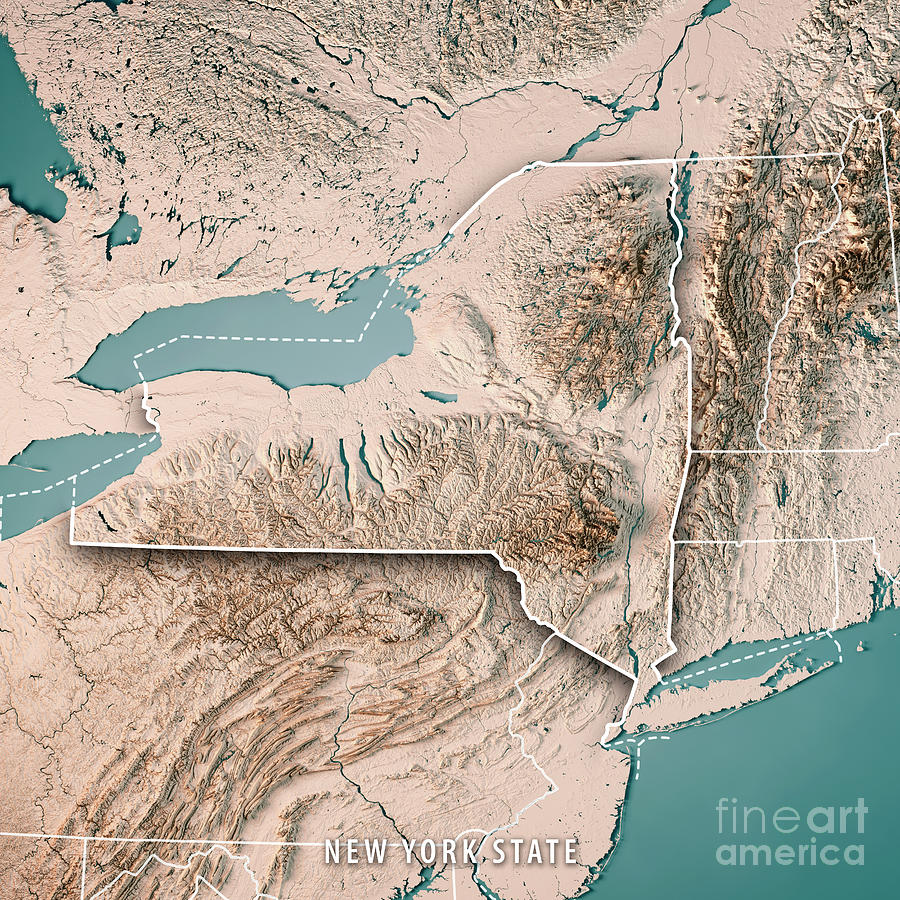
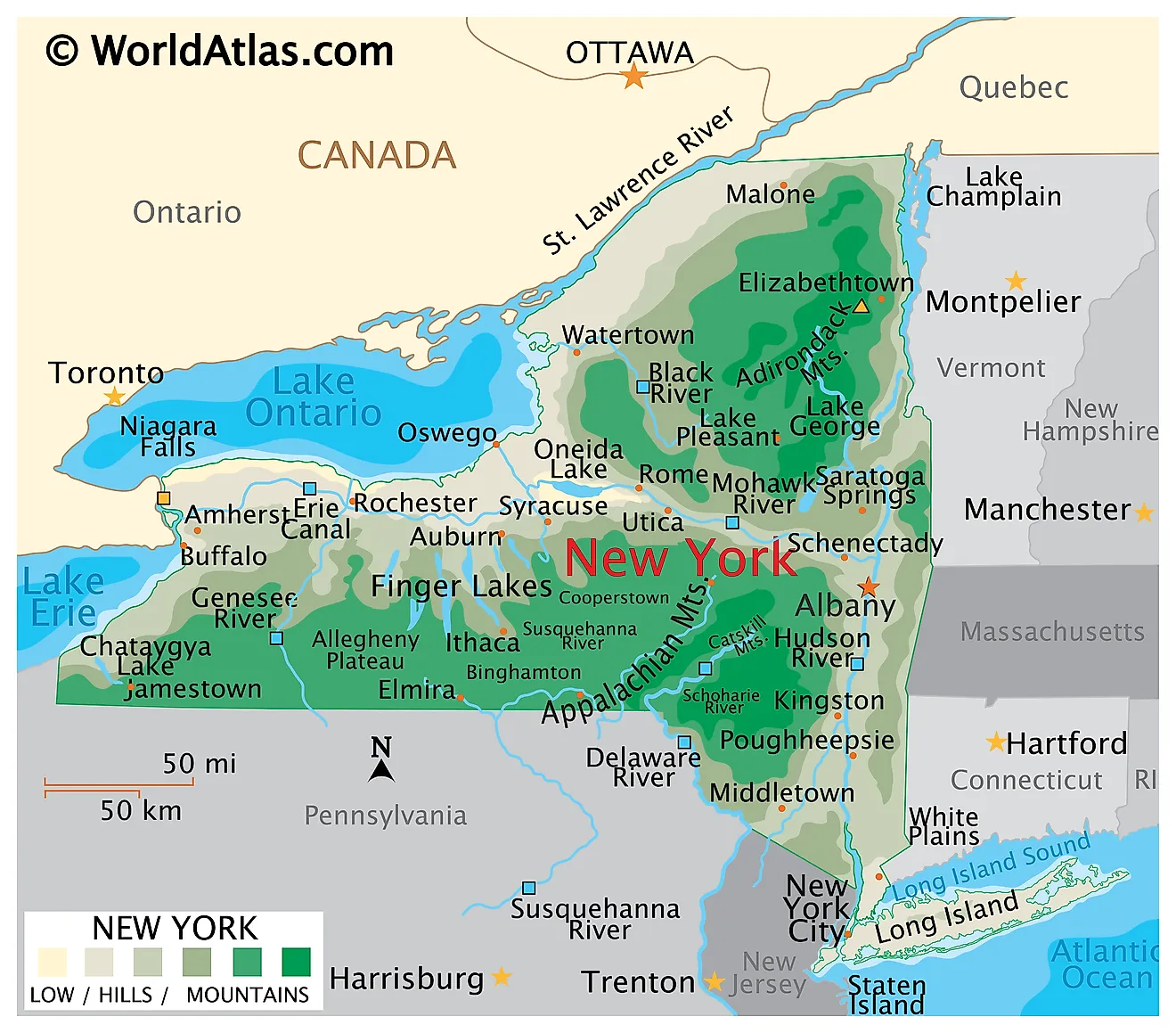
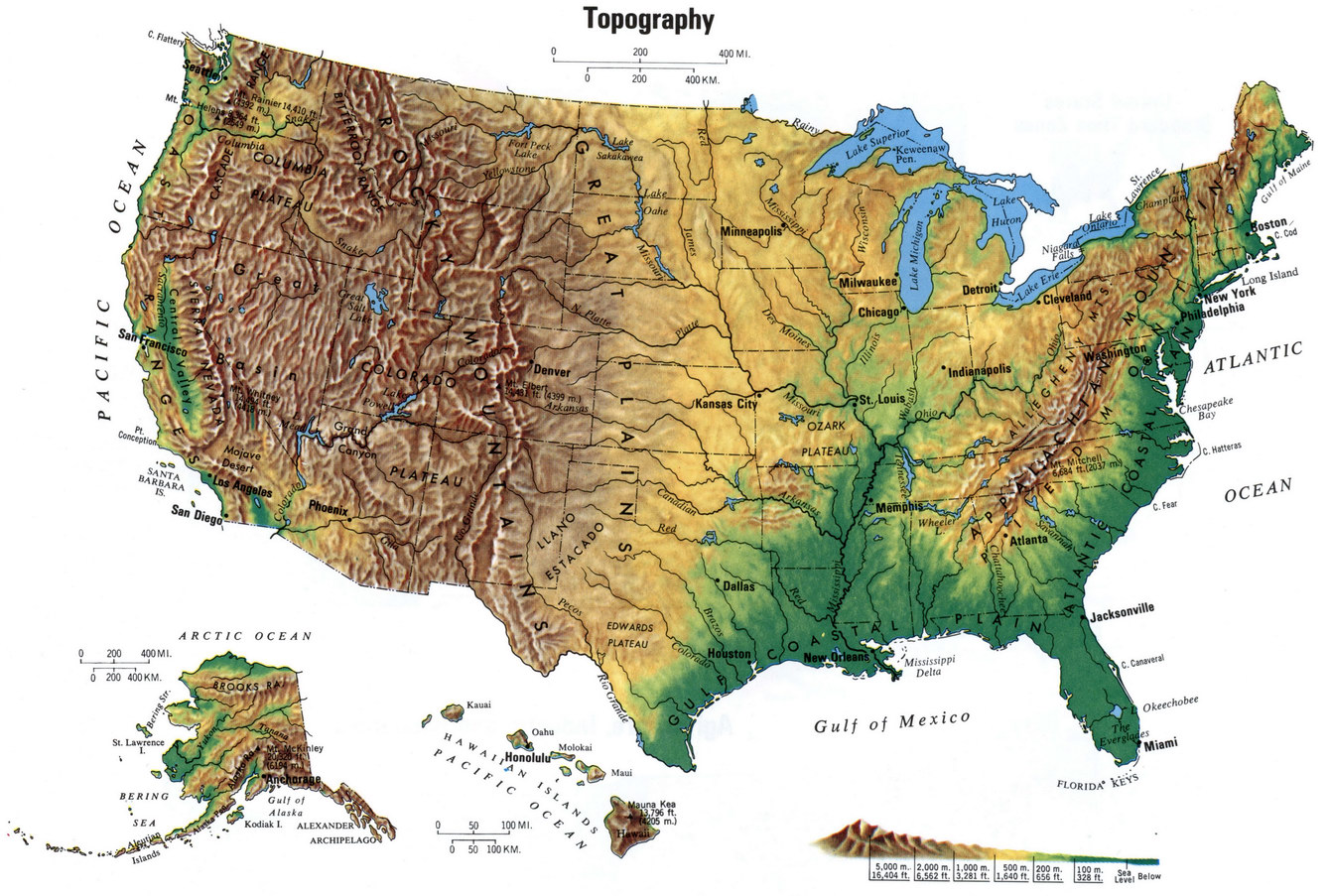
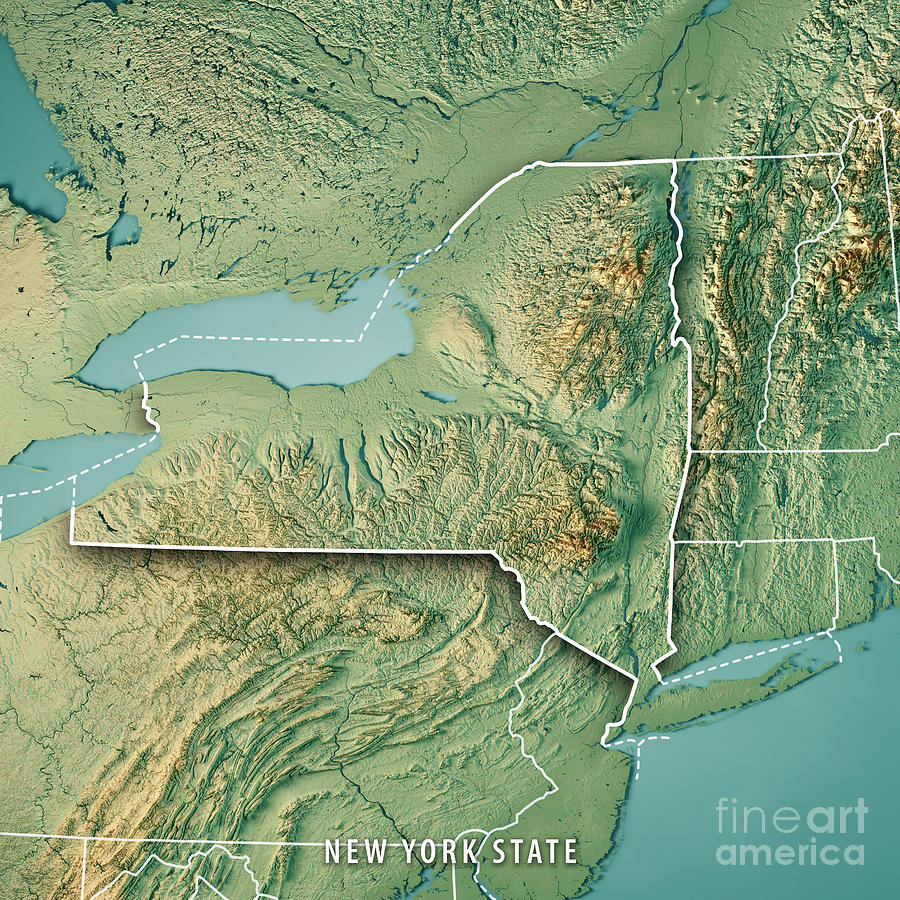
New York State, renowned for its bustling cities, iconic landmarks, and diverse landscapes, boasts a topography that is as captivating as it is complex. A topography map, a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, provides a crucial lens through which to understand the state’s varied terrain, its impact on human settlement, and its influence on the environment. This article delves into the topography map of New York State, exploring its key features, regional variations, and the significance it holds for various aspects of life in the state.
The State’s Geographic Tapestry: A Symphony of Diverse Terrain
The topography map of New York State reveals a captivating tapestry of diverse terrain, ranging from the majestic Adirondack Mountains in the north to the rolling hills of the Hudson Valley, and the sprawling plains of the Great Lakes region. Each region possesses unique characteristics that have shaped its history, culture, and ecology.
The Adirondack Mountains: A Rugged Wilderness
The Adirondack Mountains, a geological marvel, dominate the northern portion of New York State. This vast, rugged region, renowned for its towering peaks, dense forests, and pristine lakes, is a testament to the power of ancient geological forces. The highest point in New York State, Mount Marcy, stands at an impressive 5,344 feet, offering breathtaking views of the surrounding wilderness. The Adirondacks are a playground for outdoor enthusiasts, attracting hikers, skiers, climbers, and paddlers eager to explore its untamed beauty.
The Catskill Mountains: A Scenic Retreat
To the south of the Adirondacks lie the Catskill Mountains, a gentler range known for its rolling hills, verdant forests, and picturesque waterfalls. The Catskills offer a more accessible and less demanding experience for outdoor recreation, attracting hikers, campers, and nature lovers seeking a tranquil escape. The region is also known for its scenic beauty, with its lush valleys and winding rivers providing inspiration for artists and writers for centuries.
The Hudson Valley: A Cradle of History and Culture
The Hudson Valley, a fertile and scenic region, is nestled between the Catskill Mountains and the Taconic Mountains. The valley is defined by the majestic Hudson River, which flows southwards, carving a path through the landscape. The region is steeped in history, with its towns and cities playing a significant role in the development of the state and the nation. The Hudson Valley is also a hub for art and culture, attracting artists, writers, and musicians drawn to its beauty and inspiration.
The Great Lakes Region: A Vast and Diverse Landscape
The Great Lakes region of New York State encompasses the southern shores of Lake Ontario and Lake Erie, offering a unique blend of coastal landscapes, agricultural plains, and urban centers. The region is known for its fertile soils, which support a thriving agricultural industry, and its vast stretches of shoreline, attracting visitors seeking water sports and recreational activities. The Great Lakes region also plays a crucial role in the state’s economy, with its ports serving as gateways for international trade.
The Importance of Topography: Shaping Life in New York State
The topography of New York State has played a profound role in shaping the state’s history, culture, and economy. The rugged terrain of the Adirondacks and Catskills, while posing challenges for early settlers, provided a wealth of natural resources, including timber, minerals, and water power. The fertile valleys of the Hudson Valley and the Great Lakes region became centers of agriculture, supporting the growth of towns and cities.
The Topography’s Impact on Human Settlement
The topography of New York State has heavily influenced the distribution of human settlements. The fertile valleys, easily accessible by water routes, attracted early settlers, leading to the development of major cities like New York City, Albany, and Buffalo. The rugged mountains, while less hospitable, provided access to natural resources and served as a refuge for indigenous communities.
The Influence on Transportation and Infrastructure
The topography of New York State has presented both challenges and opportunities in the development of transportation and infrastructure. The winding rivers, particularly the Hudson River, served as crucial waterways for transportation and trade in the early years. The mountainous terrain, however, posed significant challenges for road construction and rail lines, requiring extensive engineering efforts to overcome steep inclines and rugged terrain.
The Role in Environmental Conservation
The diverse topography of New York State encompasses a wide range of ecosystems, from dense forests to pristine lakes and wetlands. The state’s topography is crucial for maintaining biodiversity, providing habitat for numerous species of plants and animals. The topography also plays a vital role in regulating water flow, ensuring the health of watersheds and the availability of clean water.
The Importance of Understanding Topography
Understanding the topography of New York State is crucial for a variety of reasons. It provides valuable insights into:
- Land Use and Development: Topography influences the suitability of land for different uses, such as agriculture, forestry, urban development, and recreation.
- Natural Hazards: The topography can influence the occurrence and impact of natural hazards, such as landslides, floods, and wildfires.
- Infrastructure Planning: Understanding the topography is essential for planning and constructing roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Environmental Management: Topography plays a crucial role in understanding and managing environmental resources, such as water quality, biodiversity, and wildlife habitat.
FAQs about the Topography Map of New York State
Q: What is the highest point in New York State?
A: The highest point in New York State is Mount Marcy, located in the Adirondack Mountains, with an elevation of 5,344 feet.
Q: What are the major geographic regions of New York State?
A: The major geographic regions of New York State include the Adirondack Mountains, the Catskill Mountains, the Hudson Valley, the Great Lakes region, and the Long Island region.
Q: How does the topography of New York State impact its climate?
A: The topography of New York State significantly impacts its climate. The elevation of the Adirondack Mountains and Catskill Mountains creates cooler temperatures and increased precipitation compared to lower-lying regions. The Great Lakes region experiences a moderating effect on temperatures due to the large bodies of water.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing New York State due to its topography?
A: Some of the environmental challenges facing New York State due to its topography include:
- Water pollution: Runoff from agricultural areas and urban development can pollute waterways, impacting water quality and aquatic ecosystems.
- Deforestation: The mountainous terrain makes forests vulnerable to deforestation due to timber harvesting and development pressures.
- Soil erosion: Steep slopes and heavy rainfall can lead to soil erosion, degrading soil fertility and impacting water quality.
Tips for Using a Topography Map of New York State
- Identify key features: Familiarize yourself with the major geographic features of the state, such as mountain ranges, valleys, rivers, and lakes.
- Interpret elevation: Understand the relationship between elevation and color on the map, allowing you to visualize the terrain’s steepness and variations in altitude.
- Analyze slope and aspect: Analyze the slope and aspect of the terrain, which can influence factors such as sunlight exposure, drainage, and wind patterns.
- Consider scale: Remember that the scale of the map can influence the level of detail and the accuracy of the information presented.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Terrain, A Legacy of Influence
The topography map of New York State is more than just a visual representation of the land; it is a window into the state’s rich history, its diverse cultures, and its complex environmental systems. It reveals the interplay of geological forces, human settlement, and natural processes that have shaped the state’s unique character. By understanding the topography, we gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities that New York State faces, and we can better inform decisions that impact the state’s future. As we continue to explore and learn from the topography of New York State, we can ensure that its diverse landscapes and rich heritage are preserved for generations to come.
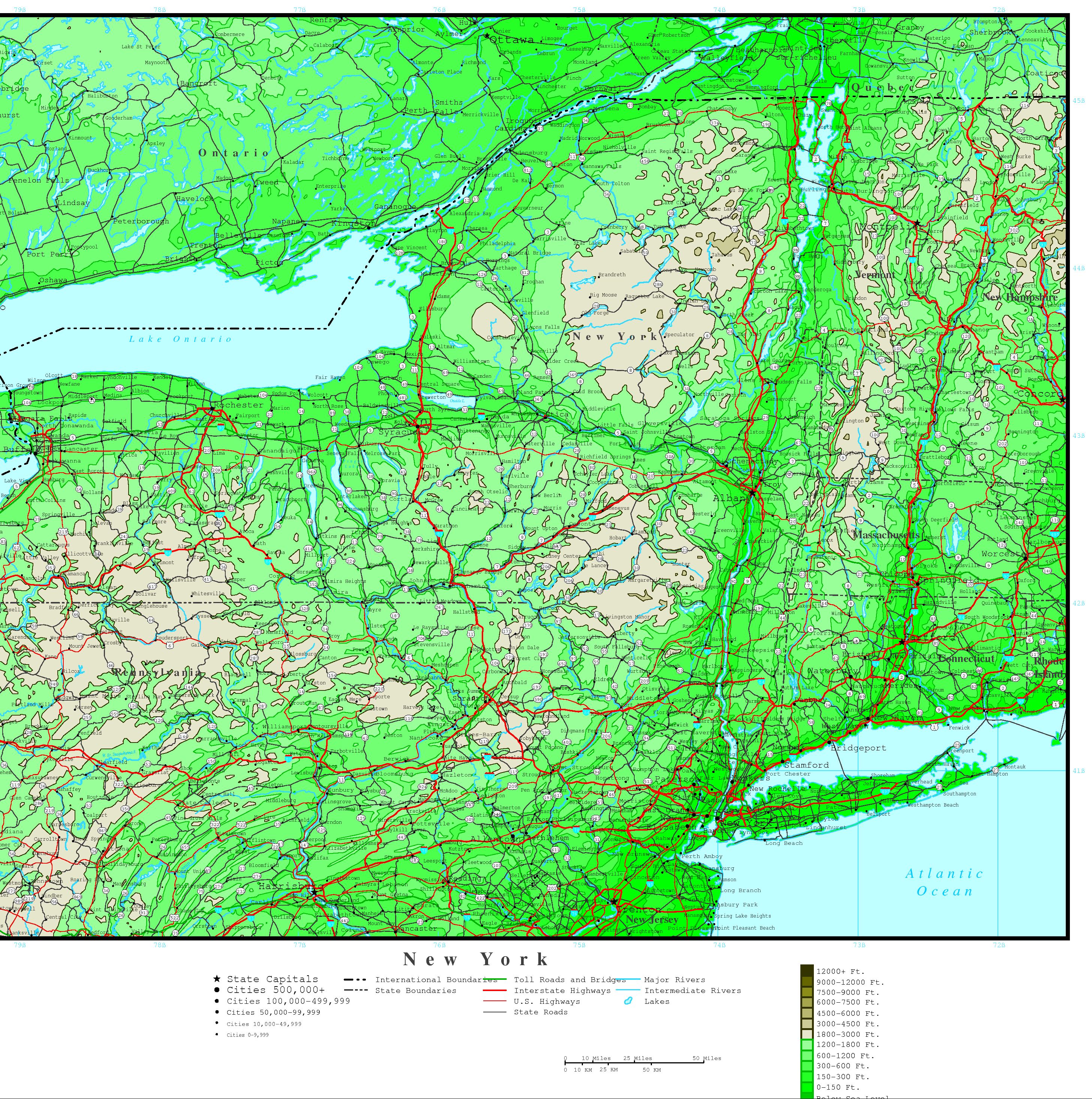
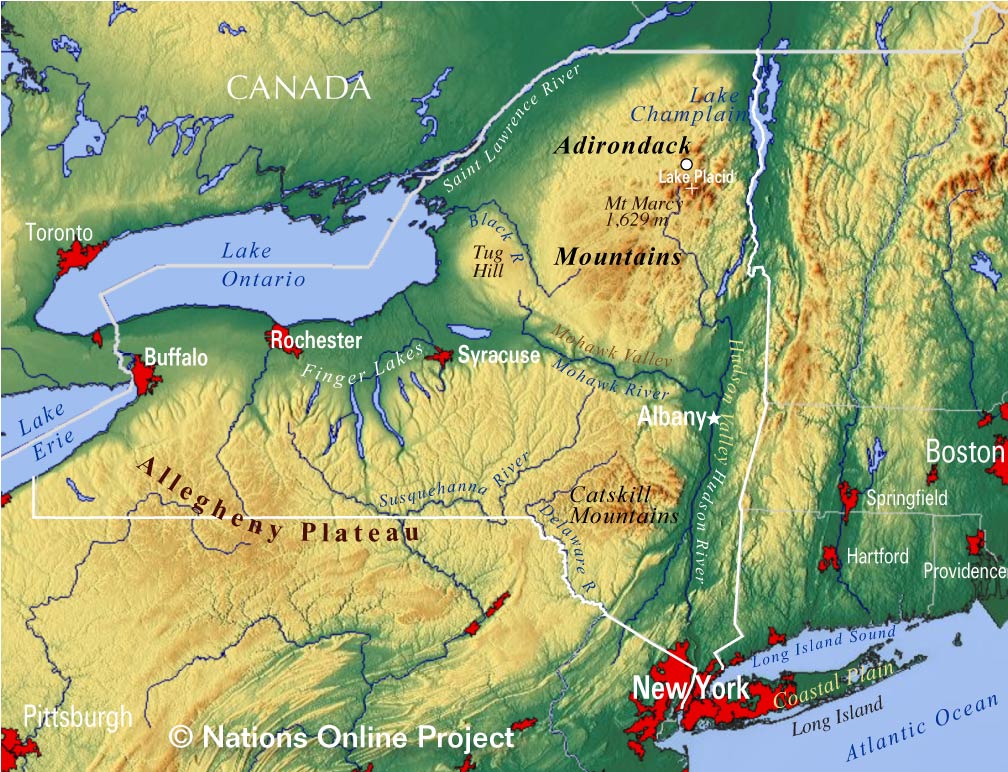
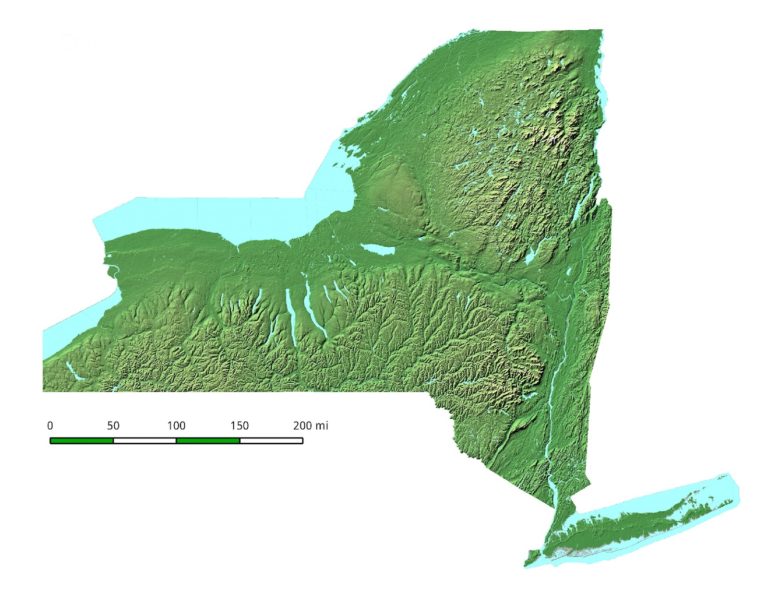

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topography Map of New York State. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!