Unveiling the Power of Number Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Number Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Number Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Number Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data

In the realm of data analysis and visualization, the human mind often struggles to grasp complex relationships and patterns buried within vast datasets. This is where number maps, also known as number grids, emerge as a powerful tool, offering a structured and intuitive approach to visualizing data and revealing hidden insights.
Understanding Number Maps: A Visual Framework for Data Exploration
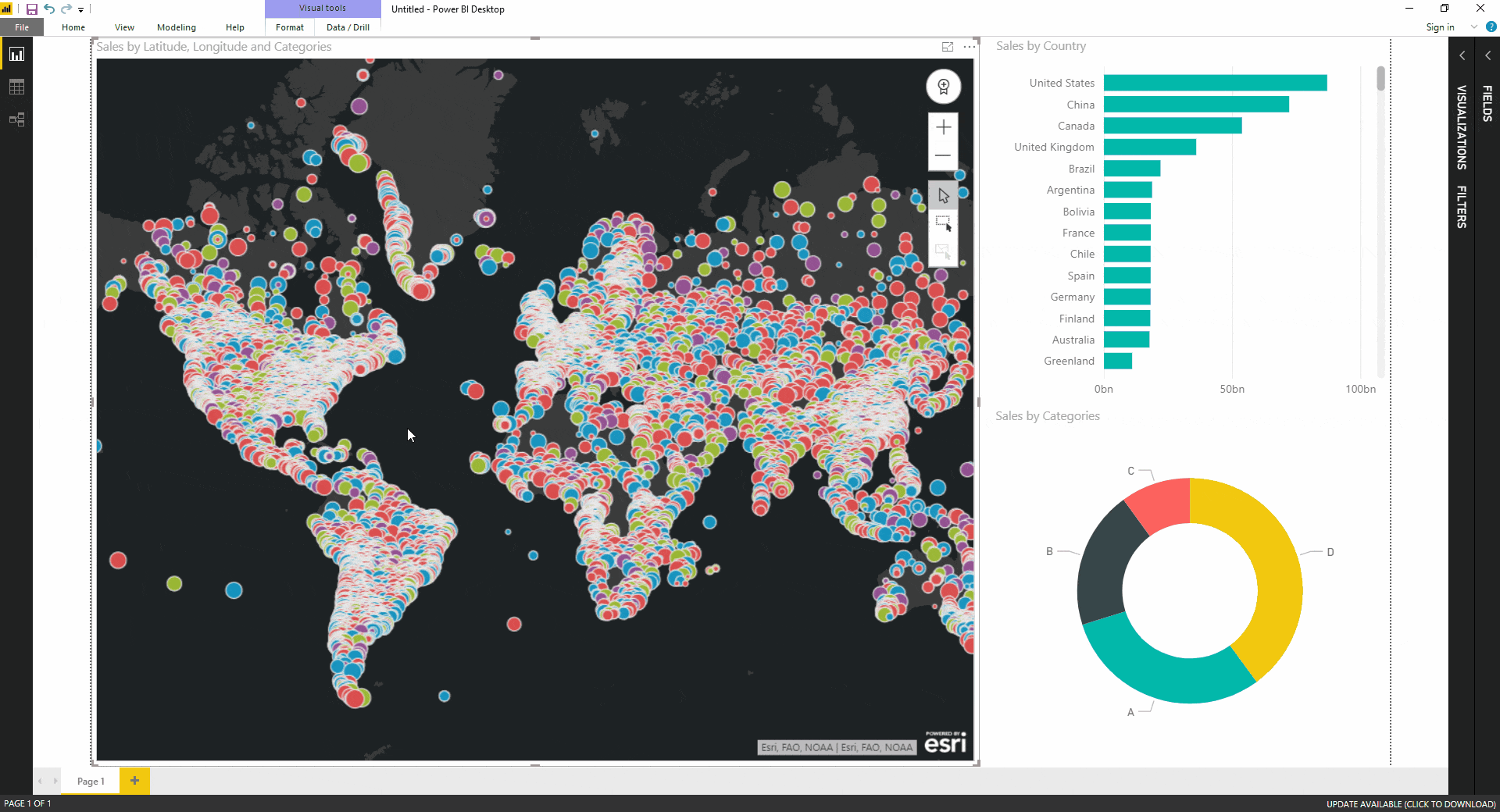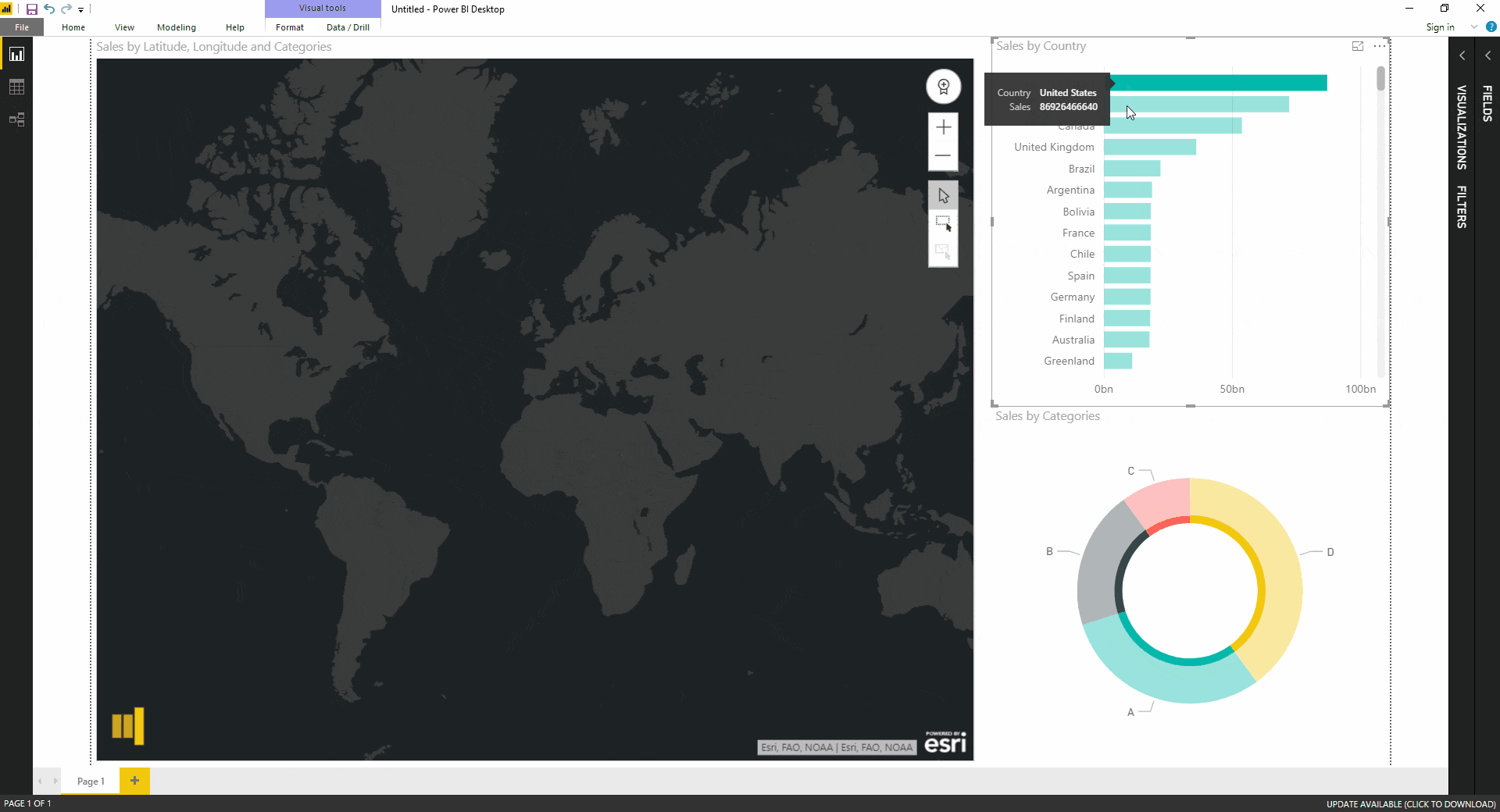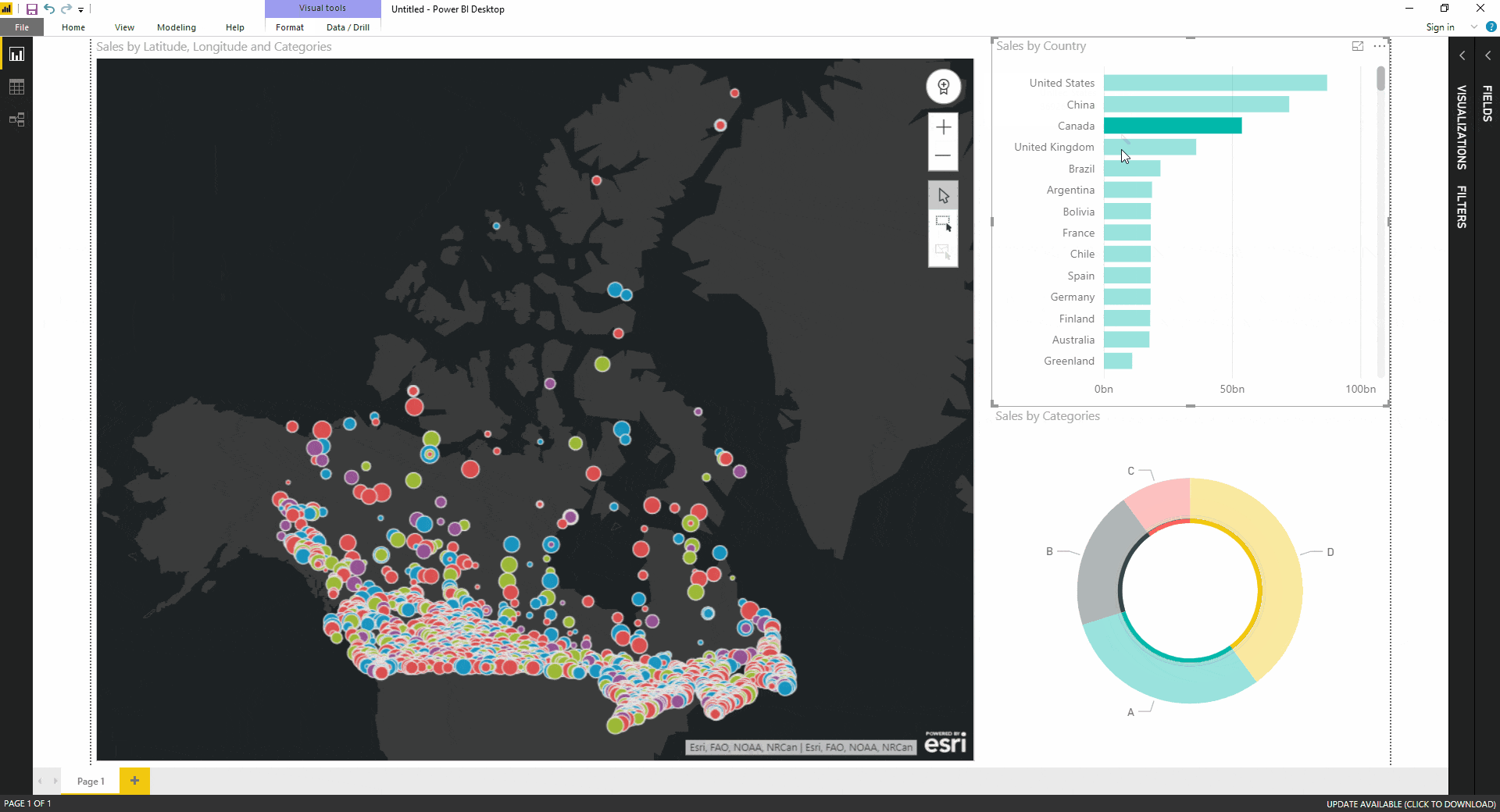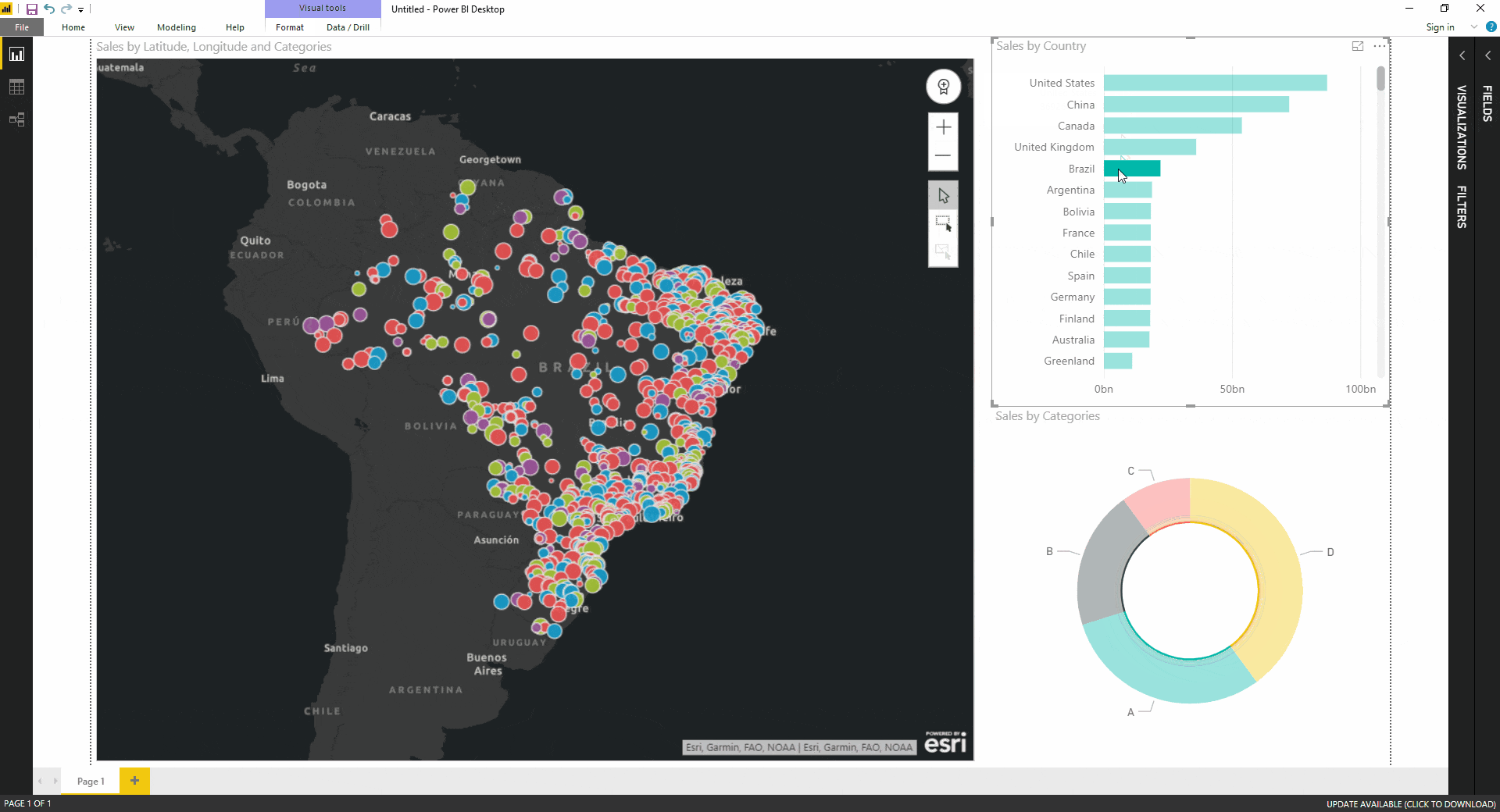
A number map is a visual representation of data arranged in a grid format. Each cell within the grid corresponds to a specific data point, represented by a number or symbol. This arrangement allows for the identification of trends, clusters, and anomalies within the data, facilitating a deeper understanding of underlying relationships.
Key Components of a Number Map:
- Grid Structure: The foundation of a number map is a grid, typically consisting of rows and columns. The number of rows and columns can vary depending on the size and complexity of the data.
- Data Points: Each cell within the grid represents a specific data point, which can be a number, a symbol, or a combination of both.
- Color Coding: Utilizing a color scheme to represent different values or categories within the data can enhance the visual clarity and readability of the map.
- Legend: A legend is essential for understanding the meaning of the colors, symbols, and values used within the number map.
Types of Number Maps:
There are various types of number maps, each tailored to specific data types and analysis needs:
- Heatmaps: Heatmaps utilize a color gradient to depict data values, with darker colors representing higher values and lighter colors representing lower values. They are particularly useful for identifying areas of high or low concentration within the data.
- Scatterplots: Scatterplots represent individual data points as dots on a two-dimensional grid, with each axis representing a different variable. They are effective in identifying correlations and relationships between variables.
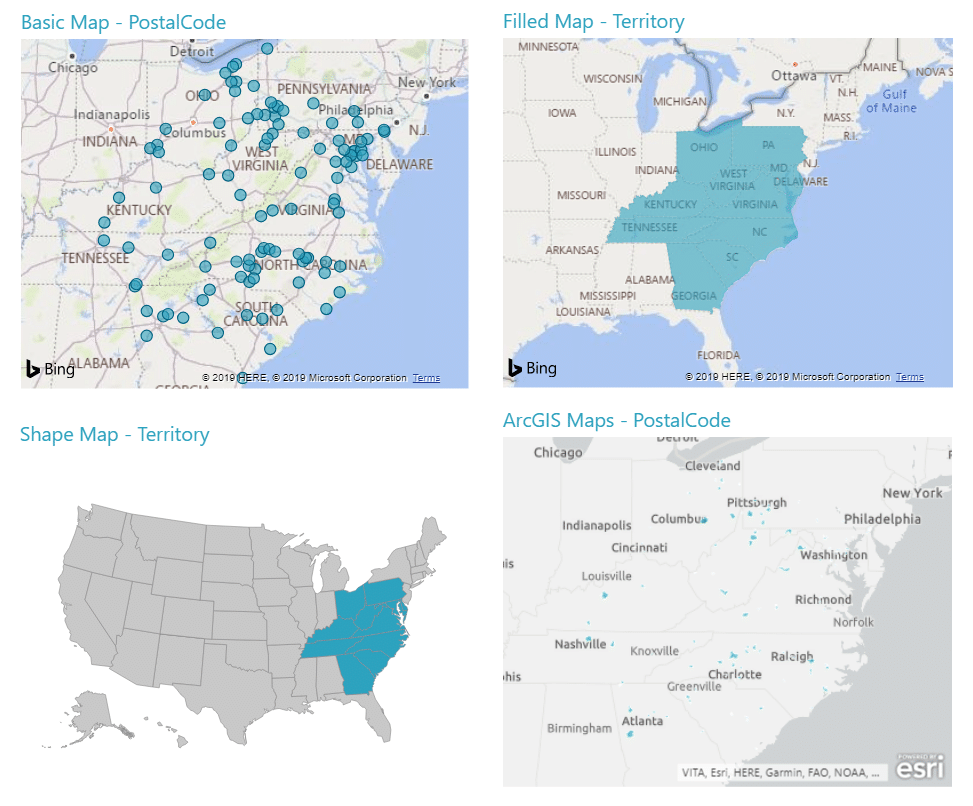
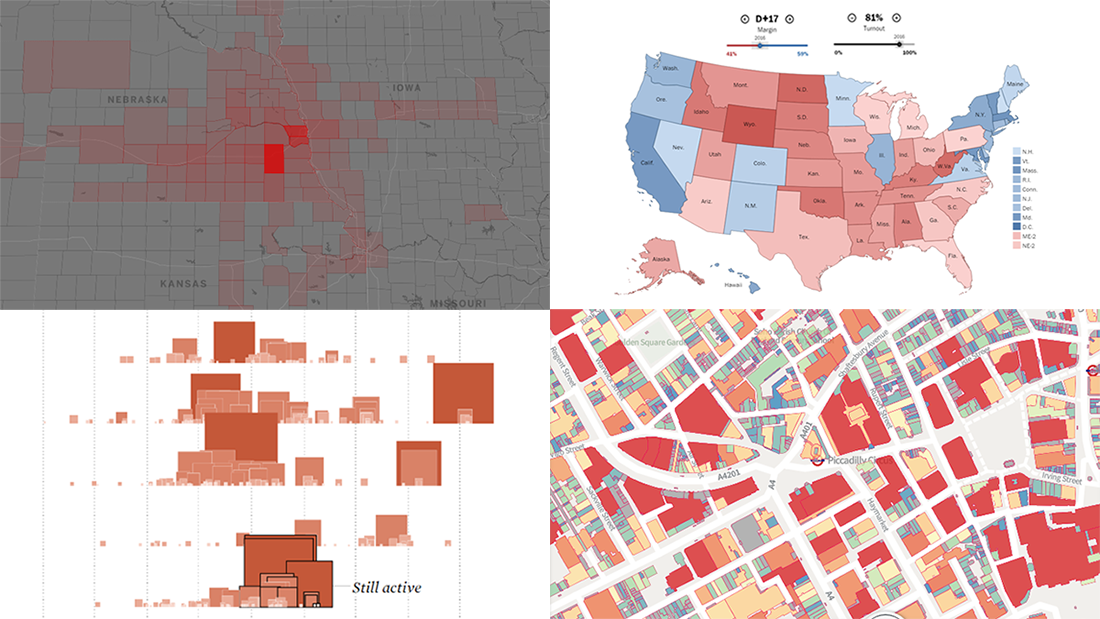
- Choropleth Maps: Choropleth maps use color gradients to represent data values across geographical regions. They are commonly used for visualizing population density, income levels, or disease prevalence.
- Treemaps: Treemaps use nested rectangles to represent hierarchical data, with the size of each rectangle proportional to the value it represents. They are useful for visualizing complex data structures and identifying significant contributors to a whole.
Benefits of Utilizing Number Maps:
- Enhanced Data Visualization: Number maps provide a structured and intuitive visual representation of data, making it easier to identify patterns and trends that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Improved Data Understanding: By organizing data in a grid format, number maps facilitate a deeper understanding of relationships and dependencies between data points.
- Effective Communication: Number maps are a powerful tool for communicating data insights to a wider audience, as they are visually appealing and easy to comprehend.
- Identification of Anomalies: Number maps can highlight outliers and anomalies within the data, enabling further investigation and analysis.
- Support for Decision Making: By providing a clear and concise representation of data, number maps support informed decision-making based on data-driven insights.
Creating a Number Map: A Step-by-Step Guide:
- Data Preparation: The first step involves preparing the data for visualization. This includes cleaning, organizing, and selecting relevant variables for analysis.
- Grid Structure: Determine the size and dimensions of the grid based on the data and the desired level of detail.
- Data Representation: Choose a method for representing data points within the grid, such as numbers, symbols, or color coding.
- Color Scheme: Select a color scheme that effectively conveys the data values and enhances the visual clarity of the map.
- Legend: Create a legend to explain the meaning of colors, symbols, and values used within the map.
- Software Tools: Utilize specialized software tools, such as Excel, Tableau, or R, to create and customize number maps.
FAQs about Number Maps:
- What are the limitations of number maps?
While number maps offer a valuable tool for data visualization, they are not without limitations. For instance, they may struggle to represent high-dimensional data effectively, and they can be misleading if not used appropriately.
- How can I choose the right type of number map for my data?
The choice of number map depends on the specific data and the type of analysis being conducted. Consider factors such as the number of variables, the data distribution, and the desired level of detail when making this decision.
- What are some best practices for creating effective number maps?
Ensure that the grid structure is clear and easy to understand, choose a color scheme that is visually appealing and informative, and provide a comprehensive legend to explain the meaning of the map elements.
Tips for Effective Number Map Creation:
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information. Focus on presenting key insights and relationships.
- Use Clear Labels: Ensure that all axes, labels, and legends are clearly defined and easy to understand.
- Consider Colorblindness: Choose a color scheme that is accessible to all users, including those with colorblindness.
- Use Interactive Elements: Incorporate interactive elements, such as tooltips or hover effects, to provide additional information about data points.
- Iterate and Refine: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different grid structures, data representations, and color schemes to find the most effective visualization.
Conclusion:
Number maps offer a powerful and versatile approach to data visualization, enabling users to uncover hidden patterns, gain deeper insights, and communicate data effectively. By leveraging the structured grid format and appropriate visual representations, number maps empower data analysts and decision-makers to explore complex datasets, identify key trends, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the importance of effective data visualization tools like number maps will only continue to increase.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Number Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!